Abstract
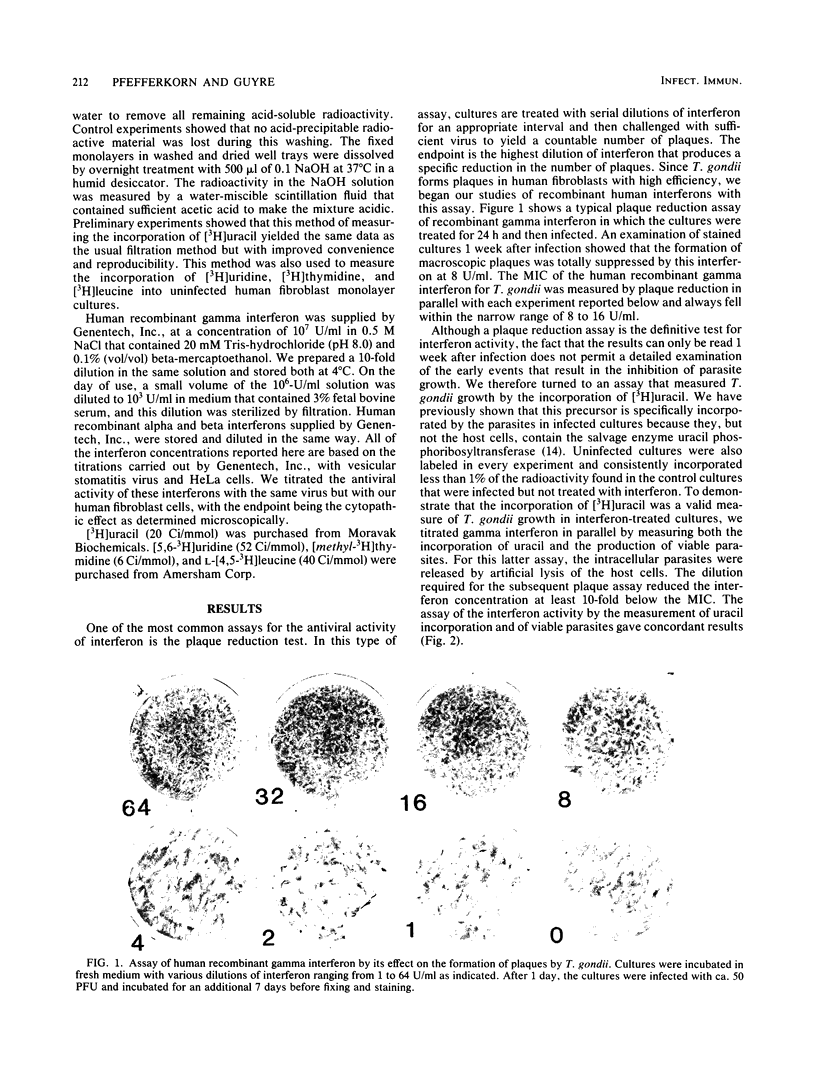
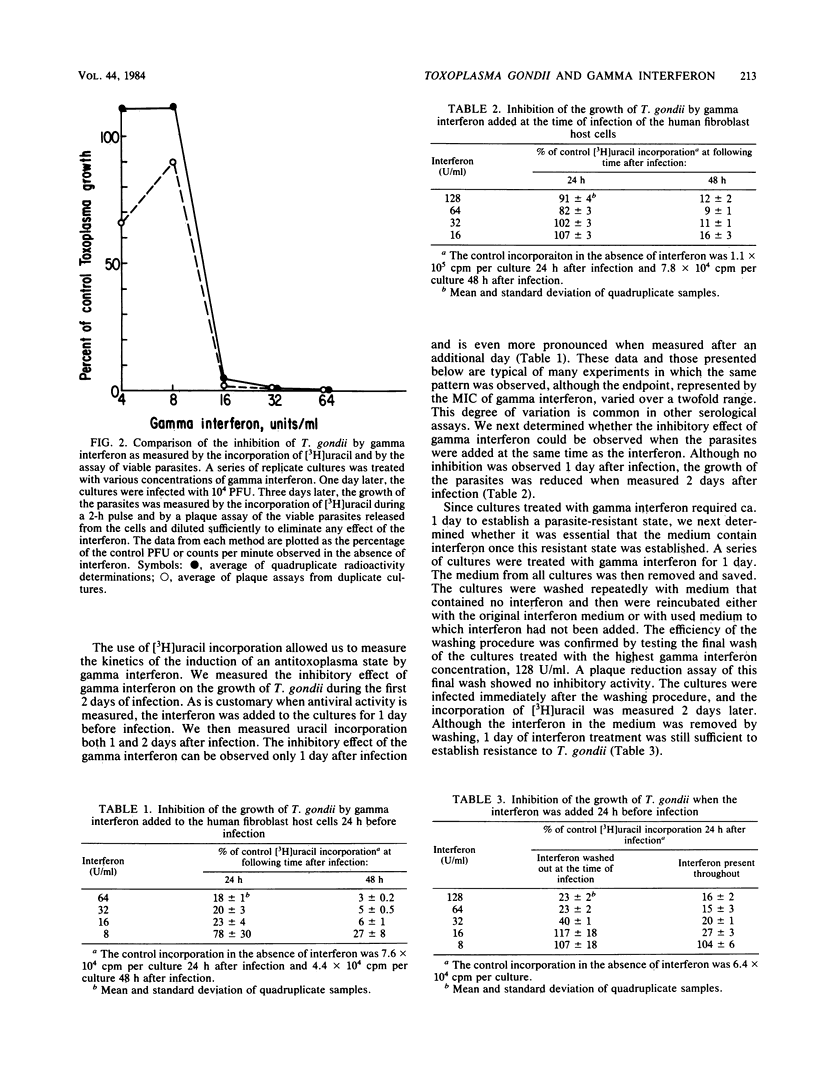
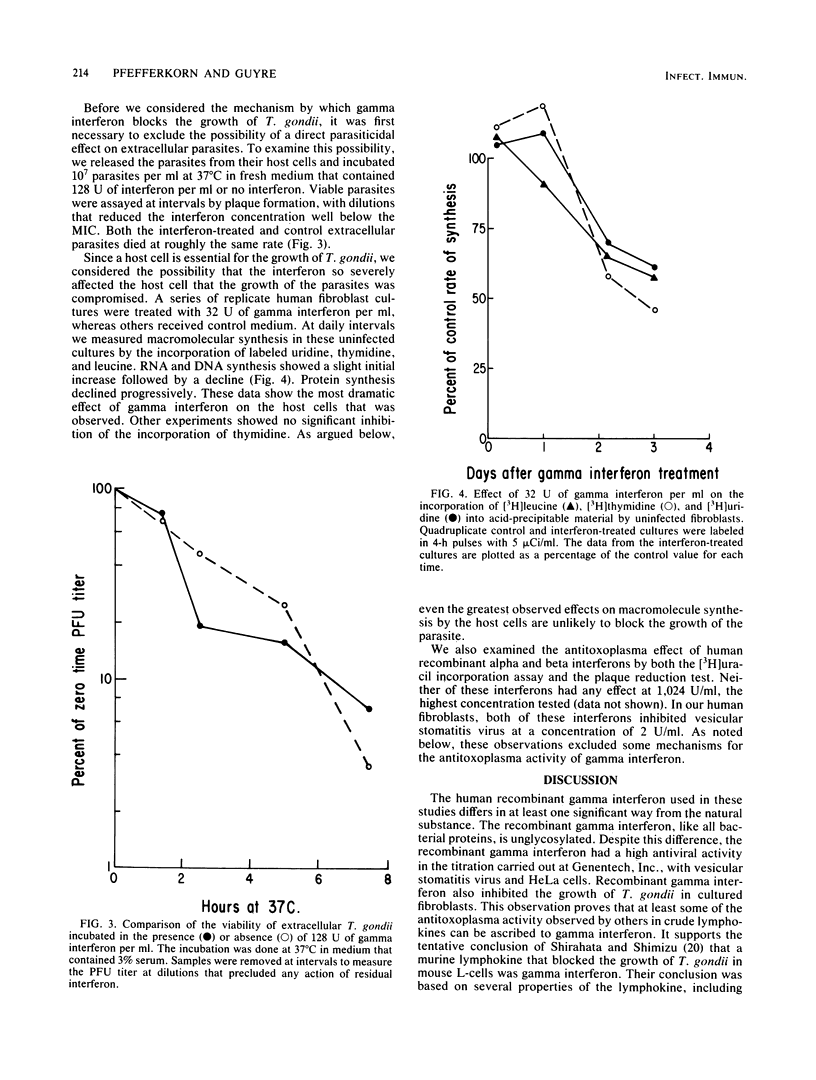
The growth of Toxoplasma gondii in cultured human fibroblasts was inhibited by recombinant human gamma interferon at concentrations of 8 to 16 U/ml. The interferon was titrated by observing a total inhibition of parasite plaque formation 7 days after infection. Inhibition of the growth of T. gondii in the early days after infection was measured by marked reductions in the incorporation of radioactive uracil, a precursor that can only be used by the parasites. This assay showed that when cells were pretreated with gamma interferon for 1 day and then infected, inhibition of T. gondii growth could be readily detected 1 or 2 days after infection. When the pretreatment was omitted and parasites and gamma interferon were added at the same time, no inhibition of parasite growth could be detected 1 day later, although it was apparent after 2 days. Cultures from which the gamma interferon had been removed by washing after a 1-day treatment showed inhibition of T. gondii growth. Gamma interferon had no effect on the viability of extracellular parasites, but it did inhibit the synthesis of host cell RNA and protein by ca. 50% 3 days after treatment. This degree of inhibition is unlikely, of itself, to compromise the growth of T. gondii. Recombinant alpha and beta interferons had no effect on the growth of T. gondii.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahronheim G. A. Toxoplasma gondii: human interferon studies by plaque assay. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Sep;161(4):522–526. doi: 10.3181/00379727-161-40588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of normal and activated human macrophages on Toxoplasma gondii. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1154–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. E., Hagemo A., Knoblock K., Dubey J. P. Toxoplasma gondii: microassay to differentiate toxoplasma inhibiting factor and interleukin 2. Exp Parasitol. 1983 Jun;55(3):320–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(83)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. C. The mechanism of interferon production. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Sep 24;299(1094):51–57. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinchilla M., Frenkel J. K. Mediation of immunity to intracellular infection (Toxoplasma and Besnoitia) within somatic cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):999–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.999-1012.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Pang R. H. Induction of unique mRNAs by human interferons. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9234–9237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Nutrition needs of mammalian cells in tissue culture. Science. 1955 Sep 16;122(3168):501–514. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3168.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C. Multiplication of toxoplasmas in enucleate fibroblasts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Apr;142(4):1268–1271. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Cayley P. J., Silverman R. H., Knight M. The antiviral action of interferon. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Sep 24;299(1094):59–67. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Nagasawa H., Sakurai H., Sasaki S., Suzuki N. Mouse spleen cell-derived toxoplasma growth inhibitory factor: its effect on toxoplasma multiplication in the mouse kidney cells. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981 Sep;250(3):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyagami T., Takei Y., Matsumoto Y., Otake N., Mizoue K., Mizutani T., Omura S., Ozeki M., Suzuki N. An in vitro study on the toxoplasmacidal activity of lonomycin A in host cells. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1981 Feb;34(2):218–223. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.34.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Pfefferkorn L. C. Toxoplasma gondii: growth in the absence of host cell protein synthesis. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Aug;52(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Pfefferkorn L. C. Toxoplasma gondii: isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Jun;39(3):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R. Toxoplasma gondii: the enzymic defect of a mutant resistant to 5-fluorodeoxyuridine. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Feb;44(1):26–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Merigan T. C. Interferon: protection of cells infected with an intracellular protozoan (Toxoplasma gondii). Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):804–806. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmunis G., Weissenbacher M., Chowchuvech E., Sawicki L., Galin M. A., Baron S. Growth of Toxoplasma gondii in various tissue cultures treated with In-Cn or interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Sep;143(4):1153–1157. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Pelster B., Piekarski G., Brandis H. Multiplication of Toxoplasma gondii in enucleated L cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):255–256. doi: 10.1038/newbio243255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata T., Shimizu K. Growth inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii in cell cultures treated with murine type II interferon. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1982 Dec;44(6):865–871. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.44.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata T., Shimizu K. Production and properties of immune interferon from spleen cell cultures of Toxoplasma-infected mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(11):1109–1120. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Epstein C. J., Epstein L. B., Sedmak J. J., Sabran J. L., Grossberg S. E. A unique set of polypeptides is induced by gamma interferon in addition to those induced in common with alpha and beta interferons. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):437–439. doi: 10.1038/301437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]