Abstract
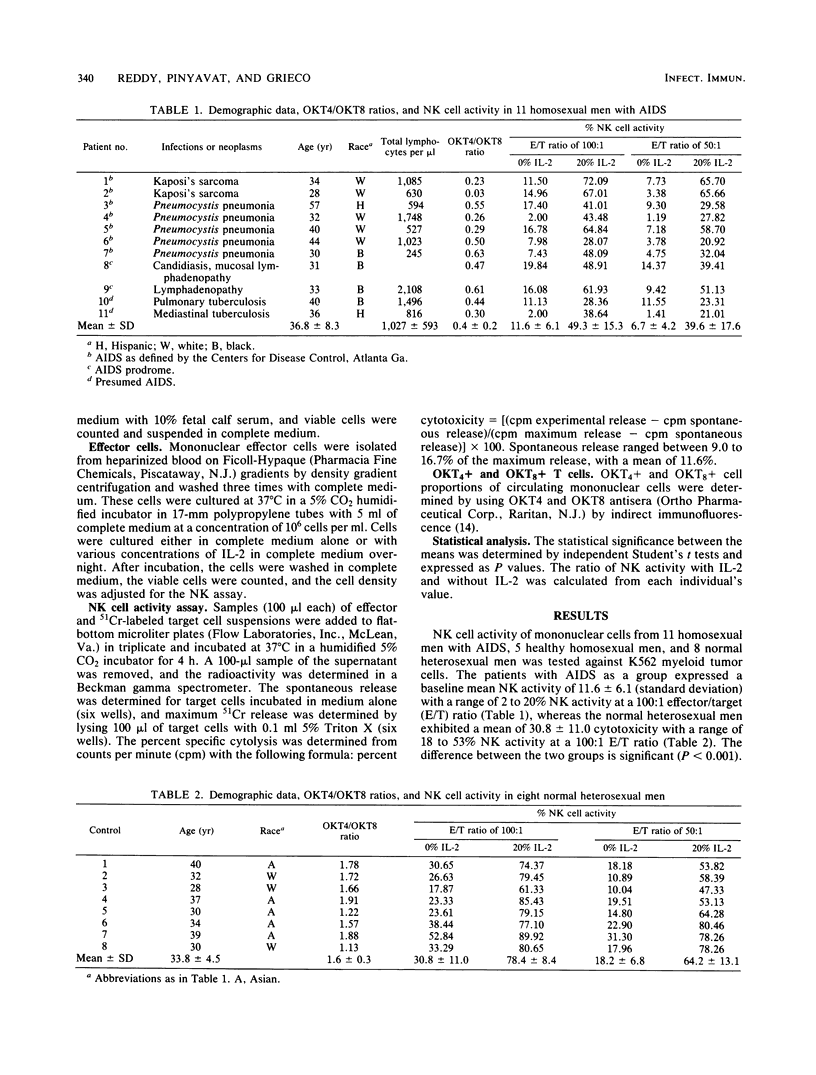
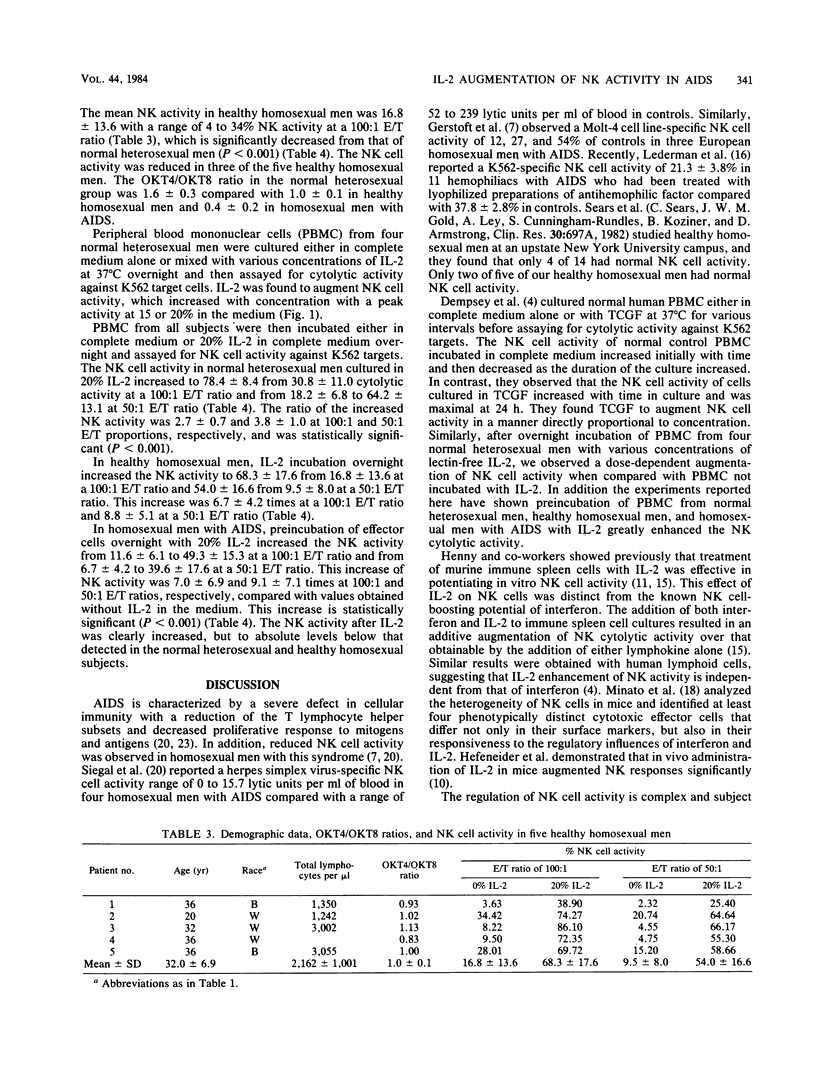
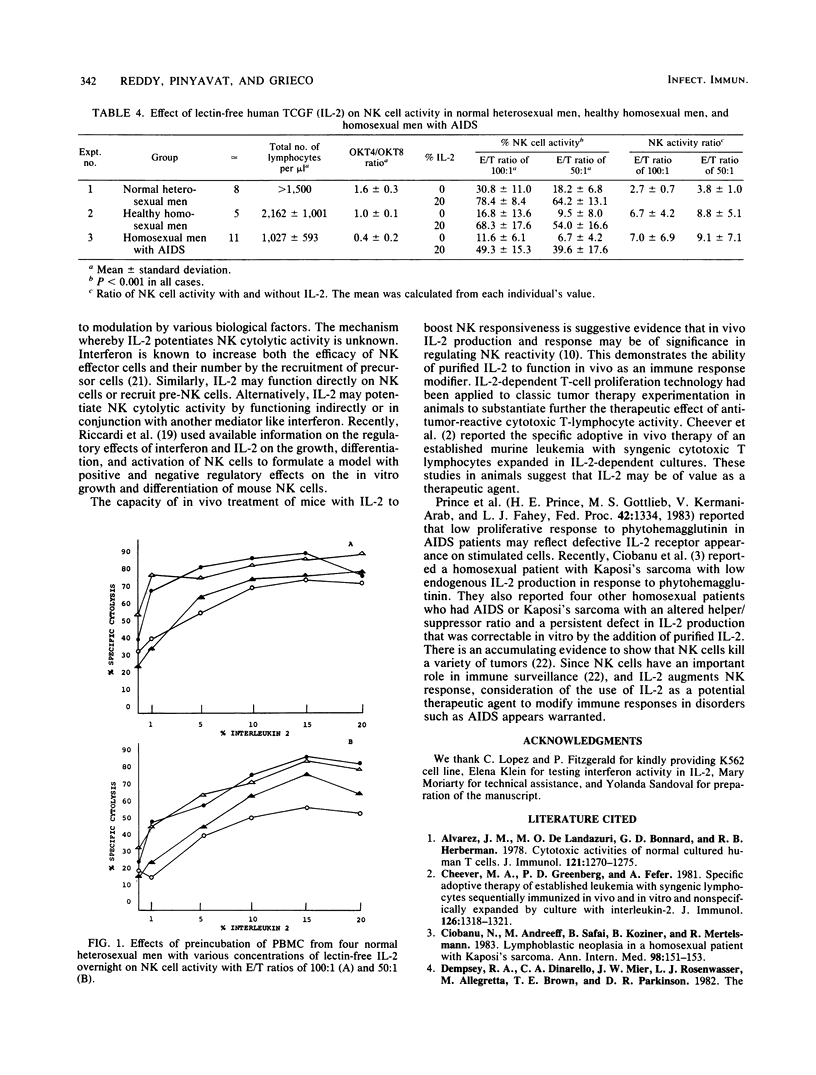
Natural killer cell activity of peripheral blood mononuclear cells against K562 myeloid cells was studied in 8 normal heterosexual men, 5 healthy homosexual men, and 11 homosexual men with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. The overall natural killer cell activity was lower in healthy homosexual men and in homosexual men with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from four normal heterosexual men were preincubated overnight in complete medium supplemented with various concentrations of lectin-free interleukin 2 lacking interferon. Cells from these cultures exhibited a dose-dependent augmentation of natural killer cell activity. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained from 8 normal heterosexuals, 5 healthy homosexuals, and 11 homosexual men with acquired immune deficiency syndrome were preincubated overnight in complete medium supplemented with 20% interleukin 2. Natural killer cell activity cultured in 20% interleukin 2 increased to 78.4 +/- 8.4 (mean +/- standard deviation) from 30.8 +/- 11.0 in normal heterosexual men, to 68.3 +/- 17.6 from 16.8 +/- 13.6 in healthy homosexual men and to 49.3 +/- 15.3 from 11.6 +/- 6.1 in homosexual men with acquired immune deficiency syndrome at a 100:1 effector/target cell ratio. These results suggest that interleukin 2 is capable of directly stimulating natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Consideration of the use of interleukin 2 as a potential therapeutic agent to modify immune responses in disorders such as acquired immune deficiency syndrome appears warranted.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez J. M., de Landazuri M. O., Bonnard G. D., Herberman R. B. Cytotoxic activities of normal cultured human T cells. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1270–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheever M. A., Greenberg P. D., Fefer A. Specific adoptive therapy of established leukemia with syngeneic lymphocytes sequentially immunized in vivo and in vitro and nonspecifically expanded by culture with Interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1318–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciobanu N., Andreeff M., Safai B., Koziner B., Mertelsmann R. Lymphoblastic neoplasia in a homosexual patient with Kaposi's sarcoma. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Feb;98(2):151–155. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-2-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey R. A., Dinarello C. A., Mier J. W., Rosenwasser L. J., Allegretta M., Brown T. E., Parkinson D. R. The differential effects of human leukocyte pyrogen/lymphocyte-activating factor, T cell growth factor, and interferon on human natural killer activity. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2504–2510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Yogeeswaran G., Yamagata S. Cloned cell lines with natural killer activity. Specificity, function, and cell surface markers. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):545–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Benjamin W. R., Hilfiker M. L., Howard M., Farrar W. L., Fuller-Farrar J. The biochemistry, biology, and role of interleukin 2 in the induction of cytotoxic T cell and antibody-forming B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:129–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstoft J., Malchow-Møller A., Bygbjerg I., Dickmeiss E., Enk C., Halberg P., Haahr S., Jacobsen M., Jensen K., Mejer J. Severe acquired immunodeficiency in European homosexual men. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jul 3;285(6334):17–19. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6334.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Watson J. Interleukin-2 induction of hapten-specific cytolytic T cells in nude mice. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1245–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefeneider S. H., Conlon P. J., Henney C. S., Gillis S. In vivo interleukin 2 administration augments the generation of alloreactive cytolytic T lymphocytes and resident natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):222–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. R., Ortaldo J. R., Bonnard G. D. Augmentation by interferon of human natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):221–223. doi: 10.1038/277221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Vande Stouwe R. A., Lange M., Reddy M. M., Grieco M. H. T-lymphocyte subpopulations in homosexual men. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 16;307(12):729–731. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209163071206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuribayashi K., Gillis S., Kern D. E., Henney C. S. Murine NK cell cultures: effects of interleukin-2 and interferon on cell growth and cytotoxic reactivity. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2321–2327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman M. M., Ratnoff O. D., Scillian J. J., Jones P. K., Schacter B. Impaired cell-mediated immunity in patients with classic hemophilia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 13;308(2):79–83. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301133080205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier J. W., Gallo R. C. Purification and some characteristics of human T-cell growth factor from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocyte-conditioned media. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6134–6138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minato N., Reid L., Bloom B. R. On the heterogeneity of murine natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):750–762. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi C., Vose B. M., Herberman R. B. Modulation of IL 2-dependent growth of mouse NK cells by interferon and T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):228–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Lopez C., Hammer G. S., Brown A. E., Kornfeld S. J., Gold J., Hassett J., Hirschman S. Z., Cunningham-Rundles C., Adelsberg B. R. Severe acquired immunodeficiency in male homosexuals, manifested by chronic perianal ulcerative herpes simplex lesions. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1439–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S., Dorey F. Interferon activation of "pre-spontaneous killer" (pre-SK) cells and alteration in kinetics of lysis of both "pre-SK" and active SK cells. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2157–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. F., Dennert G. Effects of a cloned cell line with NK activity on bone marrow transplants, tumour development and metastasis in vivo. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):31–34. doi: 10.1038/300031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterson A. P. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Mar 5;286(6367):743–746. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6367.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


