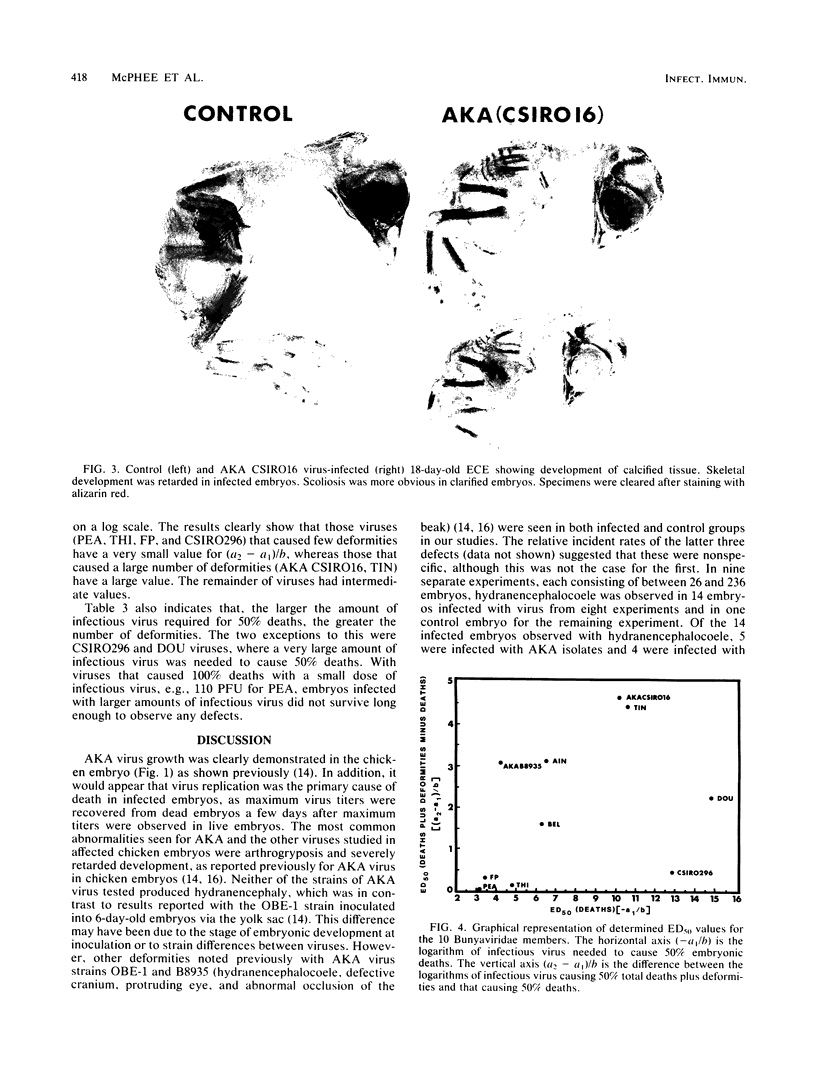
Abstract
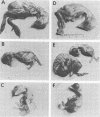
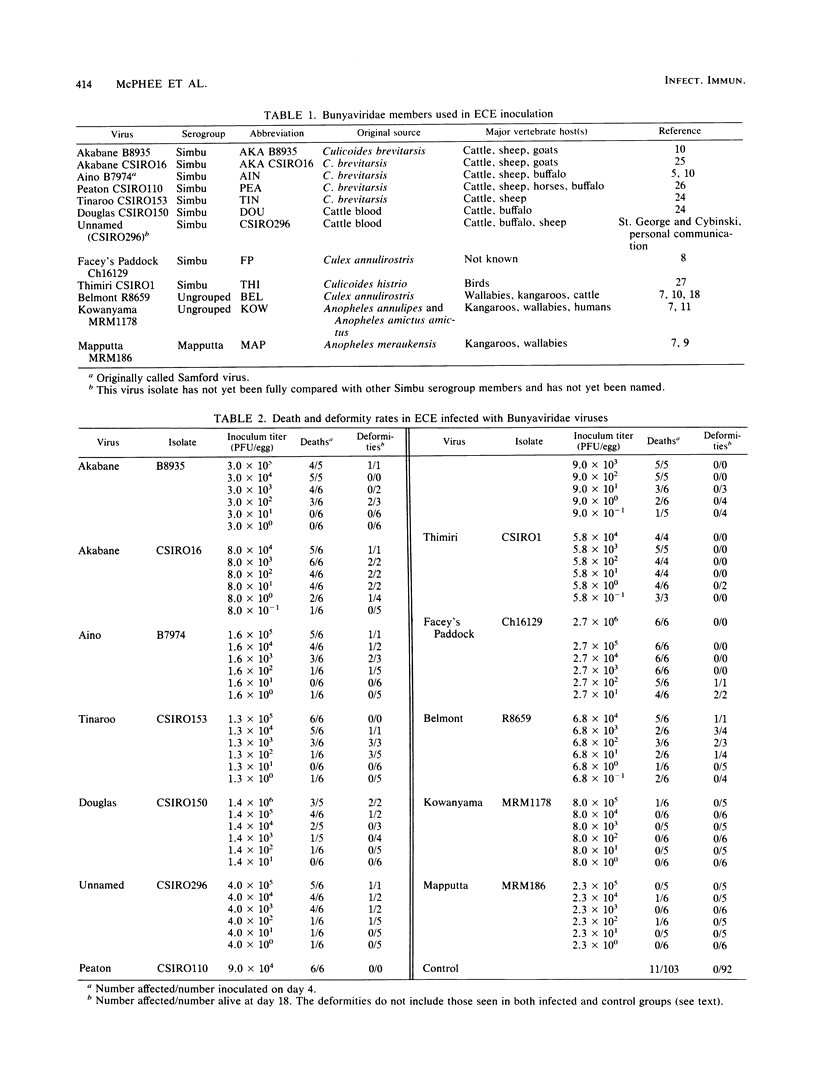
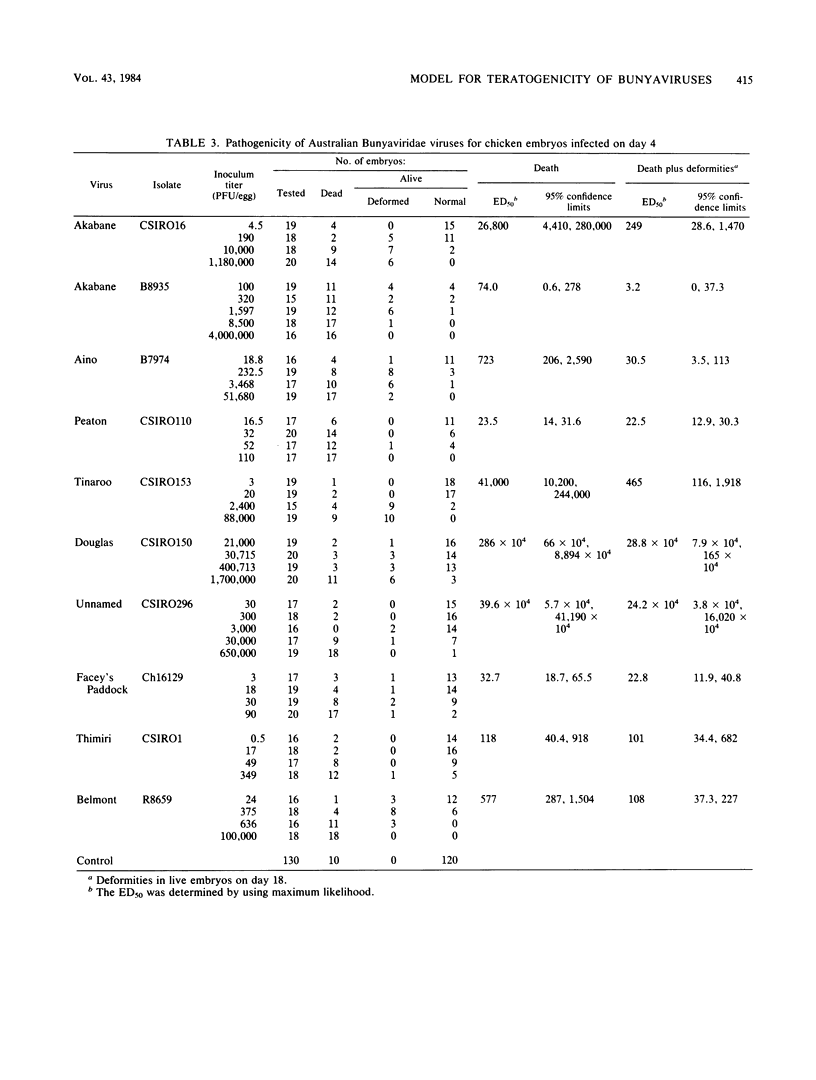
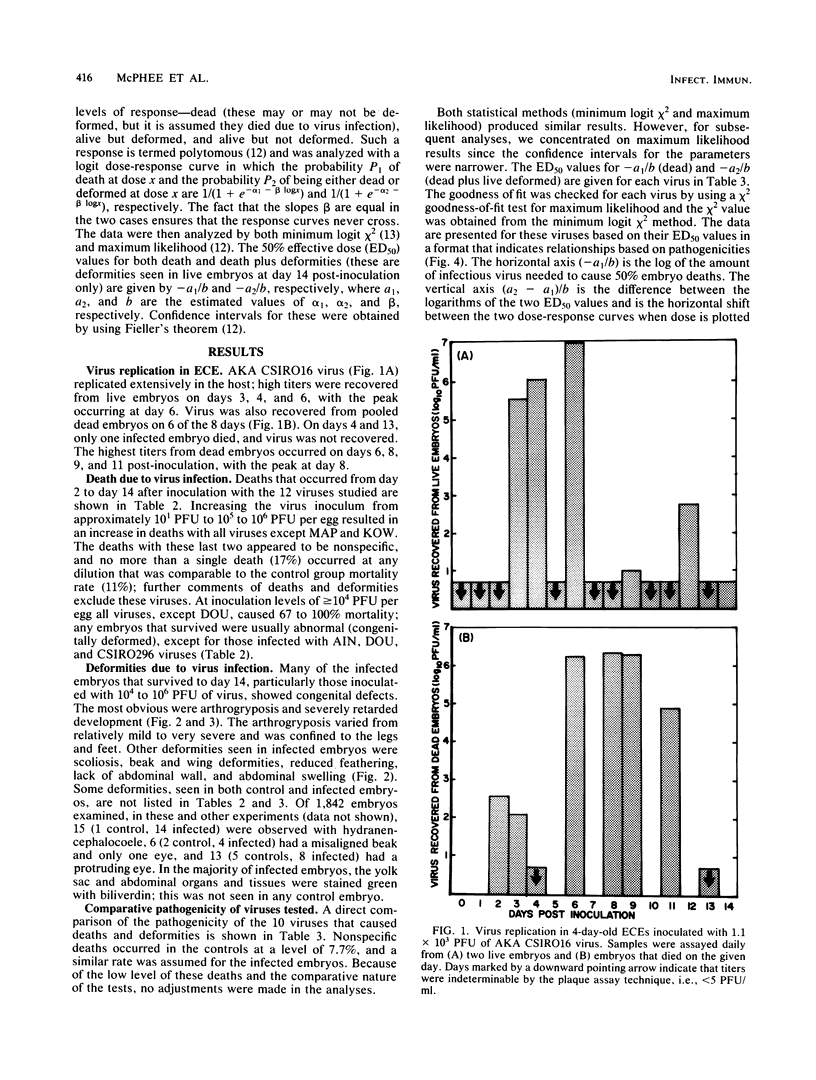
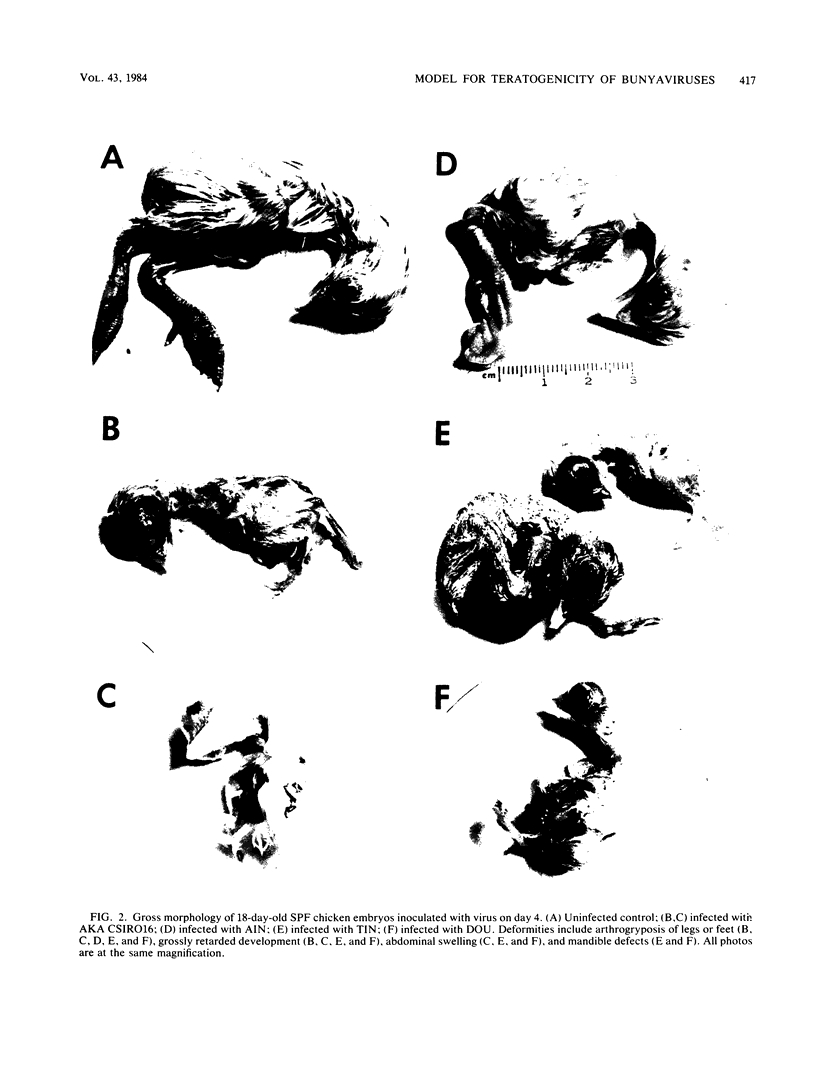
The use of embryonated chicken eggs as a model for assessing the teratogenic potential of animal viruses was investigated with 12 members of the Bunyaviridae family. Infection of 4-day-old embryonated chicken eggs via the yolk sac with 10 of the viruses resulted in deaths or congenital deformities that were similar to those observed in Akabane virus infections of fetal ruminants and included arthrogryposis, scoliosis, mandible defects, and retarded development. Statistical analysis showed that the viruses fell into three main groupings, namely, those that caused both death and deformities (Akabane, Aino, Tinaroo, and Belmont viruses), those that mainly caused death (Peaton, Thimiri, and Facey's Paddock viruses), and those that required very high doses to cause either death or deformities (Douglas and CSIR0296 viruses). In addition, two viruses (Kowanyama and Mapputta viruses) caused neither death nor deformities. A difference in the pathogenic potential between two Akabane isolates (B8935 and CSIR016) in the embryonated chicken egg model was found to correlate with differences previously observed in experimentally infected sheep; Akabane CSIR016 was the more pathogenic. It is concluded that the embryonated chicken egg model should also be of value in assessing the teratogenic potential of other Bunyaviridae and attenuated vaccine viruses, although it does not assess the ability of the virus to cross the placenta.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blattner R. J., Williamson A. P., Heys F. M. Role of viruses in the etiology of congenital malformations. Prog Med Virol. 1973;15:1–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverdale O. R., Cybinski D. H., St George T. D. Congenital abnormalities in calves associated with Akabane virus and Aino virus. Aust Vet J. 1978 Mar;54(3):151–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1978.tb05538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybinski D. H., St George T. D. A survey of antibody to Aino virus in cattle and other species in Australia. Aust Vet J. 1978 Aug;54(8):371–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1978.tb02504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOHERTY R. L., CARLEY J. G., MACKERRAS M. J., MARKS E. N. Studies of arthropod-borne virus infections in Queensland. III. Isolation and characterization of virus strains from wild-caught mosquitoes in North Queensland. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1963 Feb;41:17–39. doi: 10.1038/icb.1963.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty R. L. Arboviruses of Australia. Aust Vet J. 1972 Apr;48(4):172–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1972.tb09267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty R. L., Carley J. G., Kay B. H., Filippich C., Marks E. N., Frazier C. L. Isolation of virus strains from mosquitoes collected in Queensland, 1972-1976. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1979 Oct;57(5):509–520. doi: 10.1038/icb.1979.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty R. L., Carley J. G., Standfast H. A., Dyce A. L., Snowdon W. A. Virus strains isolated from arthropods during an epizootic of bovine ephemeral fever in Queensland. Aust Vet J. 1972 Mar;48(3):81–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1972.tb02220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty R. L., Whitehead R. H., Wetters E. J., Gorman B. M. Studies of the epidemiology of arthropod-borne viru infections at Mitchell River Mission, Cape York Peninsula, North Queensland. II. Arbovirus infections of mosquitoes, man and domestic fowls, 1963-1966. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(3):430–438. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S., Yonaiyama K. Deformities of chick embryos in experimental Akabane virus infection. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1978 Winter;18(3-4):89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhee D. A., Parsonson I. M., Della-Porta A. J. Comparative studies on the growth of Australian bluetongue virus serotypes in continuous cell lines and embryonated chicken eggs. Vet Microbiol. 1982 Nov;7(5):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(82)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPhee D. A., Westaway E. G. Comparisons of Belmont virus, a possible bunyavirus unique to Australia, with bunyamwera virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):135–147. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miah A. H., Spradbrow P. B. The growth of akabane virus in chicken embryos. Res Vet Sci. 1978 Sep;25(2):253–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura Y., Hayashi S., Ishihara T., Inaba Y., Omori T. Neutralizing antibody against Akabane virus in precolostral sera from calves with congenital arthrogryposis-hydranencephaly syndrome. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;46(3-4):377–380. doi: 10.1007/BF01240082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonson I. M., Della-Porta A. J., Snowdon W. A. Developmental disorders of the fetus in some arthropod-borne virus infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 May;30(3):660–673. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George T. D., Cybinski D. H., Filippich C., Carley J. G. The isolation of three Simbu group viruses new to Australia. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1979 Dec;57(6):581–582. doi: 10.1038/icb.1979.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George T. D., Standfast H. A., Cybinski D. H., Filippich C., Carley J. G. Peaton virus: a new Simbu group arbovirus isolated from cattle and Culicoides brevitarsis in Australia. Aust J Biol Sci. 1980 May;33(2):235–243. doi: 10.1071/bi9800235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George T. D., Standfast H. A., Cybinski D. H. Isolations of akabane virus from sentinel cattle and Culicoides brevitarsis. Aust Vet J. 1978 Dec;54(12):558–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1978.tb02412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standfast H. A., Dyce A. L. Isolation of Thimiri virus from Culicoides histrio (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) collected in Northern Australia. J Med Entomol. 1982 Mar 24;19(2):212–212. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/19.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]