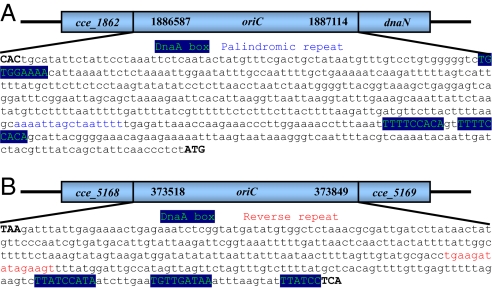
Welsh et al. (1) recently reported the complete genome of Cyanothece 51142 in PNAS. The authors concluded that “The origin of replication could not be determined for either the circular or linear chromosome by using standard GC skew and DnaA box analysis” (1). However, by utilizing a web-based system Ori-Finder (2), we have identified the locations of oriC for both the circular and linear chromosomes in Cyanothece 51142. For the circular chromosome, the oriC is predicted within the intergenic region between the ORF cce_1862 and the dnaN gene (cce_1864), from 1,886,587 nt to 1,887,114 nt of the chromosome. The feature that oriC is adjacent to the dnaN gene is universal among the bacteria within the class Cyanobacteria (for more detail, please visit DoriC, a database of oriC regions in bacterial genomes at http://tubic.tju.edu.cn/doric/). This oriC region also contains 3 putative DnaA boxes (Fig. 1A), each with perfect match to TTTTCCACA, the “species-specific” DnaA box motif for the class Cyanobacteria. For the linear chromosome, the oriC is predicted within the intergenic region between 2 ORFs, cce_5168 and cce_5169, from 373,518 nt to 373,849 nt of the chromosome. This identified oriC region is around the minimum of the GC disparity curve (348,971 nt) and contains 3 putative DnaA boxes (Fig. 1B), each with no more than 1 mismatch from TTATCCACA, the DnaA box motif of Escherichia coli. It is also observed that the oriC for the linear chromosome contains a reverse repeat, TGAAGATATAGAAGT (Fig. 1B).
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of the replication origins in Cyanothece 51142 for the circular chromosome (A) and linear chromosome (B). DnaA box, palindromic repeat, and reverse repeat are marked in green, blue, and red, respectively.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Welsh EA, et al. The genome of Cyanothece 51142, a unicellular diazotrophic cyanobacterium important in the marine nitrogen cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:15094–15099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805418105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gao F, Zhang CT. Ori-Finder: A web-based system for finding oriCs in unannotated bacterial genomes. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:79. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]