Abstract
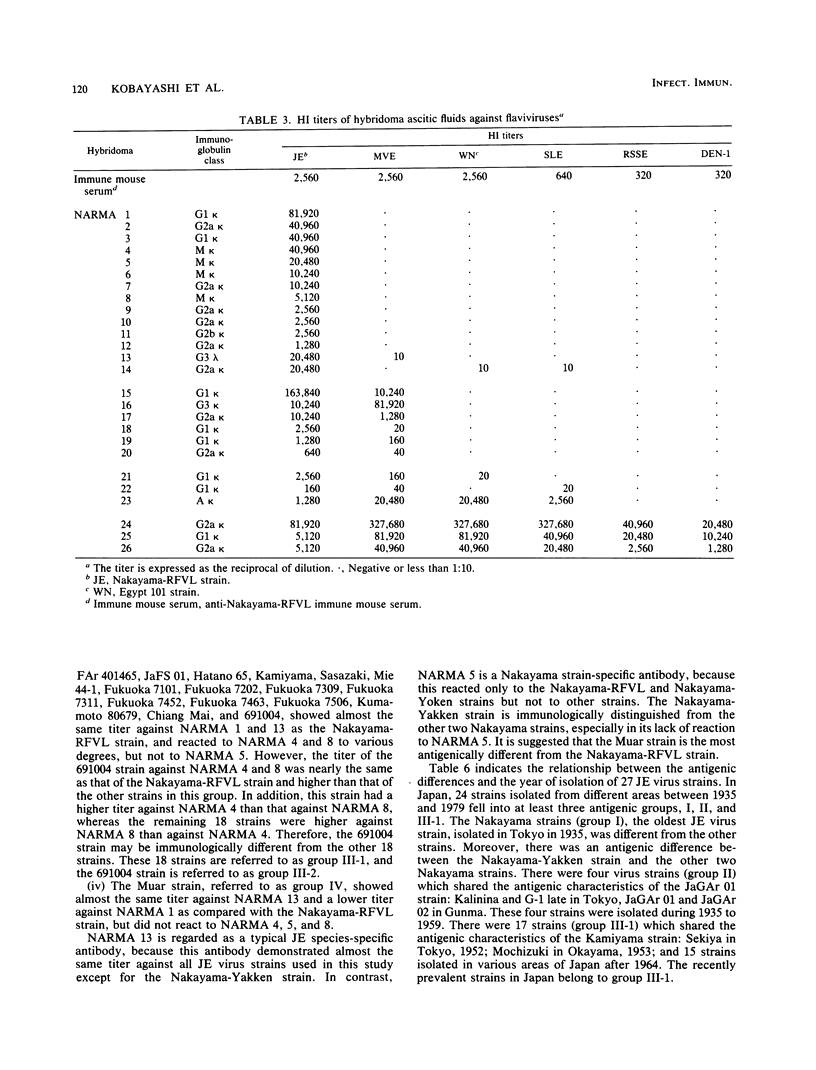
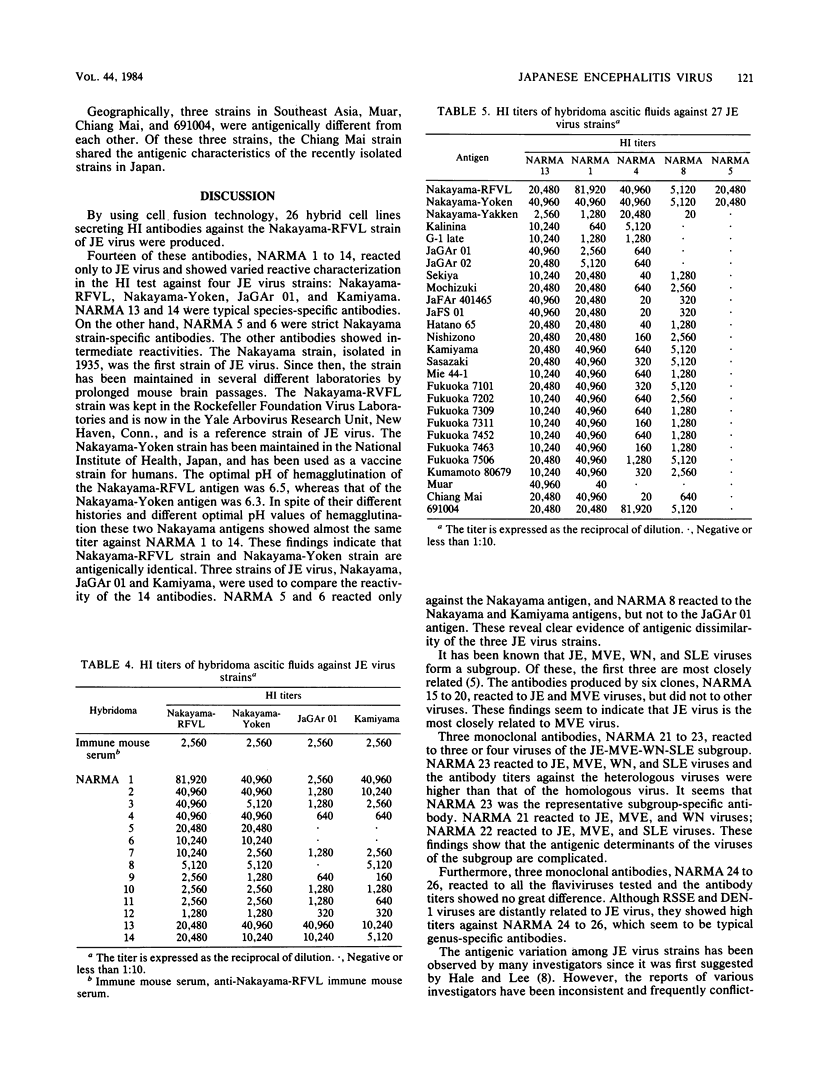
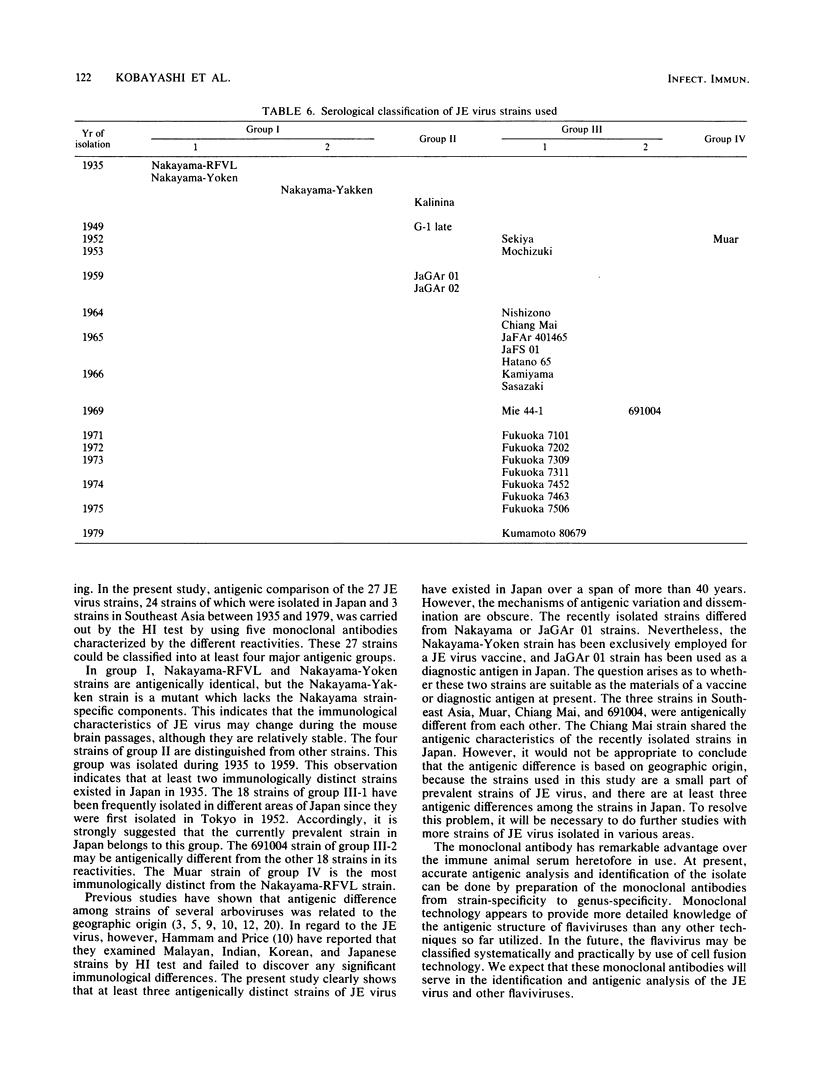
Hybridoma cells were produced by fusing P3X63Ag8.653 mouse myeloma cells with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with Japanese encephalitis (JE) virus, Nakayama-RFVL strain. The resulting 26 clones produced hemagglutination inhibition antibodies against the homologous strain. The hemagglutination inhibition reactivity of each clone was tested against six flaviviruses: JE, Murray Valley encephalitis (MVE), Egypt 101 strain of West Nile (WN), St. Louis encephalitis (SLE), Russian spring summer encephalitis, and dengue type 1. The 26 monoclonal antibodies fell into four groups: 14 JE species-specific antibodies, 6 antibodies reactive to JE and MVE viruses, 3 antibodies to three or four viruses in the JE-MVE-WN-SLE subgroup, and 3 antibodies to all six flaviviruses. Furthermore, antigenic comparison of 27 strains of JE virus was carried out by using five JE species-specific monoclonal antibodies. Of these, 24 strains were isolated in various parts of Japan, and 3 strains came from Southeast Asia. In reactivity, the 27 strains were classified into at least four antigenic groups. The results showed that the Nakayama-Yakken strain is a mutant strain which lacks the Nakayama strain-specific antigen and that the recently isolated strains are immunologically different from Nakayama and JaGAr 01 strains. One clone (NARMA 13) produced a JE species-specific antibody which showed almost the same titer against 26 JE virus strains, whereas one clone (NARMA 5) produced a Nakayama strain-specific antibody which reacted only to the Nakayama-RFVL and Nakayama-Yoken strains.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CASALS J. ANTIGENIC VARIANTS OF EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS. J Exp Med. 1964 Apr 1;119:547–565. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASALS J., BROWN L. V. Hemagglutination with arthropod-borne viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 May 1;99(5):429–449. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.5.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASALS J. Viruses: the versatile parasites; the arthropod-borne group of animal viruses. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Jan;19(3):219–235. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1957.tb00526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H. Antigenic analysis of certain group B arthropodborne viruses by antibody absorption. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:21–32. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmar D., Haines H. G., Castro A. Monoclonal antibodies specific for dengue virus type 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):74–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.74-78.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE J. H., LEE L. H. A serological investigation of six encephalitis viruses isolated in Malaya. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Oct;35(5):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammam H. M., Price W. H. Further observations on geographic variation in the antigenic character of West Nile and Japanese B viruses. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Jan;83(1):113–122. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F. X., Berger R., Majdic O., Knapp W., Kunz C. Monoclonal antibodies to the structural glycoprotein of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):869–874. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.869-874.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARABATSOS N., BOURKE A. T., HENDERSON J. R. ANTIGENIC VARIATION AMONG STRAINS OF WESTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALOMYELITIS VIRUS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 May;12:408–412. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno T., Okada T., Kondo A., Suzuki M., Kobayashi M., Oya A. Immunotyping of different strains of Japanese encephalitis virus by antibody-absorption, haemagglutination-inhibition and complement-fixation tests. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(4):547–563. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peiris J. S., Gordon S., Unkeless J. C., Porterfield J. S. Monoclonal anti-Fc receptor IgG blocks antibody enhancement of viral replication in macrophages. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):189–191. doi: 10.1038/289189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent D. W. Antigenic characterization of flavivirus structural proteins separated by isoelectric focusing. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):608–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.608-618.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. A., Johnson K. M. Antigenic variants of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus: their geographic distribution and epidemiologic significance. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Mar;89(3):286–307. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


