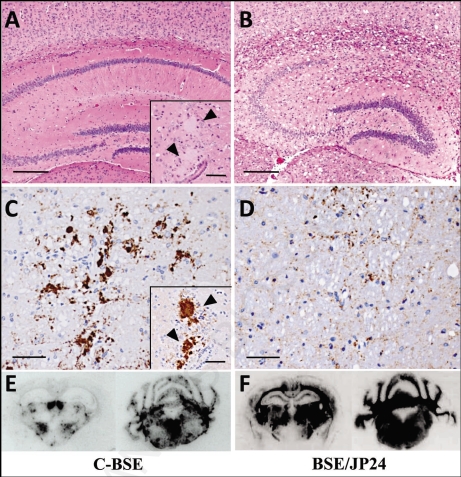
Figure 3.
Histopathological (A and B), immunohistochemical (C and D) and PET-blot (E and F) analysis of TgBoPrP mice inoculated with C-BSE and BSE/JP24 prions. No distinct vacuolation in the presence of PrP plaques was detected in the cerebral cortex and hippocampal region in C-BSE prion affected TgBoPrP mice (A), whereas severe vacuolation in the absence of PrP-positive deposits was prominent in BSE/JP24 prion affected TgBoPrP mice (B). Immunolabelled PrPSc showed coarse granular and coalescing-like patterns in the gigantocellular nucleus of medulla oblongata of C-BSE prion affected TgBoPrP mice (C). A diffused fine granular pattern was observed in BSE/JP24 prion affected TgBoPrP mice (D). Immunohistochemical labelling with mAb F99/97.6.1. The insets at the lower right corner (A and C) are PrP plaques detected in the periventricular area of frontal lobe (arrowheads). PET blot reveals that immunolabelled PrPSc was marked in particular nuclei of brainstems in C-BSE prion affected TgBoPrP mice (E). On the other hand, widespread and homogeneous PrPSc immunolabelling was obvious in BSE/JP24 prion affected TgBoPrP mice (F). PET blots of the representative coronal section at the level of the hippocampus (left) and medulla oblongate (right) are shown. The mAb SAF84 was used in PET-blot analysis. Bar: 200 µm (A and B); 50 µm (C and D); 20 µm (inset of A and C).