Abstract
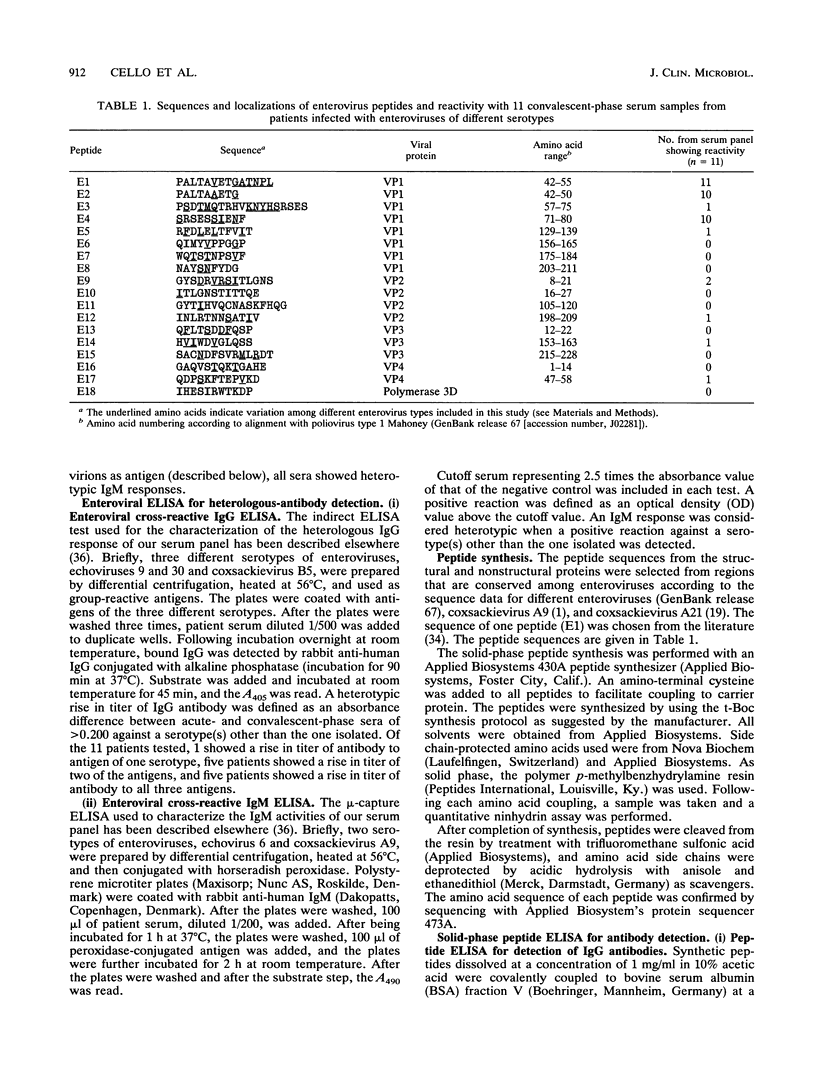
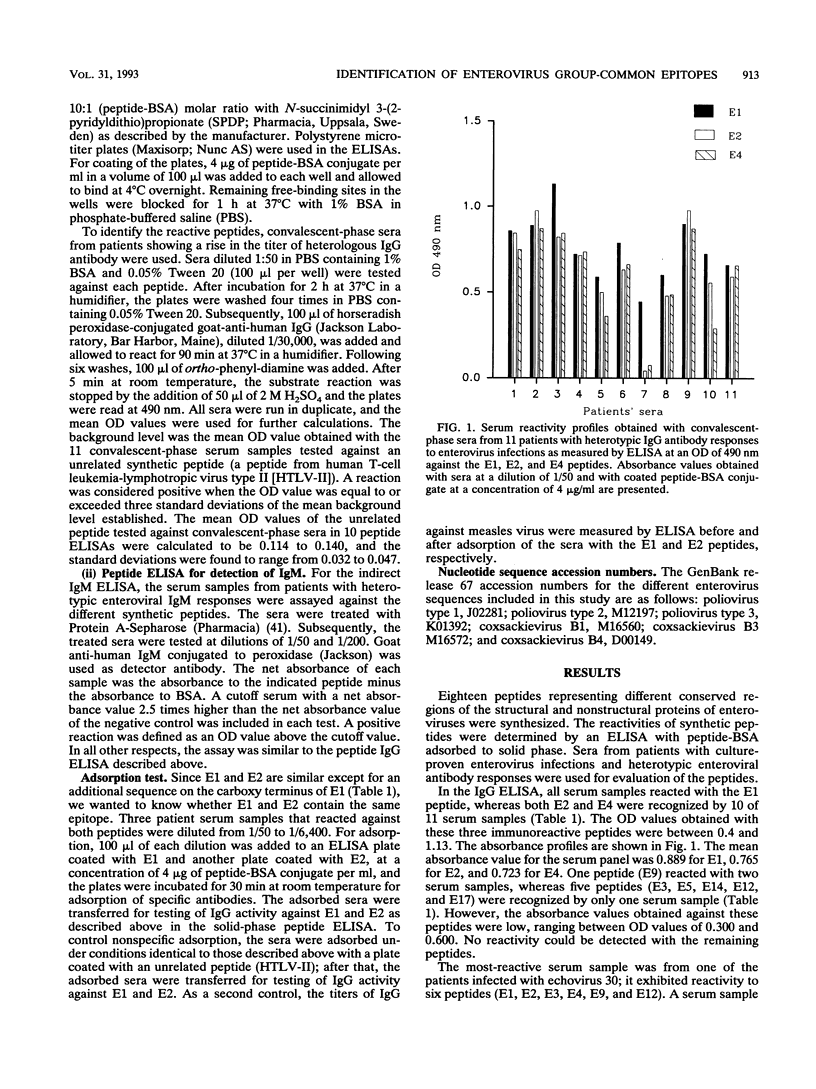
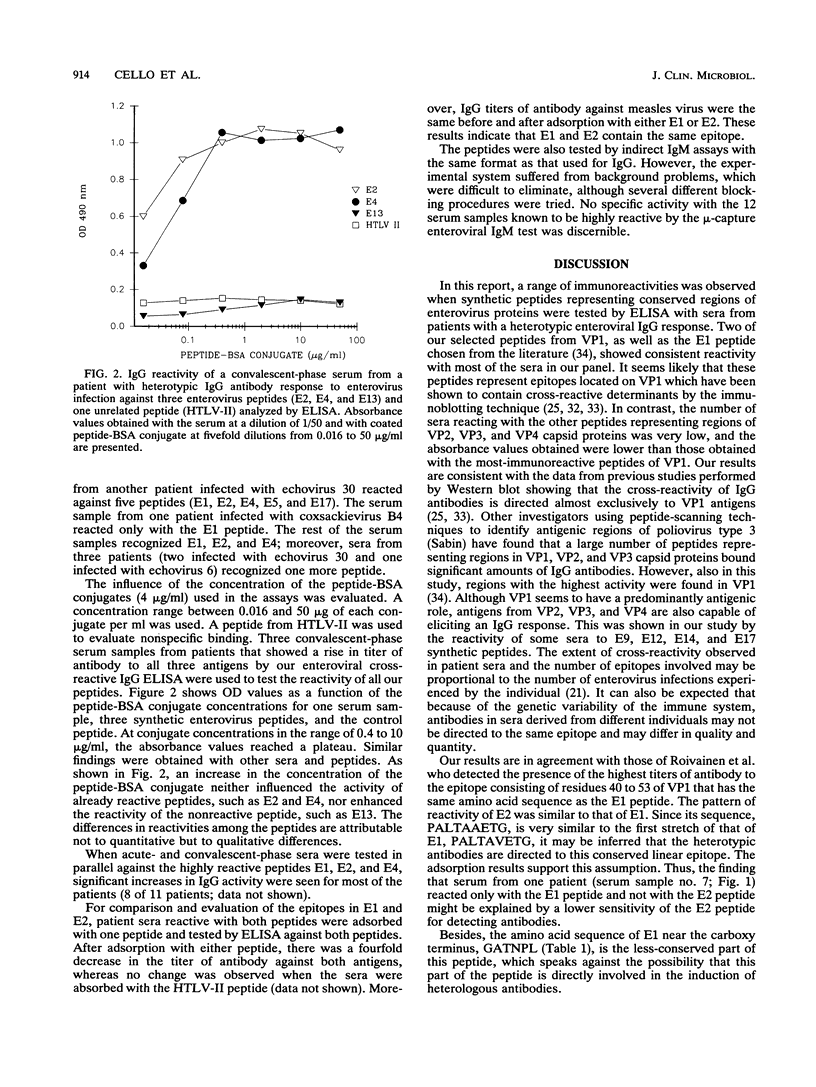
Synthetic peptides were employed in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays to identify group-common linear epitopes in the structural and nonstructural proteins of enteroviruses. Nine linear epitopes were recognized by using sera from patients with heterotypic immunoglobulin G antibody responses to enterovirus infections. The most-reactive peptides were derived from conserved regions of the amino-terminal part of VP1, whereas peptides representing sequences from other conserved regions of VP1, as well as VP2, VP3, and VP4, and from a nonstructural region showed no or poor reactivity. These findings may be useful in the development of serological tests for the diagnosis of infections caused by a broad range of enteroviruses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang K. H., Auvinen P., Hyypiä T., Stanway G. The nucleotide sequence of coxsackievirus A9; implications for receptor binding and enterovirus classification. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3269–3280. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., von Gegerfeldt A., Albert J., Fenyö E. M., Gaines H., von Sydow M., Biberfeld G., Parks E., Norrby E. Site-directed ELISA with synthetic peptides representing the HIV transmembrane glycoprotein. J Med Virol. 1987 Sep;23(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890230102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Yabrov R., Bittle J., Hogle J., Baltimore D. Synthetic peptides from four separate regions of the poliovirus type 1 capsid protein VP1 induce neutralizing antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörries R., ter Meulen V. Specificity of IgM antibodies in acute human coxsackievirus B infections, analysed by indirect solid phase enzyme immunoassay and immunoblot technique. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):159–167. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Priming for and induction of anti-poliovirus neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):699–703. doi: 10.1038/304699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren M. Relationship between poliovirus and echovirus 6 antigens. I. Immunization experiments in guinea pigs. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;39(1):108–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01241534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren M. Relationship between poliovirus and echovirus 6 antigens. I. Immunization experiments in guinea pigs. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;39(1):108–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01241534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren M. Studies of echovirus type 6 antigens in immunodiffusion. 3. Antibody response against echovirus 6 antigens in human infections with homologous and heterologous enteroviruses. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;74(4):611–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricks C. E., Hogle J. M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1934–1945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1934-1945.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimåker M., Ehrnst A., Magnius L., Berglund P., Forsgren M., Vikerfors T., Olcén P. Early diagnosis of enteroviral meningitis by a solid-phase reverse immunosorbent test and virus isolation. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990;22(5):519–526. doi: 10.3109/00365549009027090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Fine mapping of an immunodominant domain in the transmembrane glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2639–2641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2639-2641.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALONEN P., ROSEN L., HUEBNER R. J. Homologous and heterologous complement fixing antibody in persons infected with ECHO; Coxsackie and poliomyelitis viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jun;101(2):236–241. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-24896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMELER K., HAMPARIAN V. V. Studies on the complement fixing antigens of poliomyelitis. I. Demonstration of type and group specific antigens in native and heated viral preparations. J Immunol. 1958 Dec;81(6):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P. Protein surface analysis. Methods for identifying antigenic determinants and other interaction sites. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Apr 3;88(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horal P., Hall W. W., Svennerholm B., Lycke J., Jeansson S., Rymo L., Kaplan M. H., Vahlne A. Identification of type-specific linear epitopes in the glycoproteins gp46 and gp21 of human T-cell leukemia viruses type I and type II using synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5754–5758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P. J., North C., Minor P. D., Stanway G. The complete nucleotide sequence of coxsackievirus A21. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):2943–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-2943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Crowell R. L. Immunological studies of the group B coxsackieviruses by the sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunoprecipitation. J Gen Virol. 1980 Oct;50(2):357–367. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Crowell R. L. Indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of Coxsackievirus group B antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1980 May;48(1):225–229. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-1-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens T., Pika U., Eggers H. J. Cross antigenicity among enteroviruses as revealed by immunoblot technique. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middeldorp J. M., Meloen R. H. Epitope-mapping on the Epstein-Barr virus major capsid protein using systematic synthesis of overlapping oligopeptides. J Virol Methods. 1988 Sep;21(1-4):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrow S., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F., Wolf H. Computer-assisted analysis of envelope protein sequences of seven human immunodeficiency virus isolates: prediction of antigenic epitopes in conserved and variable regions. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.570-578.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir P., Banatvala J. E. Reactivity of enterovirus-specific IgM with infective and defective coxsackie B virions in patients with monotypic and multitypic IgM responses. J Virol Methods. 1990 Aug;29(2):209–224. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90114-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S., Plaue S., Couppez M., Van Regenmortel M. H. Comparison of different methods for localizing antigenic regions in histone H2A. Mol Immunol. 1986 Jun;23(6):593–601. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzetto B., Gaudin O. G., Lucht F. R., Hafid J., Ros A. Detection of immunoglobulin G, M, and A antibodies to enterovirus structural proteins by immunoblot technique in echovirus type 4-infected patients. J Virol Methods. 1990 Aug;29(2):143–155. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90108-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reigel F., Burkhardt F., Schilt U. Cross-reactions of immunoglobulin M and G antibodies with enterovirus-specific viral structural proteins. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Oct;95(2):469–481. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roivainen M., Närvänen A., Korkolainen M., Huhtala M. L., Hovi T. Antigenic regions of poliovirus type 3/Sabin capsid proteins recognized by human sera in the peptide scanning technique. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., LENNETTE E. H. Gel double diffusion studies with group B and group A, type 9 Coxsackie viruses. I. The technique and reactions obtained with hyperimmune animal sera and human sera. J Immunol. 1962 Jul;89:85–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., LENNETTE E. H. Gel double diffusion studies with group B and group A, type 9 Coxsackie viruses. II. Serologic diagnosis of Coxsackie virus infections by the gel double diffusion technique. J Immunol. 1962 Jul;89:96–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. S., Naso R. B., Rosen J., Whalley A., Hom Y. L., Hoey K., Kennedy C. J., McCutchan J. A., Spector S. A., Richman D. D. Antibody to a synthetic oligopeptide in subjects at risk for human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1498–1504. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1498-1504.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G. Structure, function and evolution of picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2483–2501. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torfason E. G., Frisk G., Diderholm H. Indirect and reverse radioimmunoassays and their apparent specificities in the detection of antibodies to enteroviruses in human sera. J Med Virol. 1984;13(1):13–31. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890130103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torfason E. G., Galindo R., Keyserling H. L. Comparison of five ELISA assays for IgG antibody against coxsackievirus B1. J Med Virol. 1988 May;25(1):53–60. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890250108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifilieff E., Dubs M. C., Van Regenmortel M. H. Antigenic cross-reactivity potential of synthetic peptides immobilized on polyethylene rods. Mol Immunol. 1991 Aug;28(8):889–896. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90053-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Regenmortel M. H. Structural and functional approaches to the study of protein antigenicity. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


