Abstract
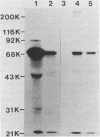
Hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibodies specific for exotoxin A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PA103 were derived from the fusion of spleen cells from mice immunized with: (i) purified exotoxin A, (ii) Formalin-treated exotoxin A, (iii) exotoxin A covalently coupled to Sepharose 4B, or (iv) P. aeruginosa-infected mice. All hybridomas were screened and selected by using an enzyme-linked immuno-adsorbent assay. All antibody isotypes were represented (immunoglobulins G, A, and M) as determined by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. The most productive fusions resulted from immunization with antigens coupled to an insoluble matrix, such as Sepharose 4B, or by infection of mice. Several hybridomas were selected and cloned by limiting dilution. The specificity of the monoclonal antibodies for exotoxin A was demonstrated by indirect immunoprecipitation of 125I-labeled exotoxin A followed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis and by the immunoblotting technique. The protective ability of certain monoclonal antibodies was demonstrated in vitro by toxin neutralization in tissue culture and in vivo by prolonged survival time in the burned mouse infection model, after passive immunization. One monoclonal antitoxin displayed specificity for PA103-derived exotoxin yet failed to react with exotoxin purified from PAO-PR1 or PAO1, suggesting that structural differences exist between these exotoxins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H., Sokol P. A. Evidence for the role of toxin A in the pathogenesis of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in humans. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):538–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant producing a nontoxic, immunologically crossreactive toxin A protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7199–7203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick M. R., Cluff L. E. Pseudomonas bacteremia. Review of 108 cases. Am J Med. 1976 Apr;60(4):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90716-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom R. C., Pavlovskis O. R., Galloway D. R. Antibody response of infected mice to outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.49-53.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder I. A., Jogan M. Enhanced survival in burned mice treated with antiserum prepared against normal and burned skin. J Trauma. 1971 Dec;11(12):1041–1046. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197112000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J. C. Toxin inhibitors of protein synthesis: production, purification, and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:780–793. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppla S. H. Large-scale purification and characterization of the exotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1077–1086. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1077-1086.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. II. Effects of lecithinase and protease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Feb;116(1):112–116. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman D. E., Sadoff J. C., Iglewski B. H. Toxin A-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):899–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.899-908.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Edman D. C., Leppla S. H., Wretlind B., Lewis L. R., Martin K. E. Protection against experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in mice by active immunization with exotoxin A toxoids. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):681–689. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.681-689.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskis O. R., Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Iglewski B. H. Passive protection by antitoxin in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn infections. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):596–602. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.596-602.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Taylor N. S. Neutralizing antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin in human sera: evidence for in vivo toxin production during infection. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):942–947. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.942-947.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 12;302(24):1360–1362. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006123022410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Young L. S. Protective activity of antibodies to exotoxin A and lipopolysaccharide at the onset of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):276–286. doi: 10.1172/JCI109300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieritz D. D., Holder I. A. Experimental studies of the pathogenesis of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa: description of a burned mouse model. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):688–691. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stähli C., Staehelin T., Miggiano V. Spleen cell analysis and optimal immunization for high-frequency production of specific hybridomas. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:26–36. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson J. R., Lerner A. M. Characteristics of nonbacteremic Pseudomonas pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Feb;68(2):295–307. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]