Abstract
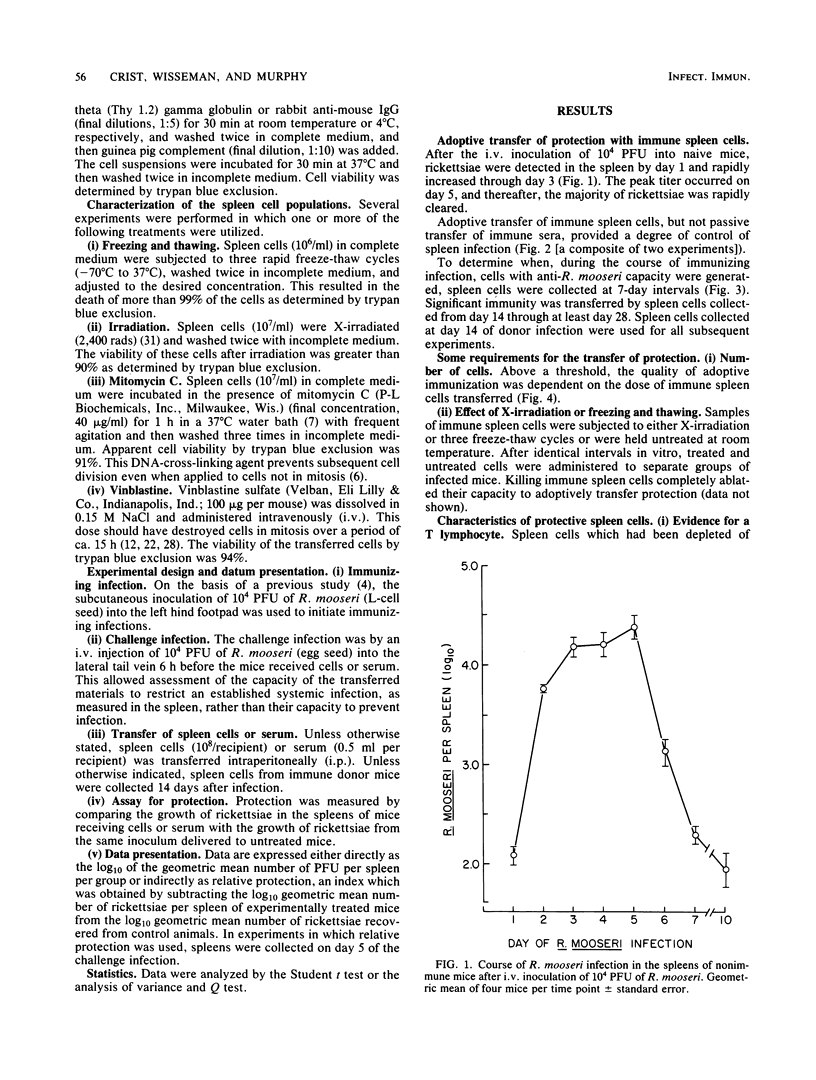
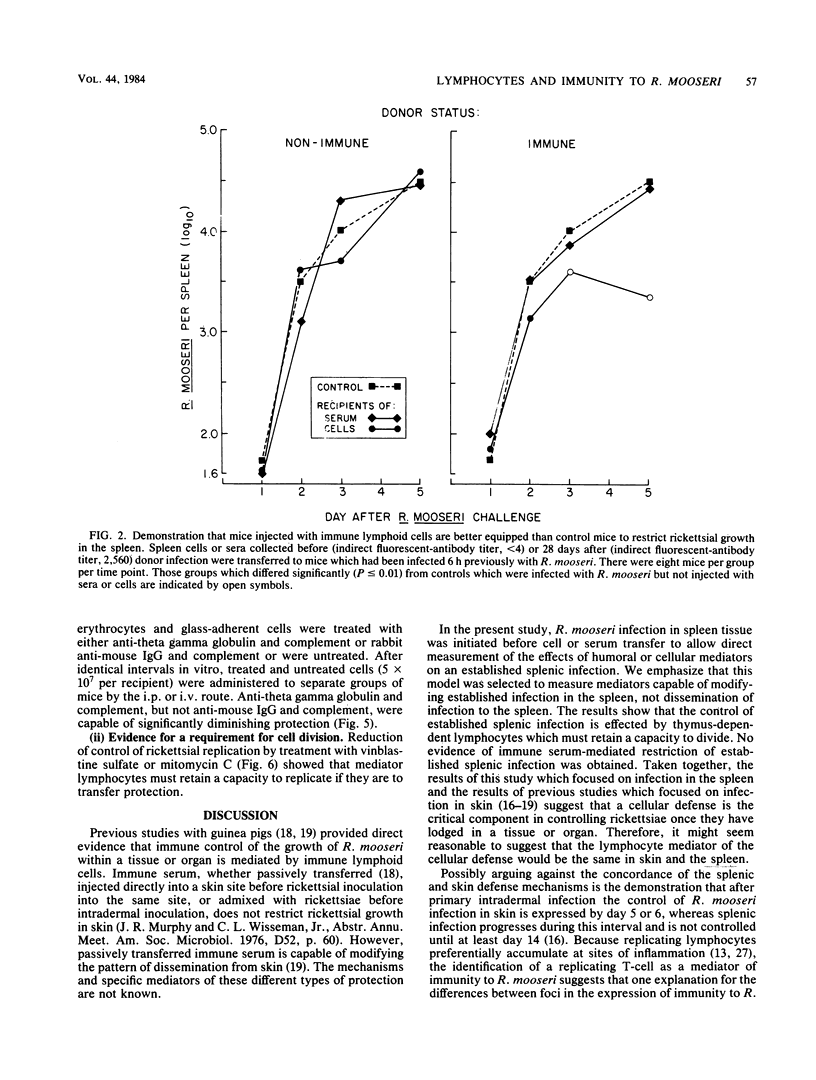
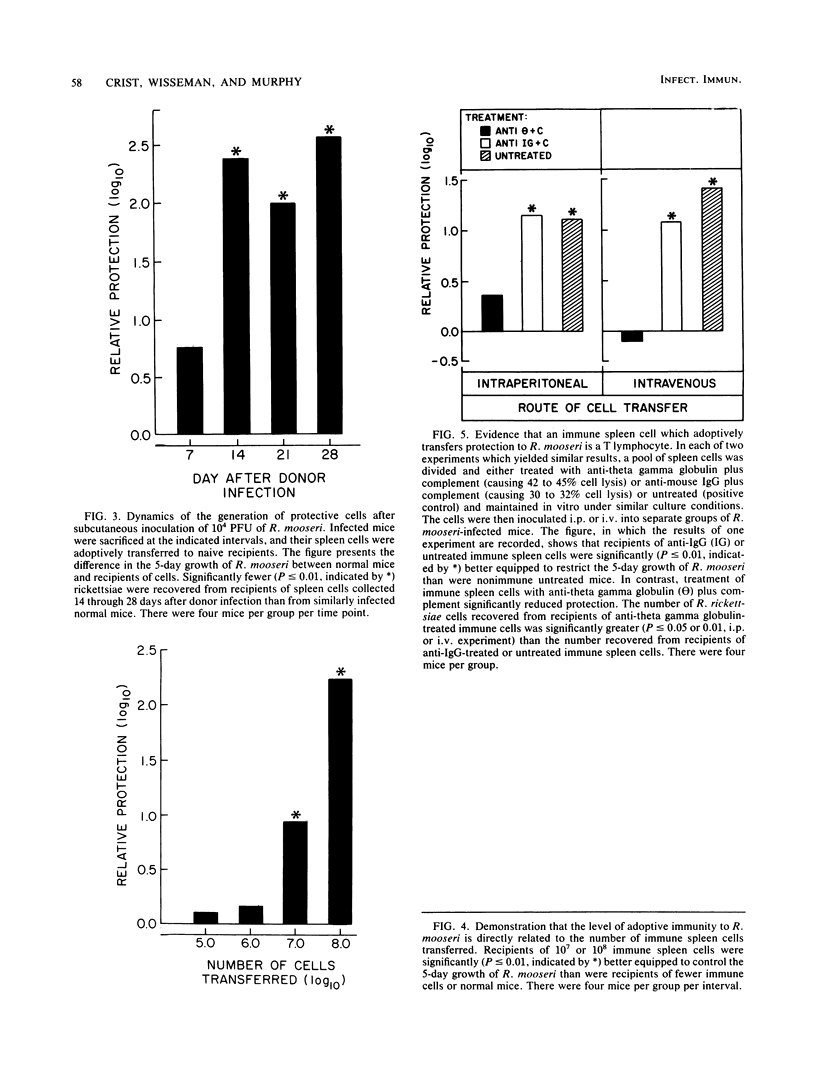
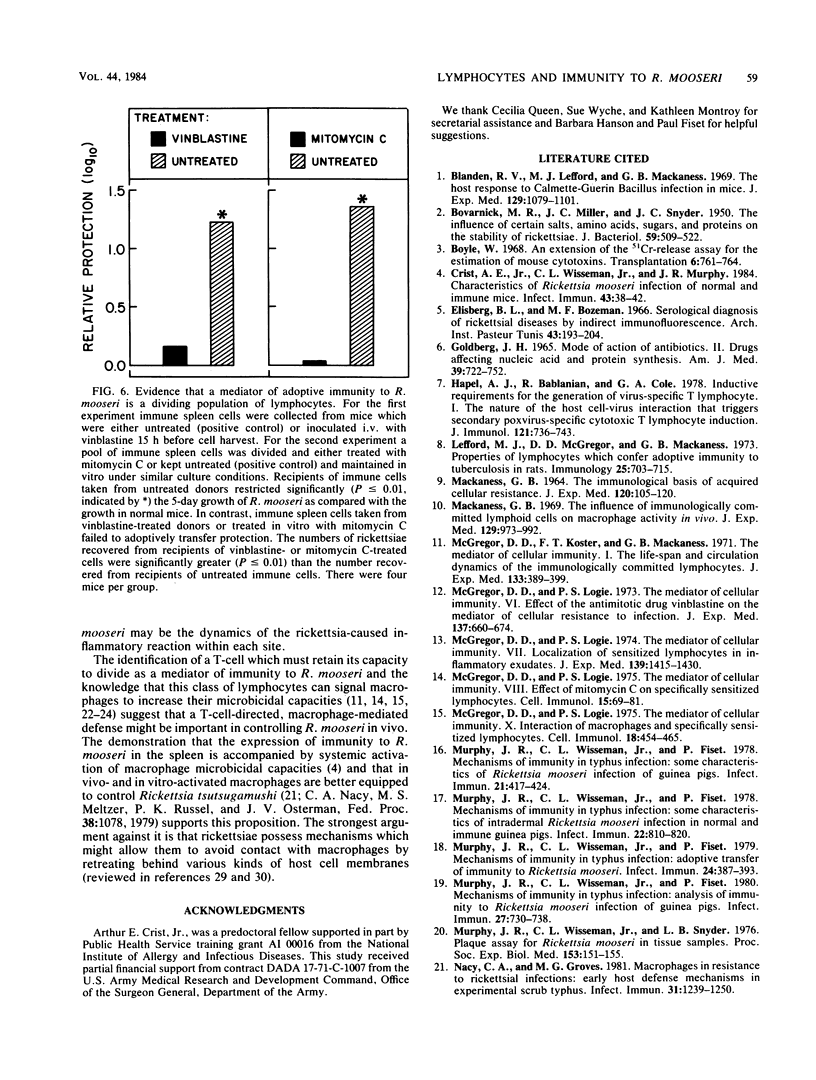
The capacity of adoptively transferred immune lymphoid cells or passively transferred immune serum to alter the course of an established Rickettsia mooseri (R. typhi) infection in the spleen was evaluated in BALB/c mice. Immune cells, but not immune serum, controlled the established infection. An effective lymphocyte was a T-cell which had to possess a capacity to divide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOVARNICK M. R., MILLER J. C., SNYDER J. C. The influence of certain salts, amino acids, sugars, and proteins on the stability of rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):509–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.509-522.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Lefford M. J., Mackaness G. B. The host response to Calmette-Guérin bacillus infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1079–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. An extension of the 51Cr-release assay for the estimation of mouse cytotoxins. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):761–764. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crist A. E., Jr, Wisseman C. L., Jr, Murphy J. R. Characteristics of Rickettsia mooseri infection of normal and immune mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):38–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.38-42.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. H. Mode of action of antibiotics. II. Drugs affecting nucleic acid and protein synthesis. Am J Med. 1965 Nov;39(5):722–752. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapel A. J., Bablanian R., Cole G. A. Inductive requirements for the generation of virus-specific T lymphocytes. I. The nature of the host cell-virus interaction that triggers secondary poxvirus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte induction. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):736–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefford M. J., McGregor D. D., Mackaness G. B. Properties of lymphocytes which confer adoptive immunity to tuberculosis in rats. Immunology. 1973 Oct;25(4):703–715. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Koster F. T., Mackaness G. B. The mediator of cellular immunity. I. The life-span and circulation dynamics of the immunologically committed lymphocyte. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):389–399. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Logie P. S. The mediator of cellular immunity. VI. Effect of the antimitotic drug vinblastine on the mediator of cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):660–674. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Logie P. S. The mediator of cellular immunity. VII. Localization of sensitized lymphocytes in inflammatory exudates. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1415–1430. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Logie P. S. The mediator of cellular immunity. VIII. Effect of mitomycin C on specifically sensitized lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jan;15(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Logie P. S. The mediator of cellular immunity. X. Interaction of macrophages and specifically sensitized lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1975 Aug;18(2):454–465. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Wisseman C. G., Jr, Fiset P. Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infection: adoptive transfer of immunity to Rickettsia mooseri. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):387–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.387-393.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Fiset P. Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infection: analysis of immunity to Rickettsia mooseri infection of guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):730–738. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.730-738.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Fiset P. Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infection: some characteristics of Rickettsia mooseri infection of guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):417–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.417-424.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Fiset P. Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infection: some characteristics of intradermal Rickettsia mooseri infection in normal and immune guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):810–820. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.810-820.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Snyder L. B. Plaque assay for Rickettsia mooseri in tissue samples. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Oct;153(1):151–155. doi: 10.3181/00379727-153-39499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Groves M. G. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infections: early host defense mechanisms in experimental scrub typhus. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1239–1250. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1239-1250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular mediators of anti-Listeria immunity as an enlarged population of short lived, replicating T cells. Kinetics of their production. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):342–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Deissler J. F. Nature of "memory" in T-cell mediated antibacterial immunity: cellular parameters that distinguish between the active immune response and a state of "memory". Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):761–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.761-767.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Nature of "memory" in T-cell-mediated antibacterial immunity: anamnestic production of mediator T cells. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):754–760. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.754-760.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Spitalny G. Inflammatory lymphocyte in cell-mediated antibacterial immunity: factors governing the accumulation of mediator T cells in peritoneal exudates. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):489–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.489-498.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. T cell dependence of macrophage activation and mobilization during infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):66–71. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.66-71.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeriote F. A., Bruce W. R. An in vitro assay for growth-inhibiting activity of vinblastine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Nov;35(5):851–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Walsh W. T. In vitro studies of the action of antibiotics on Rickettsia prowazeki by two basic methods of cell culture. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):564–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. Interferonlike factors from antigen- and mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes with antirickettsial and cytolytic actions on Rickettsia prowazekii. Infected human endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


