Abstract
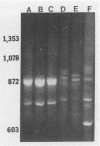
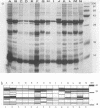
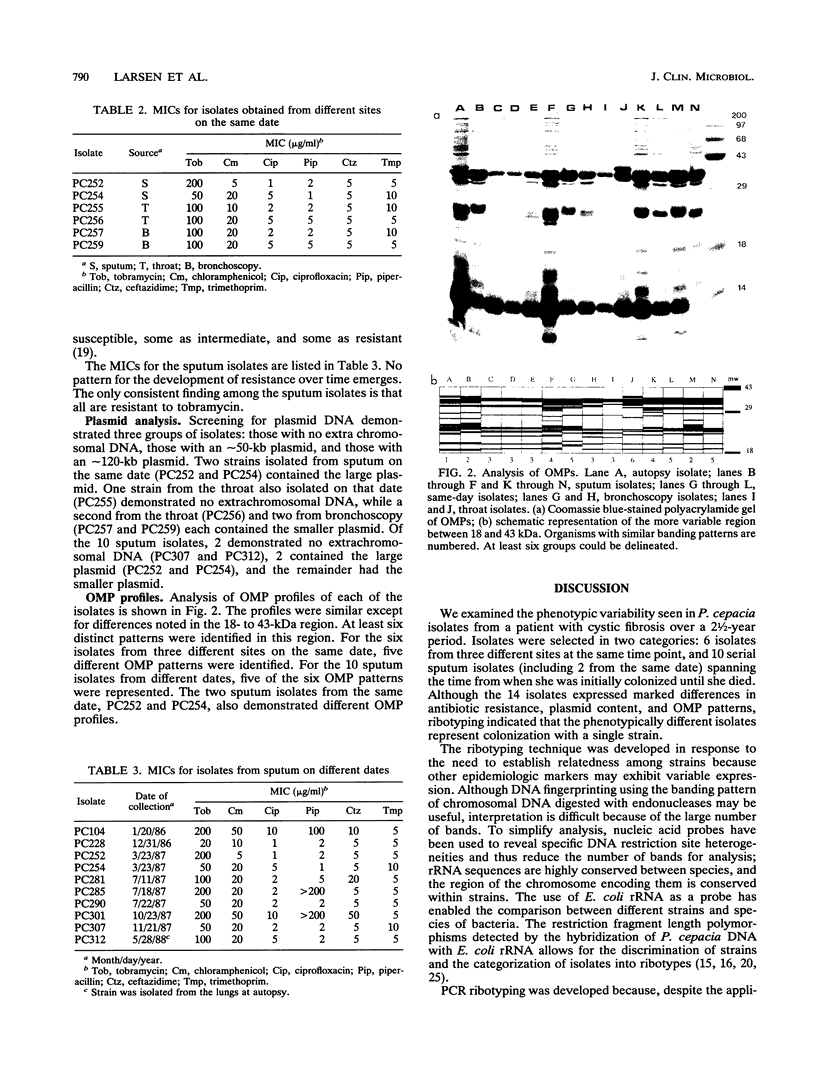
Characterization of the epidemiology of Pseudomonas cepacia colonization in cystic fibrosis is difficult because of the phenotypic variability of isolates. A single sputum culture may yield colonies which differ in morphology, antibiotic susceptibility, and pigment production. We examined serial P. cepacia isolates from a cystic fibrosis patient which the clinical laboratory identified as separate strains; these were selected on the basis of isolation date and culture site. An attempt was made to sample at multiple time points and, at a single time point, from three different culture sites. Ribotype analysis, using both the standard Southern blot technique and a recently reported method which uses the polymerase chain reaction, was used to distinguish unique P. cepacia strains. Characterization included comparison of antibiotic susceptibility, plasmid content, and outer membrane protein (OMP) patterns. rRNA analysis demonstrated that all isolates had the same ribotype, consistent with their being derivatives of the same strain. Antibiotic susceptibility testing revealed variability among both same-date and same-site isolates. Screening for plasmid DNA identified three groups of isolates; both same-date and same-site isolates demonstrated variability. OMP profiles were similar, but at least six distinct patterns were identified. For the six same-date isolates, five different OMP patterns were identified. For the 10 same-site isolates from different dates, five of the six OMP patterns were represented. We have demonstrated marked phenotypic variability in 14 strains of P. cepacia isolated from different sites and at different times from a single colonized patient. Ribotyping identified all the isolates as derivatives of a single strain; thus, the diversity of phenotypes appears to be the result of differential gene expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsomian G., Lessie T. G. IS2 activates the ilvA gene of Pseudomonas cepacia in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1777–1779. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1777-1779.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsomian G., Lessie T. G. Replicon fusions promoted by insertion sequences on Pseudomonas cepacia plasmid pTGL6. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Aug;204(2):273–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00425509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman W., Gaffney T., Lessie T. G. Correlation between auxotrophy and plasmid alteration in mutant strains of Pseudomonas cepacia. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1154–1158. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1154-1158.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman W., Lessie T. G. Response of Pseudomonas cepacia to beta-Lactam antibiotics: utilization of penicillin G as the carbon source. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1126–1128. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1126-1128.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosso J. A., Allen J. E., Matsen J. M. Changing susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients with the clinical use of newer antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):526–528. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. L., Hedin L. A., Lien D. M. Chloramphenicol resistance in Pseudomonas cepacia because of decreased permeability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):136–141. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney T. D., Lessie T. G. Insertion-sequence-dependent rearrangements of Pseudomonas cepacia plasmid pTGL1. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):224–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.224-230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isles A., Maclusky I., Corey M., Gold R., Prober C., Fleming P., Levison H. Pseudomonas cepacia infection in cystic fibrosis: an emerging problem. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80993-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Archer G. L. New mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 28;324(9):601–612. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102283240906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Fisher M. C., Dasen S. E., Mortensen J. E., Stull T. L. Ribotype stability of serial pulmonary isolates of Pseudomonas cepacia. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):133–136. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Mortensen J. E., Dasen S. E., Edlind T. D., Schidlow D. V., Burns J. L., Stull T. L. Ribotype analysis of Pseudomonas cepacia from cystic fibrosis treatment centers. J Pediatr. 1988 Nov;113(5):859–862. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner P. S., Falkinham J. O., 3rd Plasmid DNA profiles as epidemiological markers for clinical and environmental isolates of Mycobacterium avium, Mycobacterium intracellulare, and Mycobacterium scrofulaceum. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):325–331. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin C. S., Jarvis W. R., Anderson R. L., Govan J., Klinger J., LiPuma J., Martone W. J., Monteil H., Richard C., Shigeta S. Pseudomonas cepacia typing systems: collaborative study to assess their potential in epidemiologic investigations. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11(4):600–607. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.4.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Ogunariwo J., Chamberland S., Godfrey A. J., Rabin H. R., Bryan L. E. Mechanism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa persistence during treatment with broad-spectrum cephalosporins of lung infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1438–1439. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scordilis G. E., Ree H., Lessie T. G. Identification of transposable elements which activate gene expression in Pseudomonas cepacia. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):8–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.8-13.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tablan O. C., Chorba T. L., Schidlow D. V., White J. W., Hardy K. A., Gilligan P. H., Morgan W. M., Carson L. A., Martone W. J., Jason J. M. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization in patients with cystic fibrosis: risk factors and clinical outcome. J Pediatr. 1985 Sep;107(3):382–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80511-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tablan O. C., Martone W. J., Doershuk C. F., Stern R. C., Thomassen M. J., Klinger J. D., White J. W., Carson L. A., Jarvis W. R. Colonization of the respiratory tract with Pseudomonas cepacia in cystic fibrosis. Risk factors and outcomes. Chest. 1987 Apr;91(4):527–532. doi: 10.1378/chest.91.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch D. F., Muszynski M. J., Pai C. H., Marcon M. J., Hribar M. M., Gilligan P. H., Matsen J. M., Ahlin P. A., Hilman B. C., Chartrand S. A. Selective and differential medium for recovery of Pseudomonas cepacia from the respiratory tracts of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1730–1734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1730-1734.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M. S., Lory C., Lessie T. G. Activation of the lac genes of Tn951 by insertion sequences from Pseudomonas cepacia. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1719–1724. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1719-1724.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]