Abstract
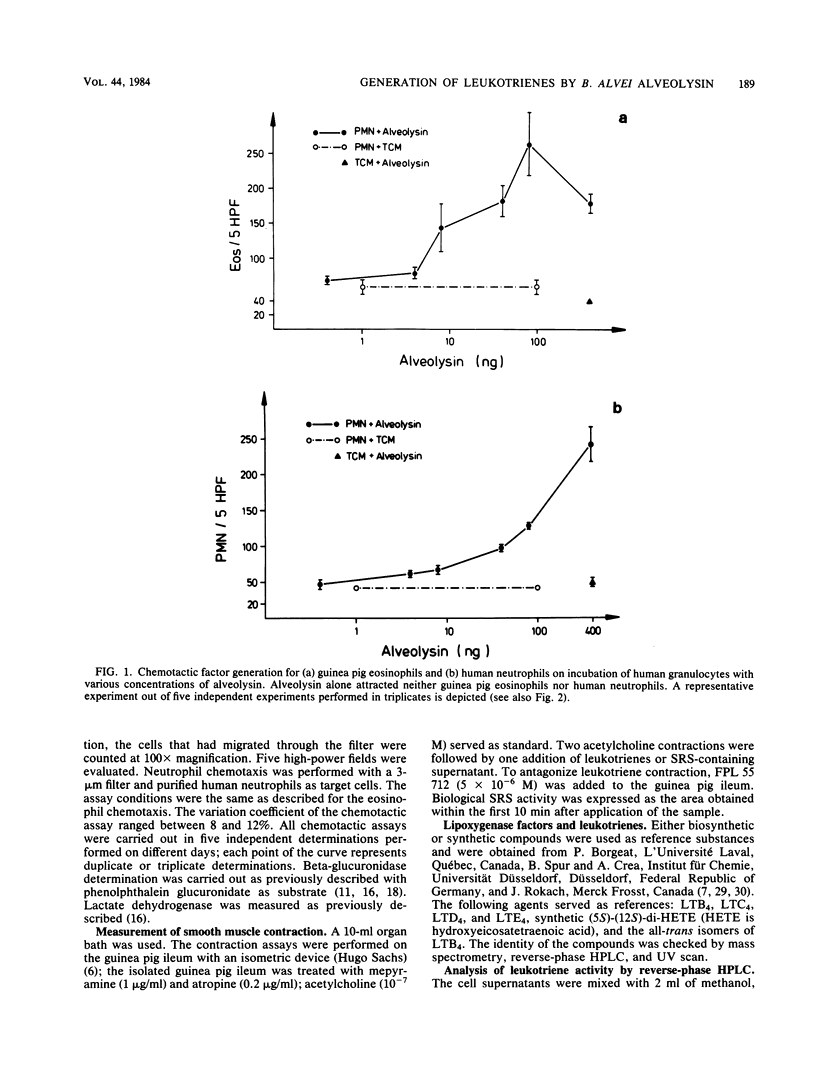
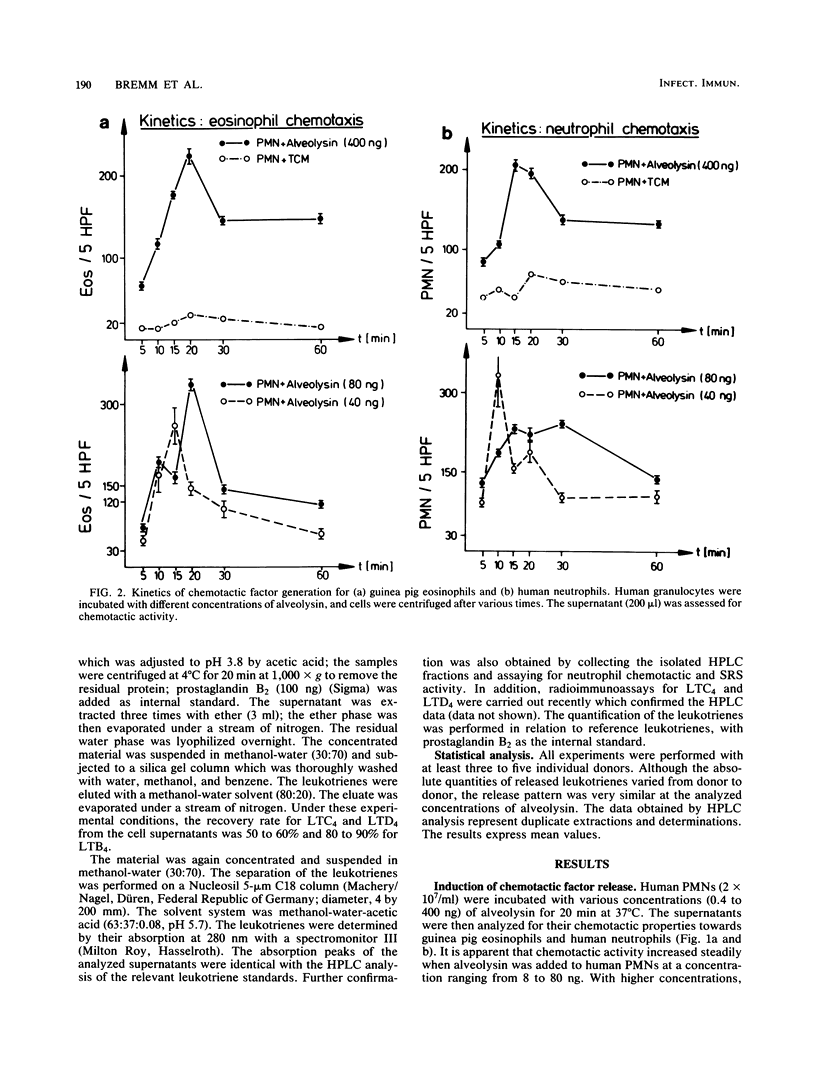
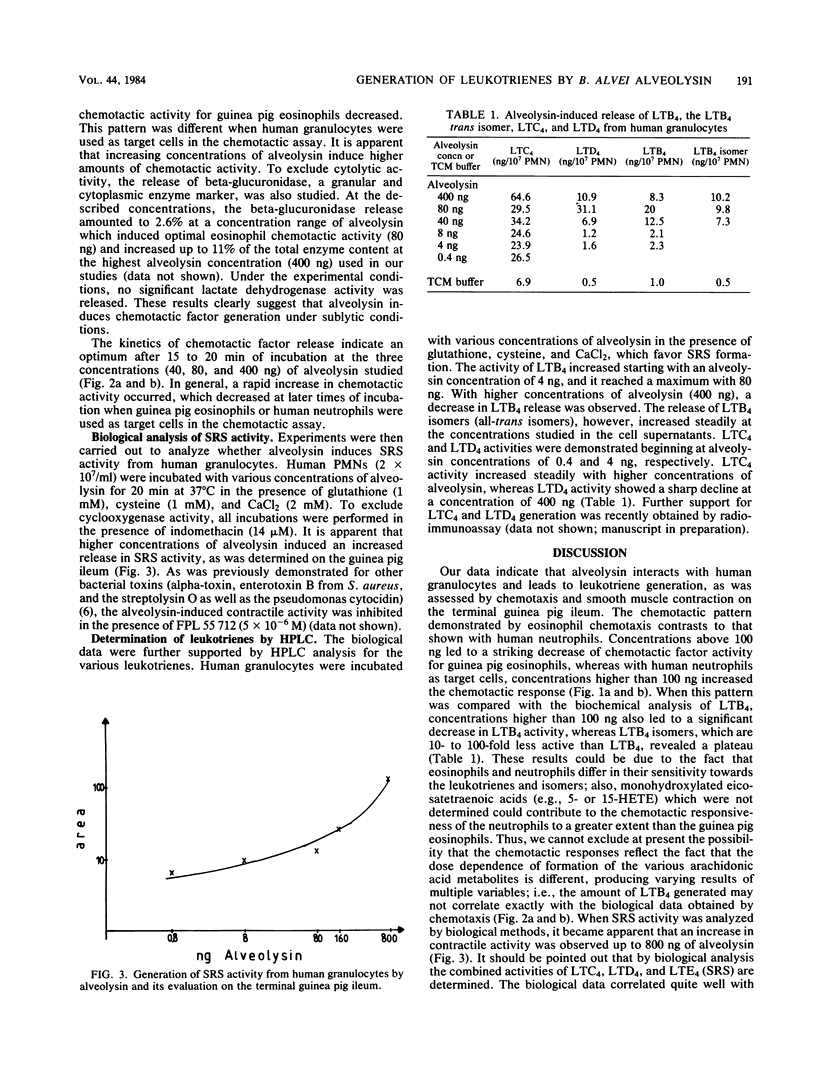
We investigated the effect of alveolysin on human granulocytes. Alveolysin is an exoprotein produced by Bacillus alvei and belongs to the group of sulfhydryl-activated cytolysins. Other members of this group are streptolysin O and theta-toxin from Clostridium perfringens. It is demonstrated that alveolysin leads to leukotriene generation from human granulocytes, which exert chemotactic (leukotriene B4) and slow-reacting substance (leukotriene C4, D4, and E4) activity under sublytic concentrations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E. Bacterial toxins: an outlook. Toxicon. 1982;20(1):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. A., Thomas M. J., Goetzl E. J., DeChatelet L. R., McCall C. E. Lipoxygenbase-derived products of arachidonic acid mediate stimulation of hexose uptake in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Füssle R., Tranum-Jensen J. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: oligomerization of hydrophilic monomers to form amphiphilic hexamers induced through contact with deoxycholate detergent micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray M. A., Cunningham F. M., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Smith M. J. Leukotriene B4: a mediator of vascular permeability. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;72(3):483–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb11000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremm K. D., Brom J., König W., Spur B., Crea A., Bhakdi S., Lutz F., Fehrenbach F. J. Generation of leukotrienes and lipoxygenase factors from human polymorphonuclear granulocytes during bacterial phagocytosis and interaction with bacterial exotoxins. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Jul;254(4):500–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Schlegel R. Effect of streptolysin O on erythrocyte membranes, liposomes, and lipid dispersions. A protein-cholesterol interaction. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):160–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehrenbach F. J., Schmidt C. M., Huser H. Early and late events in streptolysin-O induced hemolysis. Toxicon. 1982;20(1):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H. Cytolytic toxins and surface activity. Toxicon. 1982;20(1):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gzarnetzki B. M., Konig W., Lichtenstein L. M. Release of eosinophil chemotactic factor from human polymorphonuclear neutrophils by calcium ionophore A23187 and phagocytosis. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):725–726. doi: 10.1038/258725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagmann W., Keppler D. Leukotriene antagonists prevent endotoxin lethality. Naturwissenschaften. 1982 Dec;69(12):594–595. doi: 10.1007/BF00396357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakschik B. A., Lee L. H. Enzymatic assembly of slow reacting substance. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):51–52. doi: 10.1038/287051a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Bremm K. D., Müller P., Kunau W. H., Borgeat P., Spur B., Crea A. E., Falsone G. On the biological role of lipid chemotactic factors. Agents Actions Suppl. 1983;12:167–185. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-9352-7_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Czarnetzki B. M., Lichtenstein L. M. Eosinophil chemotactic factor (ECF). II. Release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes during phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Kunau H. W., Borgeat P. Induction and comparison of the eosinophil chemotactic factor with endogenous hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids: its inhibition by arachidonic acid analogs. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1982;9:301–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Tesch H., Frickhofen N. Generation and release of eosinophil chemotactic factor from human polymorphonuclear neutrophils by arachidonic acid. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jun;8(6):434–437. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G. Platelet-activating factor stimulates the phosphatidylinositol cycle. Appearance of phosphatidic acid is associated with the release of serotonin in horse platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7314–7317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz F. Purification of a cytotoxic protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Toxicon. 1979;17(5):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möllby R., Thelestam M., Geoffroy C., Alouf J. E. Two different modes of membrane damaging action by bacterial thiol-activated haemolysins. Toxicon. 1982;20(1):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Becker E. L., Borgeat P., Picard S., Vallerand P., Sha'afi R. I. Specificity of the effect of lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid on calcium homeostasis in neutrophils. Correlation with functional activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8608–8611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Lewis R. A., Corey E. J., Austen K. F. Generation of leukotriene C4 from a subclass of mast cells differentiated in vitro from mouse bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4665–4667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubin R., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Benveniste J. Release of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) and leukotrienes C and D from inflammatory macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Feb;12(2):141–146. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Hamill A. L., Liu F. T., Katz D. H., Cohn Z. A. Secretion of leukotriene C and other arachidonic acid metabolites by macrophages challenged with immunoglobulin E immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serhan C. N., Fridovich J., Goetzl E. J., Dunham P. B., Weissmann G. Leukotriene B4 and phosphatidic acid are calcium ionophores. Studies employing arsenazo III in liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4746–4752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Alouf J. E., Geoffroy C., Möllby R. Membrane-damaging action of alveolysin from Bacillus alvei. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1187–1192. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1187-1192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Sensitive assay for detection of toxin-induced damage to the cytoplasmic membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):225–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.225-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosbeck K., Handschin H., Menge E. B., Zak O. Effects of subminimal inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on adhesiveness of Escherichia coli in vitro. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Sep-Oct;1(5):845–851. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.5.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


