Abstract
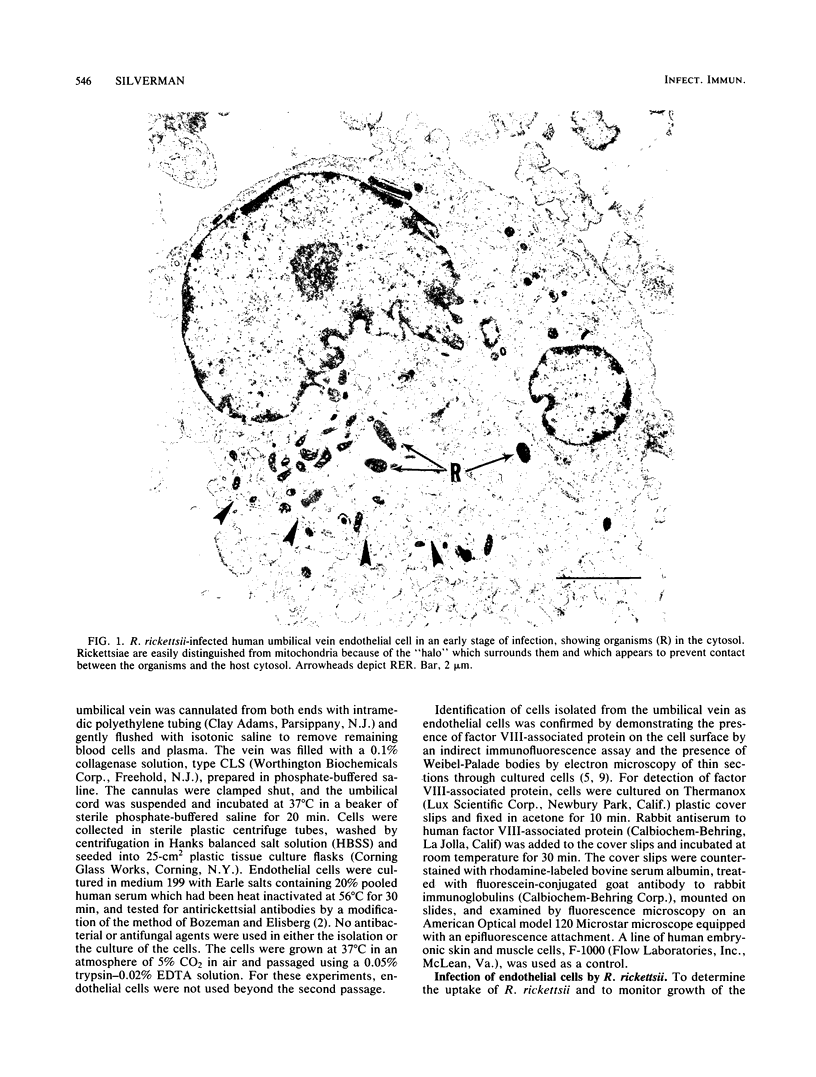
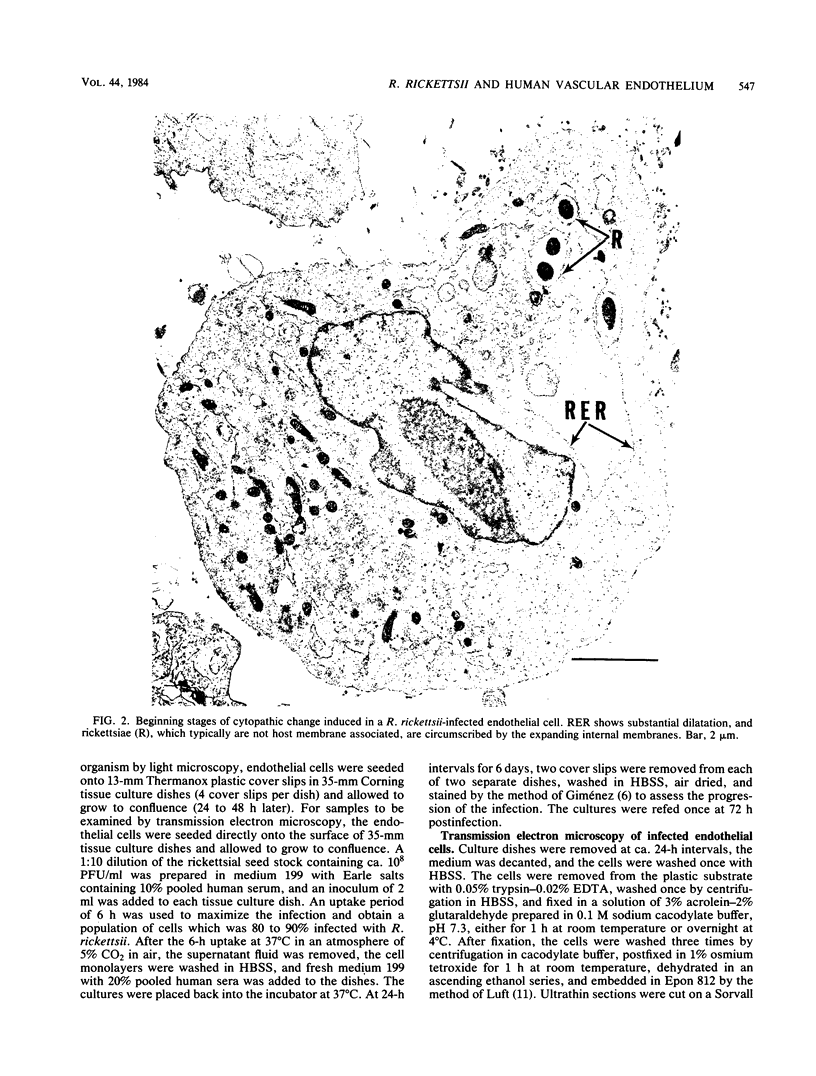
The endothelial cell is the putative primary target cell in humans infected with Rickettsia rickettsii, the etiological agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Although the clinical manifestations of infection by this organism are well documented, the mechanism of injury to the endothelial cell is not understood. The ability to culture human endothelial cells in vitro provides a unique system with which to study this host-parasite interaction directly. Human vascular endothelial cells derived from the umbilical vein, when infected by R. rickettsii, became severely damaged within a few days postinfection. The primary lesion observed at the ultrastructural level appeared to occur at intracellular membranes, specifically, the rough-surfaced endoplasmic reticulum. Widespread dilatation of these membranes eventually led to the creation of large intracellular cisternae and the apparent circumscription of rickettsiae and cellular organelles by the rough-surfaced endoplasmic reticulum. Small membrane-bound fragments of host cytosol created by dilating membranes also were present within the cisternae. Within 5 to 6 days postinfection, cells lost their osmoregulatory control and lysed. Some possible mechanisms of cell injury directed at the level of intracellular membranes are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkin M. D., Strauss H. S., Fisher G. U. A case report of "Cape Cod" Rocky Mountain spotted fever with multiple coagulation disturbances. Pediatrics. 1965 Oct;36(4):627–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOZEMAN F. M., ELISBERG B. L. Serological diagnosis of scrub typhus by indirect immunofluorescence. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Mar;112:568–573. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford W. D., Croker B. P., Tisher C. C. Kidney lesions in Rocky Mountain spotted fever: a light-, immunofluorescence-, and electron-microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1979 Nov;97(2):381–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Anacker R. L., Bird R. G., Bertram D. S. Intranuclear growth of Rickettsia rickettsii. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1415–1418. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1415-1418.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. A., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A., Silverman D. J. Some characteristics of heavy and light bands of Rickettsia prowazekii on Renografin gradients. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):596–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.596-604.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Peyton M. P., Wilcox G. M., Pisano J. J. Angiotensin metabolism by cultured human vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Microvasc Res. 1979 May;17(3 Pt 1):314–329. doi: 10.1016/s0026-2862(79)80007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., BOZEMAN F. M., SMADEL J. E. Study on the growth of Rickettsiae. II. Morphologic observations of living Rickettsiae in tissue culture cells. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):160–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Bond S. B. Infection of human vascular endothelial cells by Rickettsia rickettsii. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):201–206. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Fiset P., Wisseman C. L., Jr Simple, differential staining technique for enumerating rickettsiae in yolk sac, tissue culture extracts, or purified suspensions. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):437–440. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.437-440.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr In vitro studies of rickettsia-host cell interactions: ultrastructural changes induced by Rickettsia rickettsii infection of chicken embryo fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):714–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.714-727.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. In vitro studies of Rickettsia-host cell interactions: ultrastructural study of Rickettsia prowazekii-infected chicken embryo fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):778–790. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.778-790.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRIGG J. W., Jr HYPOFIBRINOGENEMIA IN ROCKY MOUNTAIN SPOTTED FEVER. REPORT OF A CASE. N Engl J Med. 1964 May 14;270:1042–1044. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196405142702005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Marcus A. J., Jaffe E. A. Synthesis of prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) by cultured human and bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3922–3926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wike D. A., Burgdorfer W. Plaque formation in tissue cultures by Rickettsia rickettsi isolated directly from whole blood and tick hemolymph. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):736–738. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.736-738.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Phospholipase A and the interaction of Rickettsia prowazekii and mouse fibroblasts (L-929 cells). Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):109–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.109-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Edlinger E. A., Waddell A. D., Jones M. R. Infection cycle of Rickettsia rickettsii in chicken embryo and L-929 cells in culture. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1052–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1052-1064.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]