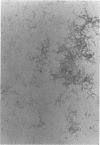
Abstract
A Rochalimaea-like organism (strain F9251) was isolated from a patient with endocarditis after blood drawn for culture before antimicrobial therapy was subcultured onto blood and chocolate agars and incubated for 2 weeks in 5% CO2. The strain was phenotypically similar to known Rochalimaea species. The cellular fatty acid composition of strain F9251 was close to but distinct from those of the three known Rochalimaea species and was most similar to that of R. vinsonii. Labeled DNA from strain F9251 was 59 to 67% related to DNAs from type strains of the three described Rochalimaea species, and its 16S rRNA gene sequence was 98.9% or more homologous to their 16S rRNA gene sequences. These findings support classification of F9251 as a new Rochalimaea species, for which the name Rochalimaea elizabethae sp. nov. is proposed. The patient infected with the organism had large bacterial vegetations on his aortic valve and was cured with antibiotics and valve-replacement surgery. Recognition of the procedures required to identify this and other Rochalimaea species suggests that clinical laboratories should prolong the incubation times of cultures of blood and tissue from patients with suspected endocarditis, patients with fever of unknown origin, and immunocompromised patients with fever so that the full spectrum of disease caused by these organisms can be recognized.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. E., Dawson J. E., Jones D. C., Wilson K. H. Ehrlichia chaffeensis, a new species associated with human ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2838–2842. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2838-2842.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birtles R. J., Harrison T. G., Fry N. K., Saunders N. A., Taylor A. G. Taxonomic considerations of Bartonella bacilliformis based on phylogenetic and phenotypic characteristics. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Oct 1;67(2):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90352-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Hollis D. G., Moss C. W., English C. K., Hall G. S., Vincent J., Radosevic J., Birkness K. A., Bibb W. F., Quinn F. D. Proposal of Afipia gen. nov., with Afipia felis sp. nov. (formerly the cat scratch disease bacillus), Afipia clevelandensis sp. nov. (formerly the Cleveland Clinic Foundation strain), Afipia broomeae sp. nov., and three unnamed genospecies. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2450–2460. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2450-2460.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., O'Connor S. P., Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Steigerwalt A. G. Molecular characterization and proposal of a neotype strain for Bartonella bacilliformis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1299–1302. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1299-1302.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Ley J. Reexamination of the association between melting point, buoyant density, and chemical base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):738–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.738-754.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drancourt M., Donnet A., Pelletier J., Raoult D. Acute meningoencephalitis associated with seroconversion to "Afipia felis". Lancet. 1992 Aug 29;340(8818):558–558. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91761-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English C. K., Wear D. J., Margileth A. M., Lissner C. R., Walsh G. P. Cat-scratch disease. Isolation and culture of the bacterial agent. JAMA. 1988 Mar 4;259(9):1347–1352. doi: 10.1001/jama.259.9.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman T., Ståhl S., Hornes E., Uhlén M. Direct solid phase sequencing of genomic and plasmid DNA using magnetic beads as solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4937–4946. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler J. E., Quinn F. D., Berger T. G., LeBoit P. E., Tappero J. W. Isolation of Rochalimaea species from cutaneous and osseous lesions of bacillary angiomatosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 3;327(23):1625–1631. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212033272303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreier J. P., Ristic M. The biology of hemotrophic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:325–338. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Lambert-Fair M. A. Location of double bonds in monounsaturated fatty acids of Campylobacter cryaerophila with dimethyl disulfide derivatives and combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1467–1470. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1467-1470.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. P., Dorsch M., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J., Stackebrandt E. 16S rRNA sequences of Bartonella bacilliformis and cat scratch disease bacillus reveal phylogenetic relationships with the alpha-2 subgroup of the class Proteobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2144–2150. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2144-2150.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkocha L. A., Geaghan S. M., Yen T. S., Nishimura S. L., Chan S. P., Garcia-Kennedy R., Honda G., Stoloff A. C., Klein H. Z., Goldman R. L. Clinical and pathological features of bacillary peliosis hepatis in association with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1581–1586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Anderson B. E., Clarridge J. E., 3rd, Rodriguez-Barradas M. C., Jones D. C., Carr J. H. Characterization of a novel Rochalimaea species, R. henselae sp. nov., isolated from blood of a febrile, human immunodeficiency virus-positive patient. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.265-274.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Olson J. G., Perkins B. A., Bibb W. Serological response to "Rochalimaea henselae" antigen in suspected cat-scratch disease. Lancet. 1992 Jun 13;339(8807):1443–1445. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92032-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R., Martin M., Olson J. Naturally occurring "Rochalimaea henselae" infection in domestic cat. Lancet. 1992 Aug 29;340(8818):557–558. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91760-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Lepp P. W., Sadler K. N., Schmidt T. M. Phylogenetic relationships among the agent of bacillary angiomatosis, Bartonella bacilliformis, and other alpha-proteobacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(13):1801–1807. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Loutit J. S., Schmidt T. M., Falkow S., Tompkins L. S. The agent of bacillary angiomatosis. An approach to the identification of uncultured pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1573–1580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scowden E. B., Schaffner W., Stone W. J. Overwhelming strongyloidiasis: an unappreciated opportunistic infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 Nov;57(6):527–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater L. N., Welch D. F., Hensel D., Coody D. W. A newly recognized fastidious gram-negative pathogen as a cause of fever and bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1587–1593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater L. N., Welch D. F., Min K. W. Rochalimaea henselae causes bacillary angiomatosis and peliosis hepatis. Arch Intern Med. 1992 Mar;152(3):602–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackebrandt E., Charfreitag O. Partial 16S rRNA primary structure of five Actinomyces species: phylogenetic implications and development of an Actinomyces israelii-specific oligonucleotide probe. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jan;136(1):37–43. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from a blue-green alga, Anacystis nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00330888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunkel A. R., Kaye D. Endocarditis with negative blood cultures. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 30;326(18):1215–1217. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199204303261809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyeryar F. J., Jr, Weiss E., Millar D. B., Bozeman F. M., Ormsbee R. A. DNA base composition of rickettsiae. Science. 1973 Apr 27;180(4084):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4084.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Scoy R. E. Culture-negative endocarditis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1982 Mar;57(3):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela G., Vinson J. W., Molina-Pasquel C. Trench fever. II. Propagation of Rickettsia quintana on cell-free medium from the blood of two patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1969 Sep;18(5):708–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson J. W. In vitro cultivation of the rickettsial agent of trench fever. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35(2):155–164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A., 2nd The role of the microbiology laboratory in the diagnosis and antimicrobial treatment of infective endocarditis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1982 Jan;57(1):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Barns S. M., Pelletier D. A., Lane D. J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):697–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Dobson M. E., Samuel J. E., Dasch G. A., Mallavia L. P., Baca O., Mandelco L., Sechrest J. E., Weiss E., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic diversity of the Rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4202–4206. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4202-4206.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Dasch G. A., Woodman D. R., Williams J. C. Vole agent identified as a strain of the trench fever rickettsia, Rochalimaea quintana. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1013-1020.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch D. F., Pickett D. A., Slater L. N., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J. Rochalimaea henselae sp. nov., a cause of septicemia, bacillary angiomatosis, and parenchymal bacillary peliosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):275–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.275-280.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]