Abstract
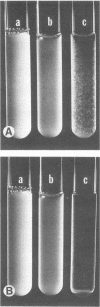
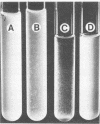
Human oral actinomyces and streptococci that exhibit specific coaggregation patterns when the cells are suspended in buffer were tested for their ability to coaggregate in saliva. Of 53 paired combinations of actinomyces (Actinomyces viscosus, A. naeslundii, or Actinomyces sp. WVa 963) and streptococci (Streptococcus sanguis or S. morbillorum) that exhibited coaggregation in buffer, all but 4 pairs also coaggregated when suspended in saliva. Twenty-four pairs exhibited lactose-inhibited coaggregation in buffer: 19 of these were identical in saliva. The other five pairs either did not coaggregate or formed coaggregates that were not inhibited by lactose. Highly specific coaggregations known to occur with buffer-suspended cells (e.g., a streptococcal strain that coaggregates with a single strain of actinomyces) were unchanged when cells were suspended in saliva. These results indicate that the coaggregation properties of both oral actinomyces and streptococci are very similar with cells suspended in either saliva or coaggregation buffer. Thus, the potential for coaggregation among bacteria in the oral cavity is evident. The possible mechanisms which mediate coaggregation in saliva are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratthall D., Carlén A. Salivary agglutinin and secretory IgA reactions with oral streptococci. Scand J Dent Res. 1978 Dec;86(6):430–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1978.tb00650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Barsumian E. L., Curl S. H., Vatter A. E., Sandberg A. L., Siraganian R. P. Detection and localization of a lectin on Actinomyces viscosus T14V by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1318–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Curl S. H., Kolenbrander P. E., Vatter A. E. Specific absence of type 2 fimbriae on a coaggregation-defective mutant of Actinomyces viscosus T14V. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):759–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.759-765.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Kolenbrander P. E., McIntire F. C. Specificity of coaggregation reactions between human oral streptococci and strains of Actinomyces viscosus or Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):742–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.742-752.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heeb M. J., Costello A. H., Gabriel O. Characterization of a galactose-specific lectin from Actinomyces viscosus by a model aggregation system. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):993–1002. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.993-1002.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Inouye Y., Holdeman L. V. New Actinomyces and Streptococcus coaggregation groups among human oral isolates from the same site. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):501–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.501-506.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E. Isolation and characterization of coaggregation-defective mutants of Actinomyces viscosus, Actinomyces naeslundii, and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1200–1208. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1200-1208.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Williams B. L. Lactose-reversible coaggregation between oral actinomycetes and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):95–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.95-102.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Williams B. L. Prevalence of viridans streptococci exhibiting lactose-inhibitable coaggregation with oral actinomycetes. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):449–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.449-452.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Herzberg M. C., Levine M. S., Ellison S. A., Stinson M. W., Li H. C., van Dyke T. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: role of terminal sialic acid residues in the interaction of salivary glycoproteins with Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.107-115.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G., Ofstehage J. C. Aggregation and adherence of Streptococcus sanguis: role of human salivary immunoglobulin A. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1104–1110. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1104-1110.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamud D., Appelbaum B., Kline R., Golub E. E. Bacterial aggregating activity in human saliva: comparisons of bacterial species and strains. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1003–1006. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1003-1006.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. H., Wittenberger C. L. Mannitol transport in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1475–1481. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1475-1481.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Gisslow M. T. Role of sialic acid in saliva-induced aggregation of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.35-40.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Vatter A. E., Baros J., Arnold J. Mechanism of coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Streptococcus sanguis 34. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):978–988. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.978-988.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. A., Levine M. J., Tabak L. A., Reddy M. S. Specificity of salivary-bacterial interactions: II. Evidence for a lectin on Streptococcus sanguis with specificity for a NeuAc alpha 2, 3Ga1 beta 1, 3Ga1NAc sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):390–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revis G. J., Vatter A. E., Crowle A. J., Cisar J. O. Antibodies against the Ag2 fimbriae of Actinomyces viscosus T14V inhibit lactose-sensitive bacterial adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1217–1222. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1217-1222.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Malamud D., Appelbaum B., Golub E. Characteristic differences between saliva-dependent aggregation and adhesion of streptococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):86–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.86-90.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]