Figure 1. The C95 residue in PITPα is located close to the lipid-headgroup-binding site.
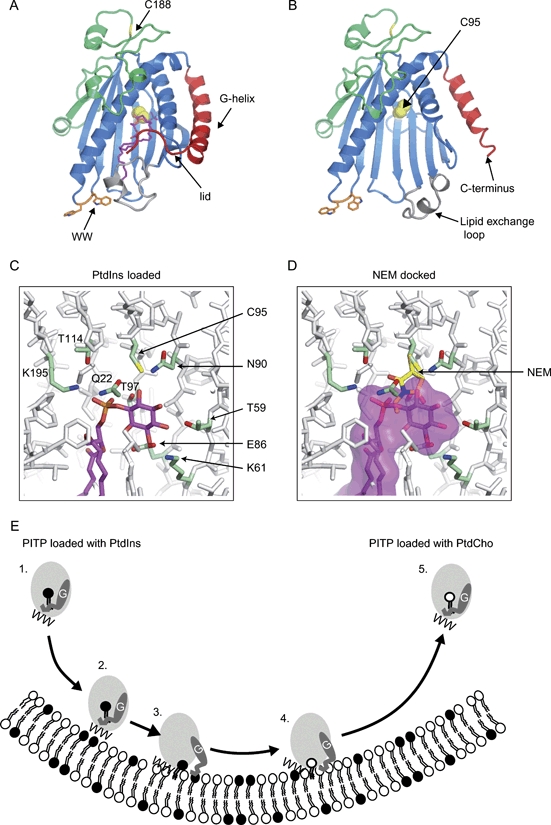
The position of C95 residue is shown in A) the closed (lipid-bound) and in B) the open (lipid-free) conformations of a PITPα molecule. The lipid-binding core residues are coloured blue, the G-helix and the extended 11 amino acids at the C-terminus that form the lid are coloured red, the regulatory loop is coloured green and the lipid exchange loop (18) is coloured grey. C95 is depicted as balls and is coloured yellow; it is inaccessible to small molecules in the closed conformation (A) but exposed in the apo structure (B). The backbone of the surface residue C188 is coloured yellow. In the apo structure, the lipid exchange loop and the G-helix have moved to the open configuration and the C-terminal region is disordered. The side chains of W203 and 204 are coloured orange. The diagrams were generated using the pymolsoftware with PDB files 1t27 and 1kcm. C) A stick model showing a PtdIns molecule (magenta carbon atoms) and the functionally important inositol-binding residues K61, N90, T59 and E86 in the lipid-binding cavity of PITPα. Also, labelled are the four residues that make contact with the phosphate moiety of the phospholipids, Q22, T97, T114 and K195. C95 (green carbon atoms and yellow sulphur atom) is seen to be in close proximity to the inositol ring (PDB code: 1UW5). D) Docking of NEM on C95 illustrates that alkylation of C95 would sterically hinder phospholipid binding. The NEM is shown with yellow carbon atoms and clashes with PtdIns (shown with a pink surface). E) Model for membrane interactions and lipid exchange by PITPs. 1) Soluble PITP bound to PtdIns in the closed conformation in the cytosol. 2) PITP initially docks onto a membrane using the two tryptophan residues (WW). 3) Conformational change of PITP at the membrane into an open form involves movement of the C-terminus and G α-helix, which exposes the hydrophobic surface of the lipid-binding cavity. This allows lipid exchange of PtdIns for PtdCho to occur. 4) Following lipid exchange, PITP bound to PtdCho undergoes a conformational change into the closed form. 5) PITP bound to PtdCho in the closed conformation is soluble and freely diffuses away from the membrane. PtdIns, solid circles; PtdCho, open circles.
