Abstract
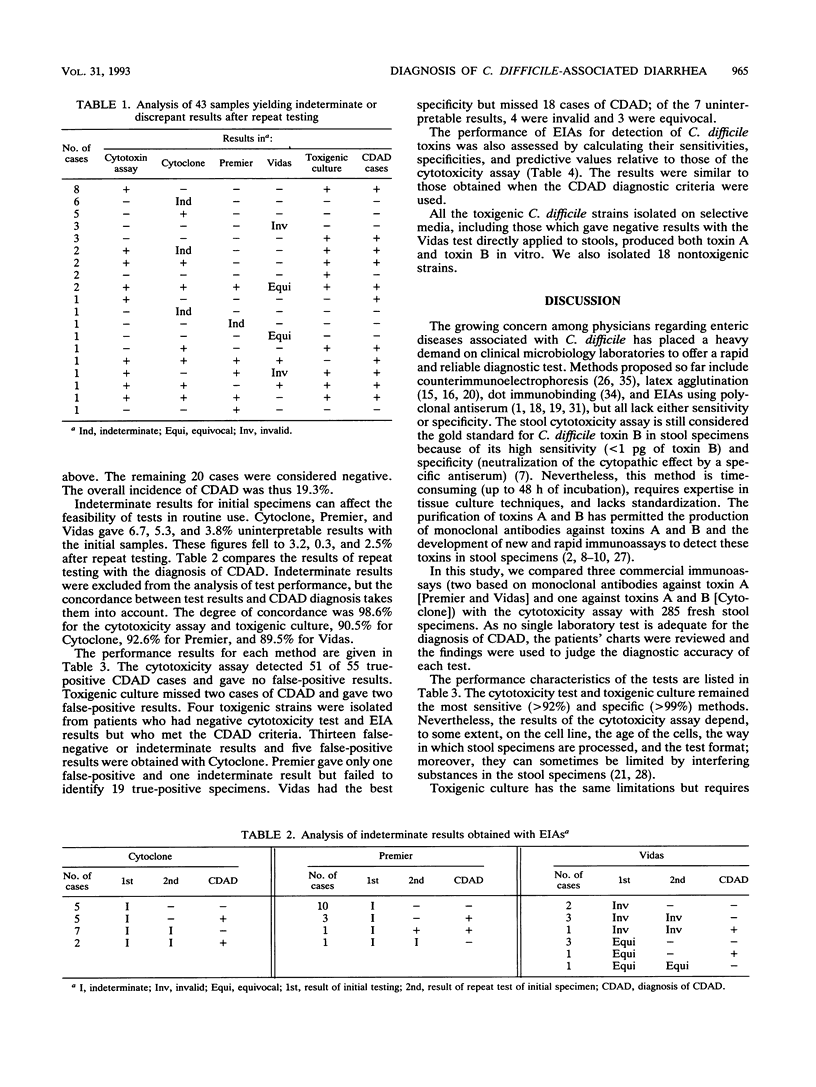
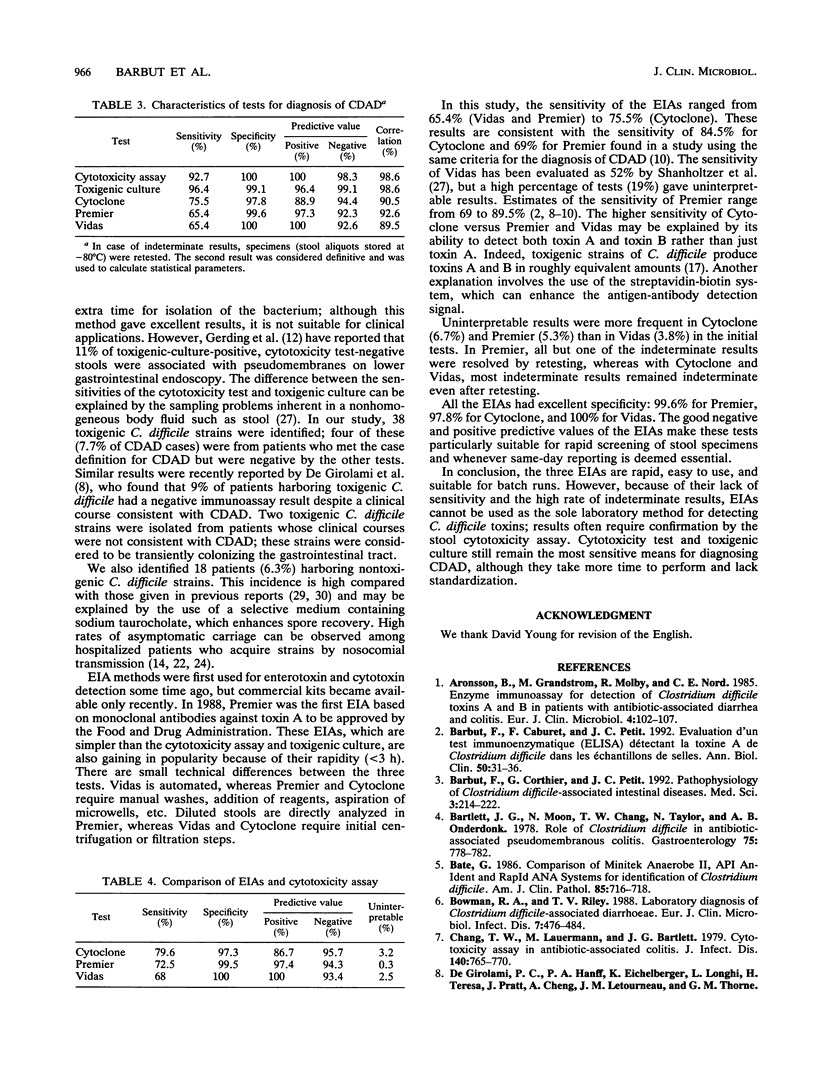
Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) based on monoclonal antibodies for the detection of Clostridium difficile toxins have recently been developed for clinical use. The aim of this study was to compare three commercially available EIAs, two for toxin A (Premier C. difficile Toxin A; Meridian, Osi, Elancourt, France; and Vidas C. difficile Toxin A; bioMérieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France) and one for toxins A and B (Cytoclone A + B EIA; Cambridge Biotech Corp., Codiapharm, Evian, France), with a cytotoxicity assay and toxigenic culture for the diagnosis of C. difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD). The study was performed with 285 fresh stools from 285 patients with suspected CDAD. In case of disagreement, the tests were repeated on a frozen aliquot of the same stool sample, and the patient's chart was reviewed. CDAD diagnosis was established in 55 cases (incidence, 19.3%). The sensitivities and specificities of the methods were, respectively, 92.7 and 100% for the cytotoxicity assay, 96.4 and 99.1% for toxigenic culture, 75.5 and 97.8% for Cytoclone, 65.4 and 99.6% for Premier, and 65.4 and 100% for Vidas. The results were uninterpretable in 3.2% of cases with Cytoclone, 0.3% with Premier, and 2.5% with Vidas. We conclude that the cytotoxicity assay and toxigenic culture remain the best methods for the diagnosis of CDAD even though they lack standardization and require 48 to 96 h to obtain the result. Despite their rapidity and simplicity, EIAs are not sensitive enough to be relied on as the sole laboratory test.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronsson B., Granström M., Möllby R., Nord C. E. Enzyme immunoassay for detection of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B in patients with antibiotic-associated diarrhoea and colitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;4(2):102–107. doi: 10.1007/BF02013572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbut F., Caburet F., Petit J. C. Evaluation d'un test immunoenzymatique (Elisa) détectant la toxine A de Clostridium difficile dans des échantillons de selles. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1992;50(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Moon N., Chang T. W., Taylor N., Onderdonk A. B. Role of Clostridium difficile in antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Nov;75(5):778–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate G. Comparison of Minitek Anaerobe II, API An-Ident, and RapID ANA systems for identification of Clostridium difficile. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jun;85(6):716–718. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/85.6.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman R. A., Riley T. V. Laboratory diagnosis of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;7(4):476–484. doi: 10.1007/BF01962596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Lauermann M., Bartlett J. G. Cytotoxicity assay in antibiotic-associated colitis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):765–770. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio J. R., Varga F. J., Conwell D. L., Kraft J. A., Kozak K. J., Willis D. H. Development of a rapid enzyme immunoassay for Clostridium difficile toxin A and its use in the diagnosis of C. difficile-associated disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2724–2730. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2724-2730.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Coughlin R. T., Wu L. Laboratory diagnosis of Clostridium difficile-associated gastrointestinal disease: comparison of a monoclonal antibody enzyme immunoassay for toxins A and B with a monoclonal antibody enzyme immunoassay for toxin A only and two cytotoxicity assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2042–2046. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2042-2046.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D., Finegold S. M. Selective and differential medium for isolation of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.214-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerding D. N., Olson M. M., Peterson L. R., Teasley D. G., Gebhard R. L., Schwartz M. L., Lee J. T., Jr Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea and colitis in adults. A prospective case-controlled epidemiologic study. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Jan;146(1):95–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S., Clabots C. R., Linn F. V., Olson M. M., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Nosocomial Clostridium difficile colonisation and disease. Lancet. 1990 Jul 14;336(8707):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91605-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., Champagne S. G., Sherlock C. H., Noble M. A., Freeman H. J., Smith J. A. Commercial latex agglutination test for detection of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1244–1247. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1244-1247.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Barroso L. A., Wilkins T. D. Identification of the latex test-reactive protein of Clostridium difficile as glutamate dehydrogenase. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2639–2642. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2639-2642.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Krivan H. C., Wilkins T. D. Clostridium difficile: its disease and toxins. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):1–18. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Phelps C. J., Wilkins T. D. Monoclonal and specific polyclonal antibodies for immunoassay of Clostridium difficile toxin A. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):12–14. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.12-14.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Sullivan N. M., Wilkins T. D. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Clostridium difficile toxin A. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.72-78.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Wilkins T. D. Commercial latex test for Clostridium difficile toxin A does not detect toxin A. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):622–623. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.622-623.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniar A. C., Williams T. W., Hammond G. W. Detection of Clostridium difficile toxin in various tissue culture monolayers. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1999–2000. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1999-2000.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland L. V., Mulligan M. E., Kwok R. Y., Stamm W. E. Nosocomial acquisition of Clostridium difficile infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 26;320(4):204–210. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901263200402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E. Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile-induced intestinal disease. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S222–S228. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Olson M. M., Shanholtzer C. J., Gerding D. N. Results of a prospective, 18-month clinical evaluation of culture, cytotoxin testing, and culturette brand (CDT) latex testing in the diagnosis of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;10(2):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poxton I. R., Byrne M. D. Detection of Clostridium difficile toxin by counterimmunoelectrophoresis: a note of caution. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):349–349. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.349-349.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanholtzer C. J., Willard K. E., Holter J. J., Olson M. M., Gerding D. N., Peterson L. R. Comparison of the VIDAS Clostridium difficile toxin A immunoassay with C. difficile culture and cytotoxin and latex tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1837–1840. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1837-1840.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tichota-Lee J., Jaqua-Stewart M. J., Benfield D., Simmons J. L., Jaqua R. A. Effect of age on the sensitivity of cell cultures to Clostridium difficile toxin. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;8(4):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki N. M., Aquino T. I. Isolation of Clostridium difficile from hospitalized patients without antibiotic-associated diarrhea or colitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):659–662. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.659-662.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R., Willey S., Bartlett J. G. Isolation rates and toxigenic potential of Clostridium difficile isolates from various patient populations. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jul;81(1):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. C., Ruane P. J., Rosenblatt J. E., Lyerly D. M., Gleaves C. A., Smith T. F., Pierce P. F., Jr, Wilkins T. D. Comparison of culture, cytotoxicity assays, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for toxin A and toxin B in the diagnosis of Clostridium difficile-related enteric disease. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 May;5(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D. Role of Clostridium difficile toxins in disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Aug;93(2):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. H., Kennedy M. J., Fekety F. R. Use of sodium taurocholate to enhance spore recovery on a medium selective for Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):443–446. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.443-446.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods G. L., Iwen P. C. Comparison of a dot immunobinding assay, latex agglutination, and cytotoxin assay for laboratory diagnosis of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):855–857. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.855-857.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Fung J. C. Evaluation of the usefulness of counterimmunoelectrophoresis for diagnosis of Clostridium difficile-associated colitis in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):610–613. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.610-613.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


