Abstract
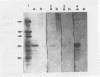
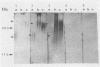
Polysaccharide of O:9,12 specificity purified from Salmonella typhi was conjugated to tetanus toxoid or bovine serum albumin in order to obtain defined antigenic material that would contain O chain free of other S. typhi antigens and that would be suitable for characterizing host humoral response to only S. typhi O-chain antigens. These artificial conjugates were strongly reactive in immunodots with 18 pooled and 3 individual serum samples from patients with typhoid fever and with rabbit anti-Salmonella O antiserum (group D, factors 1, 9, and 12). They reacted weakly with one serum sample from one human with paratyphoid A. These results suggest that the periodate oxidation and the reductive amination used in the conjugation conserved the immunogenicity of the O chain and allowed its absorption to nitrocellulose. They also suggest that the bovine serum albumin conjugate could be used in the diagnosis of S. typhi infections as normal sera may react with the protein molecule of the tetanus toxoid conjugate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agüero J., Mora G., Mroczenski-Wildey M. J., Fernandez-Beros M. E., Aron L., Cabello F. C. Cloning, expression and characterization of the 36 KDal Salmonella typhi porin gene in Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1987 Dec;3(6):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aron L., Faundez G., Gonzalez C., Roessler E., Cabello F. Lipopolysaccharide-independent radioimmunoprecipitation and identification of structural and in vivo induced immunogenic surface proteins of Salmonella typhi in typhoid fever. Vaccine. 1993;11(1):10–17. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90334-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. T., Klebba P. E. Effect of lipopolysaccharide structure on reactivity of antiporin monoclonal antibodies with the bacterial cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1063–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1063-1068.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Hormaeche C. E. The antibody response to salmonellae in mice and humans studied by immunoblots and ELISA. Microb Pathog. 1989 Jun;6(6):445–454. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderón I., Lobos S. R., Rojas H. A., Palomino C., Rodríguez L. H., Mora G. C. Antibodies to porin antigens of Salmonella typhi induced during typhoid infection in humans. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):209–212. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.209-212.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fabio J. L., Perry M. B., Brisson J. R. Structure of the antigenic O-polysaccharide of the lipopolysaccharide produced by Salmonella eimsbuttel. Biochem Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;66(2):107–115. doi: 10.1139/o88-014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Levine M. M. Summary of an international workshop on typhoid fever. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 May-Jun;8(3):329–349. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Beros M. E., Gonzalez C., McIntosh M. A., Cabello F. C. Immune response to the iron-deprivation-induced proteins of Salmonella typhi in typhoid fever. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1271–1275. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1271-1275.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Lugowski C. Immunochemistry of groups A, B, and C meningococcal polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugates. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1011–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugowski C., Kułakowska M., Romanowska E. Characterization and diagnostic application of a lipopolysaccharide core oligosaccharide-protein conjugate. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 24;95(2):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90405-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertsson J. A., Fossum C., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: specific immune reactivity against O-antigenic polysaccharide detectable in in vitro assays. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):728–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.728-736.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxén H., Nurminen M., Kuusi N., Svenson S. B., Mäkelä P. H. Evidence for the importance of O antigen specific antibodies in mouse-protective Salmonella outer membrane protein (porin) antisera. Microb Pathog. 1986 Oct;1(5):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:120–143. doi: 10.1159/000407424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ley P., Kuipers O., Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. O-antigenic chains of lipopolysaccharide prevent binding of antibody molecules to an outer membrane pore protein in Enterobacteriaceae. Microb Pathog. 1986 Feb;1(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]