Abstract
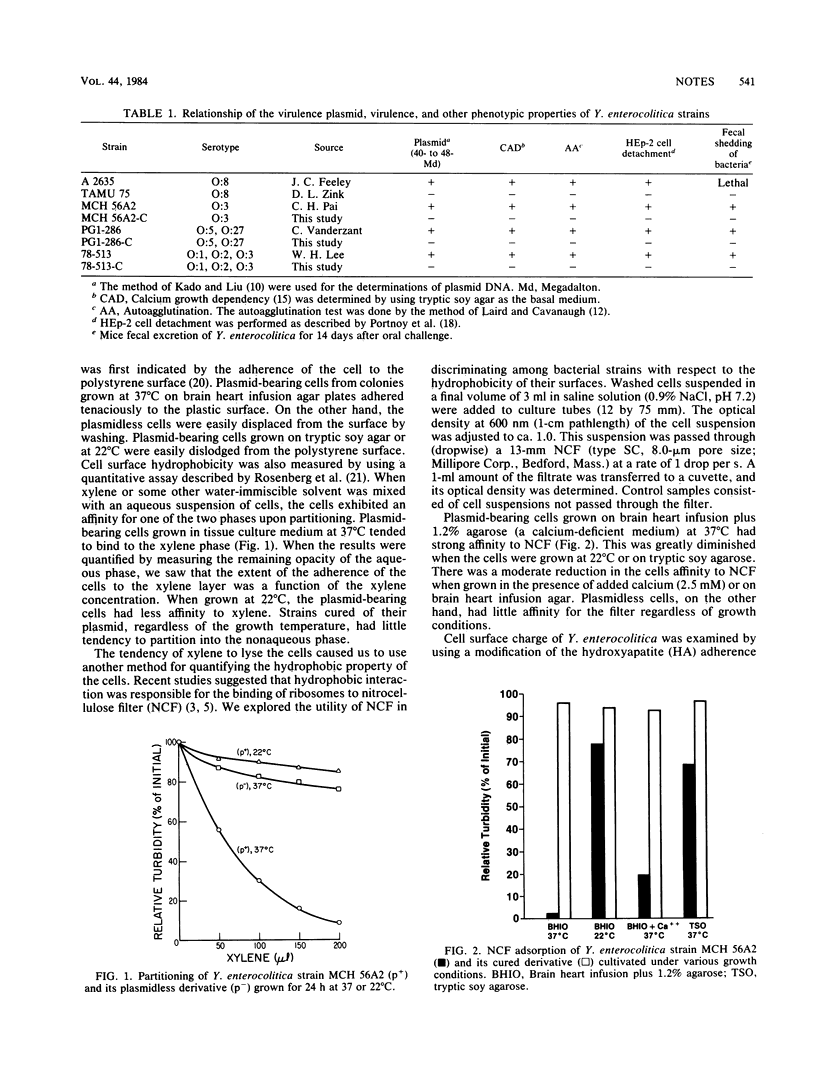
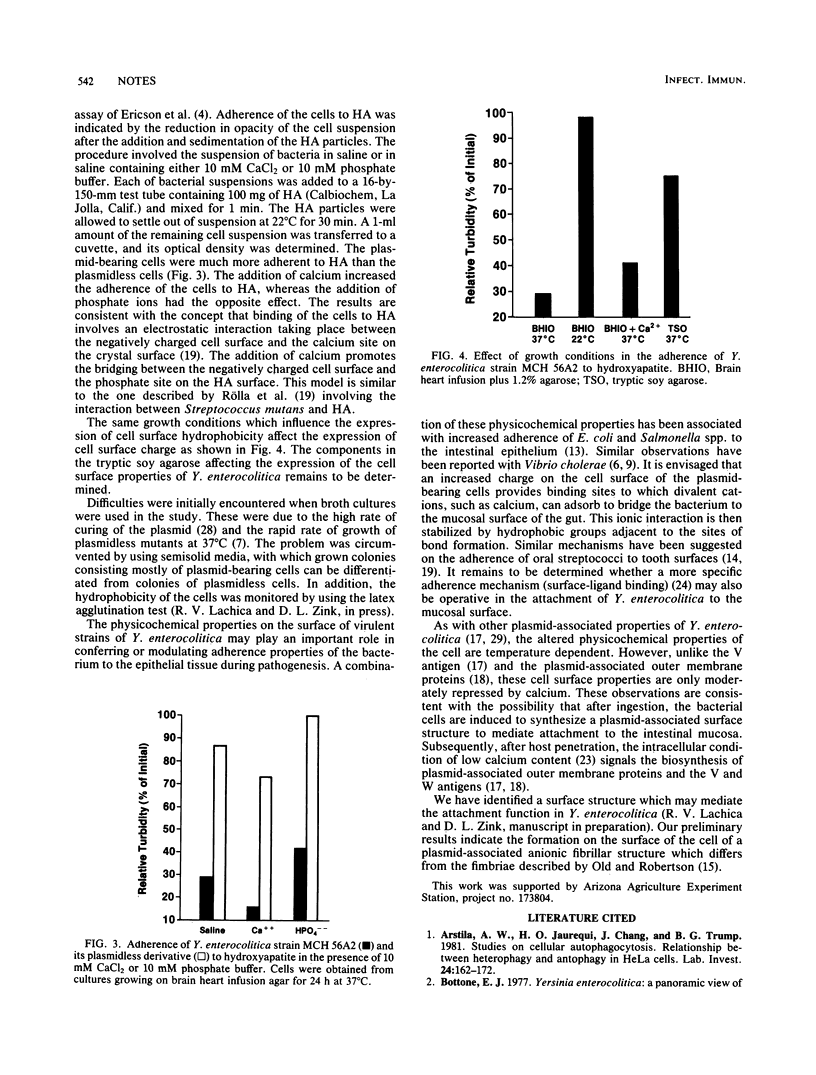
Virulent strains of Yersinia enterocolitica and their plasmidless, avirulent derivatives were examined for their cell surface properties. Increased surface charge and hydrophobicity of Y. enterocolitica were found to be associated with the possession of a 40- to 48-megadalton plasmid. These surface properties were expressed, as were other plasmid-associated properties, at 37 but not at 22 degrees C. The concentration of calcium in the growth medium had a moderate effect on the expression of the cell surface properties. These cell surface properties were greatly reduced among plasmid-bearing cells grown on tryptic soy agarose regardless of growth temperatures. These properties were also associated with the ability of Y. enterocolitica to colonize the gastrointestinal tract of mice.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arstila A. U., Jauregui H. O., Chang J., Trump B. F. Studies on cellular autophagocytosis. Relationship between heterophagy and autophagy in HeLa cells. Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;24(2):162–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashion P., Sathe G., Javed A., Kuster J. Hydrophobic affinity chromatography of nucleic acids and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):1167–1185. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson T., Sandham J., Magnusson I. Sedimentation method for studies of adsorption of microorganisms onto apatite surfaces in vitro. Caries Res. 1975;9(5):325–332. doi: 10.1159/000260165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fábry M., Kalvoda L., Rychlík I. Hydrophobic interactions of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 29;652(1):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S., Ali S. Characterization of surface properties of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1048–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1048-1058.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Magnusson K. E. Haemagglutinating, adhesive and physico-chemical surface properties of different Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia enterocolitica-like bacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):113–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Davies J., Grundström T., Kihlström E., Normark S. Surface charge and hydrophobicity of Salmonella, E. coli, Gonococci in relation to their tendency to associate with animal cells. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;Suppl 24:135–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G. Hydrophobic interactions and the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.637-644.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C., Robertson J. Adherence of fimbriate and non-fimbriate strains of Yersinia enterocolitica to human epithelial cells. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(10):993–998. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Vwa+ phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.166-171.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. Bacterial adherence to polystyrene: a replica method of screening for bacterial hydrophobicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):375–377. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.375-377.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rölla G., Iversen O. J., Bonesvoll P. Lipoteichoic acid - the key to the adhesiveness of sucrose grown Streptococcus mutans. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:607–617. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Devenish J. A. Relationship of HeLa cell infectivity to biochemical, serological, and virulence characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):497–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.497-506.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Carey A. M., Damare J. M., Hetrick F. M., Johnston R. W., Lee W. H. Evaluation of iron dextran and mucin for enhancement of the virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3 in mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):550–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.550-560.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Soderlind O., Rosengren J., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Differences in hydrophobic surface characteristics of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with or without K88 antigen as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.462-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:19–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


