Abstract
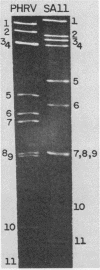
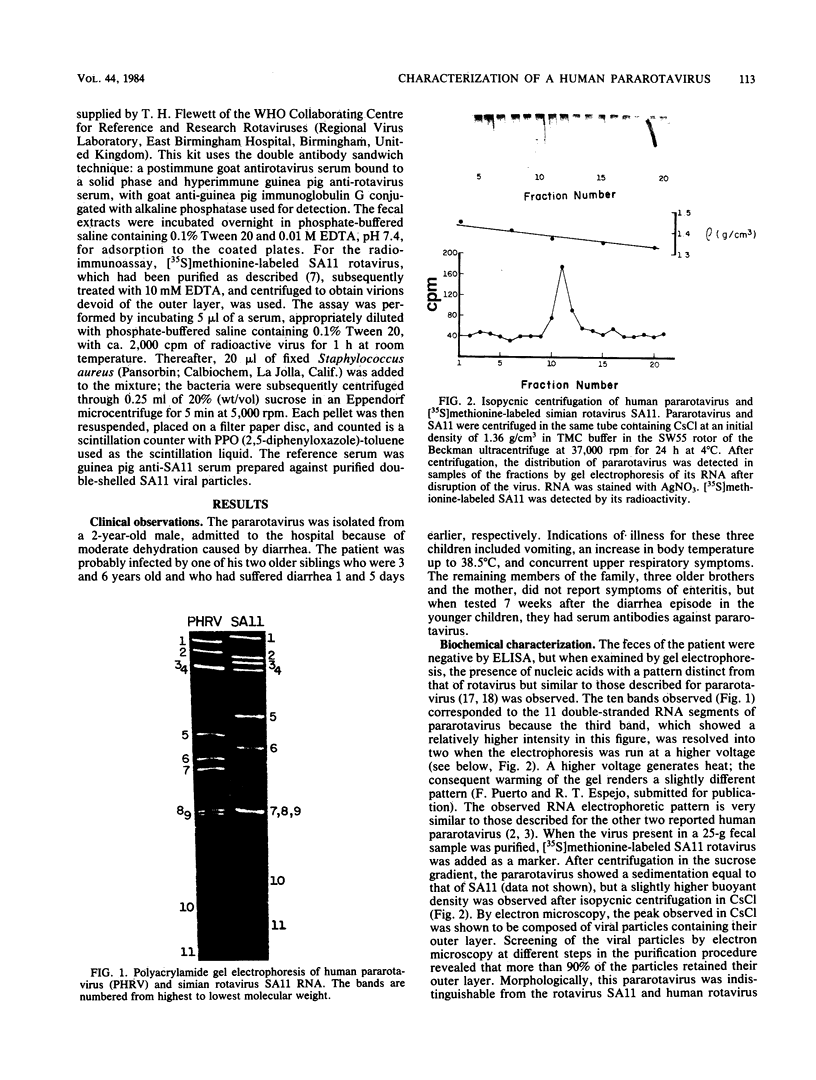
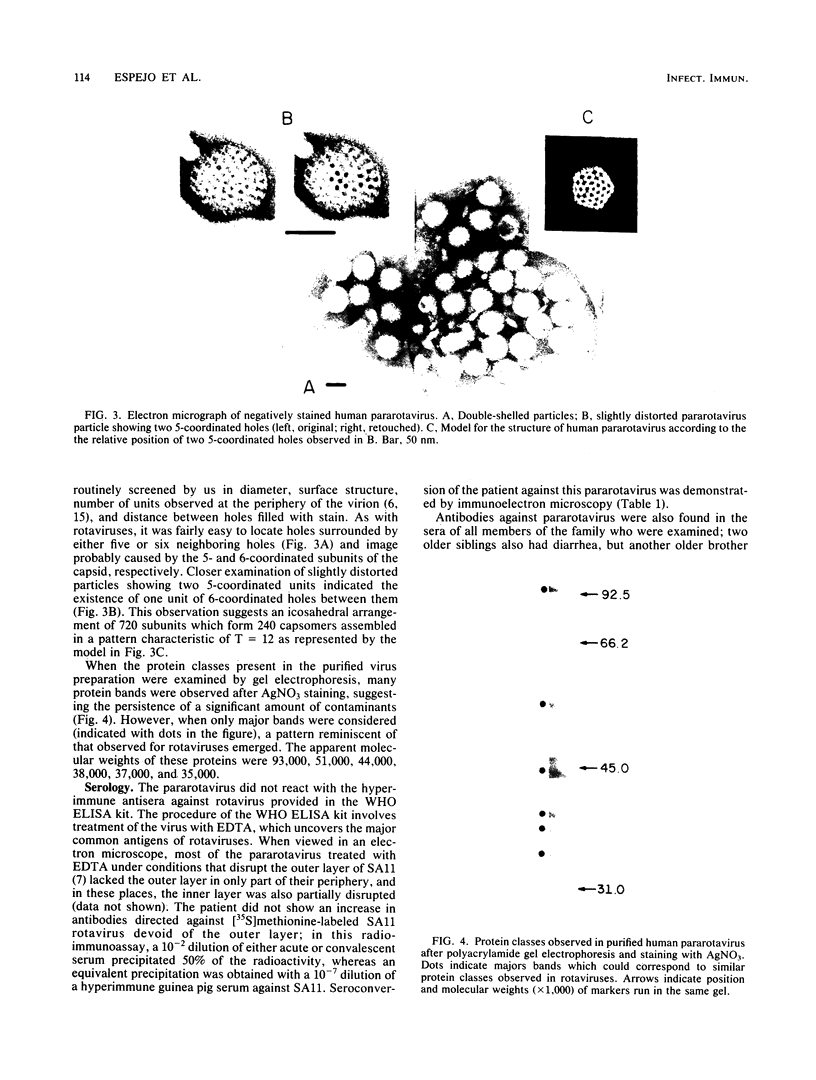
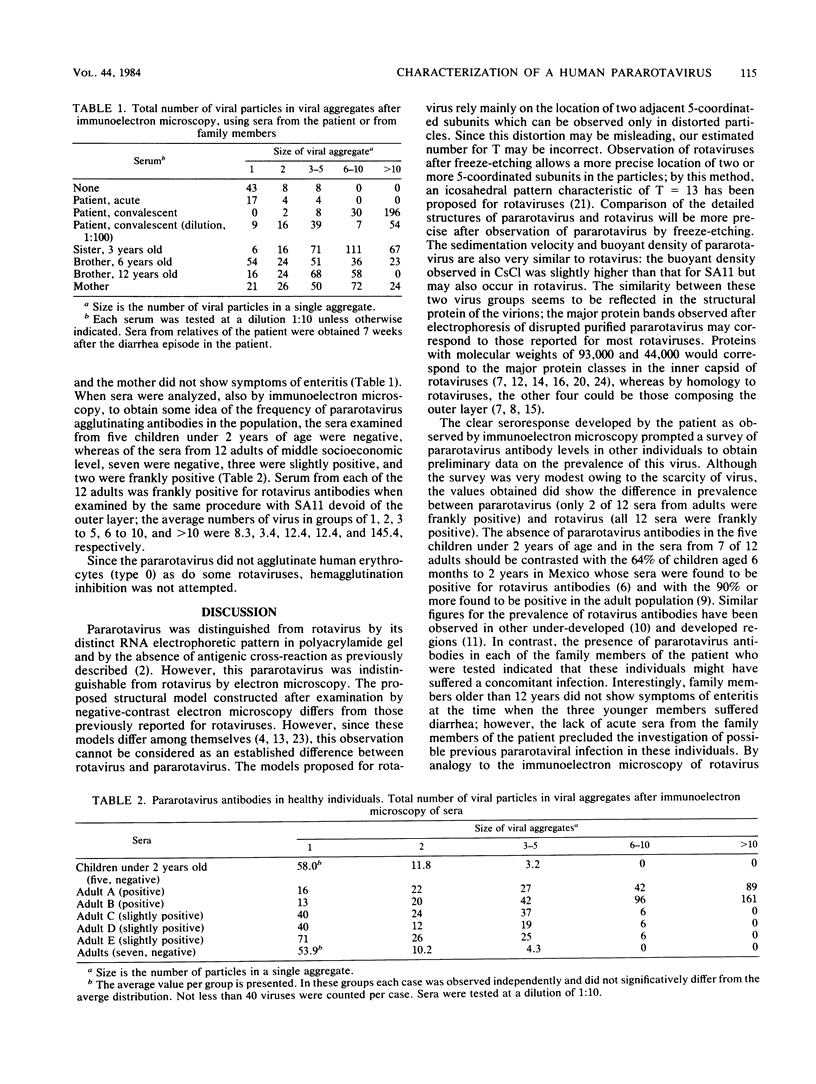
A virus isolate with the properties of a pararotavirus was found after routine analysis by RNA electrophoresis of 658 samples of diarrheic feces from hospitalized infants and young children in Mexico City. Of the patients included in this survey, which was initiated in 1977, 29% excreted rotaviruses which were detected by their characteristic RNA pattern after gel electrophoresis. The morphology and sedimentation coefficient of this pararotavirus, which was the apparent cause of a diarrhea with moderate dehydration in a 2-year-old male infant, were indistinguishable from those of rotaviruses, but its buoyant density in CsCl was slightly higher than that of simian rotavirus SA11. By electron microscopy, the viral particles showed a regular pattern of cavities or holes that constituted the 5- and 6-coordinated units of the virion with a structure characteristic of T = 12. The virion also was apparently composed of protein classes similar to those found in rotaviruses. Seroconversion in the patient and presence of anti-pararotavirus antibodies in most of the members of the family of the patient was shown by immunoelectron microscopy. Of the sera from 12 healthy adults which were examined by this technique, seven were negative, three were slightly positive, and only two were strongly positive.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beidler J. L., Hilliard P. R., Rill R. L. Ultrasensitive staining of nucleic acids with silver. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 1;126(2):374–380. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90530-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Clarke I. N., McCrae M. A. Characterization of an antigenically distinct porcine rotavirus. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1058–1062. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1058-1062.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eepejo R. T., Calderón E., González N., Salomón A., Martuscelli A., Romero P. Rotavirus gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children in Mexico City. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1978 Oct-Dec;20(4):239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza J., Gil F. A study on the ultrastructure of human rotavirus. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90362-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., López S., Arias C. Structural polypeptides of simian rotavirus SA11 and the effect of trypsin. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.156-160.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R., Martínez E., López S., Muñoz O. Different polypeptide composition of two human rotavirus types. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):230–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.230-237.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Ramig R. F., Ericson B. L. Heterogeneity in the structural glycoprotein (VP7) of simian rotavirus SA11. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):8–14. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghose L. H., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Comparison of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of rotavirus antibodies with complement fixation in an epidemiological survey. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Sep;8(3):268–276. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.3.268-276.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesudoss E. S., John T. J., Mathan M., Spence L. Prevalence of rotavirus antibody in infants and children. Indian J Med Res. 1978 Sep;68:383–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. L., Palmer E. L., Middleton P. J. Ultrastructure of infantile gastroenteritis virus. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):146–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Mukoyama A. Polypeptides of bovine rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):309–316. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Faulkner-Valle G. P. Molecular biology of rotaviruses. I. Characterization of basic growth parameters and pattern of macromolecular synthesis. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.490-496.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., Todd D., McFerran J. B., McCracken R. M. Isolation from chickens of a rotavirus lacking the rotavirus group antigen. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. C., Cohen J., Fortier B., Lourenco M. H., Bricout F. Isolation of a human pararotavirus. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Bishop R. F., Holmes I. H. Detection of a rotavirus-like agent associated with diarrhea in an infant. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):724–726. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.724-726.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Comparison of the genomes of simian, bovine, and human rotaviruses by gel electrophoresis and detection of genomic variation among bovine isolates. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.839-846.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Further biochemical characterization, including the detection of surface glycoproteins, of human, calf, and simian rotaviruses. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):91–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.91-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseto A., Escaig J., Delain E., Cohen J., Scherrer R. Structure of rotaviruses as studied by the freeze-drying technique. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):471–475. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90571-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler C., Musalem C., Loroño M., Espejo R. T. Association of viral particles and viral proteins with membranes in SA11-infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):983–992. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.983-992.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stannard L. M., Schoub B. D. Observations on the morphology of two rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Nov;37(2):435–439. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-2-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E. Rotavirus polypeptides. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):187–197. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]