Abstract
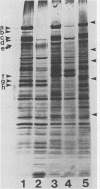
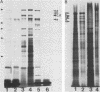
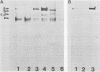
Hydrophobic strains of Streptococcus mutans were compared with paired variants showing reduced hydrophobicity. Extracts of hydrophobic cells contained a number of high-molecular-weight proteins which were not present on cells with decreased hydrophobicity. The proteins were found in purified cell walls, suggesting that they are located on the bacterial surface. Trypsin treatment of whole cells destroyed the proteins and reduced the hydrophobicity. Chemical analysis did not reveal any marked differences in the proportion of cell wall constituents. The amino acid compositions and lipoteichoic acid contents of hydrophobic and hydrophilic cell walls were similar. Culture supernatants from the hydrophilic variants contained high-molecular-weight proteins similar to those extracted from the cell walls of the hydrophobic parent strains, indicating that the variants were impaired in their ability to incorporate the hydrophobicity-associated proteins into the cell wall. The dominant protein had a molecular weight of 190,000, similar to that of antigen I/II (B) of S. mutans.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Binding of group A streptococci to human oral mucosal cells by lipoteichoic acid. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1975;88:285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. K., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Influence of growth conditions on adherence of Streptococcus mutans ingbritt to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):445–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.445-448.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J. Nutritional requirements of Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1970;4(4):305–320. doi: 10.1159/000259653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I., Skobe Z. Association of fimbriae with the hydrophobicity of Streptococcus sanguis FC-1 and adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):414–417. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.414-417.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy L., Jacques N. A., Forester H., Campbell L. K., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Effect of fructose and other carbohydrates on the surface properties, lipoteichoic acid production, and extracellular proteins of Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt grown in continuous culture. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):78–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.78-87.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques N. A., Hardy L., Campbell L. K., Knox K. W., Evans J. D., Wicken A. J. Effect of carbohydrate source and growth conditions on the production of lipoteichoic acid by Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1079–1087. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1079-1087.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Jacques N. A., Campbell L. K., Wicken A. J., Hurst S. F., Bleiweis A. S. Phenotypic stability of the cell wall of Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt grown under various conditions. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1071–1078. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1071-1078.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Gisslow M. T. Role of sialic acid in saliva-induced aggregation of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.35-40.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miörner H., Johansson G., Kronvall G. Lipoteichoic acid is the major cell wall component responsible for surface hydrophobicity of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):336–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.336-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moro I., Russell M. W. Ultrastructural localization of protein antigens I/II and III in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):410–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.410-413.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G. Hydrophobic interactions and the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.637-644.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Staat R. H., Rosan B., Taylor K. G., Doyle R. J. Association of protein with the cell wall of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.118-126.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik J., Orstavik D. Influence of in vitro propagation on the adhesive qualities of Streptococcus mutans isolated from saliva. Acta Odontol Scand. 1982;40(1):57–63. doi: 10.3109/00016358209019810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staat R. H., Doyle R. J., Langley S. D., Suddick R. P. Modification of in vitro adherence of Streptococcus mutans by plant lectins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:639–647. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Jacobs T. Cell wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus salivarius: purification, properties, and function in adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):233–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.233-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergren G., Olsson J. Hydrophobicity and adherence of oral streptococci after repeated subculture in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):432–435. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.432-435.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Gibbens J. W., Knox K. W. Comparative studies on the isolation of membrane lipoteichoic acid from Lactobacillus fermenti. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):365–372. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.365-372.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Separation and characterization of a protein antigen from cells of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Feb;122(2):217–225. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]