Abstract
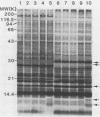
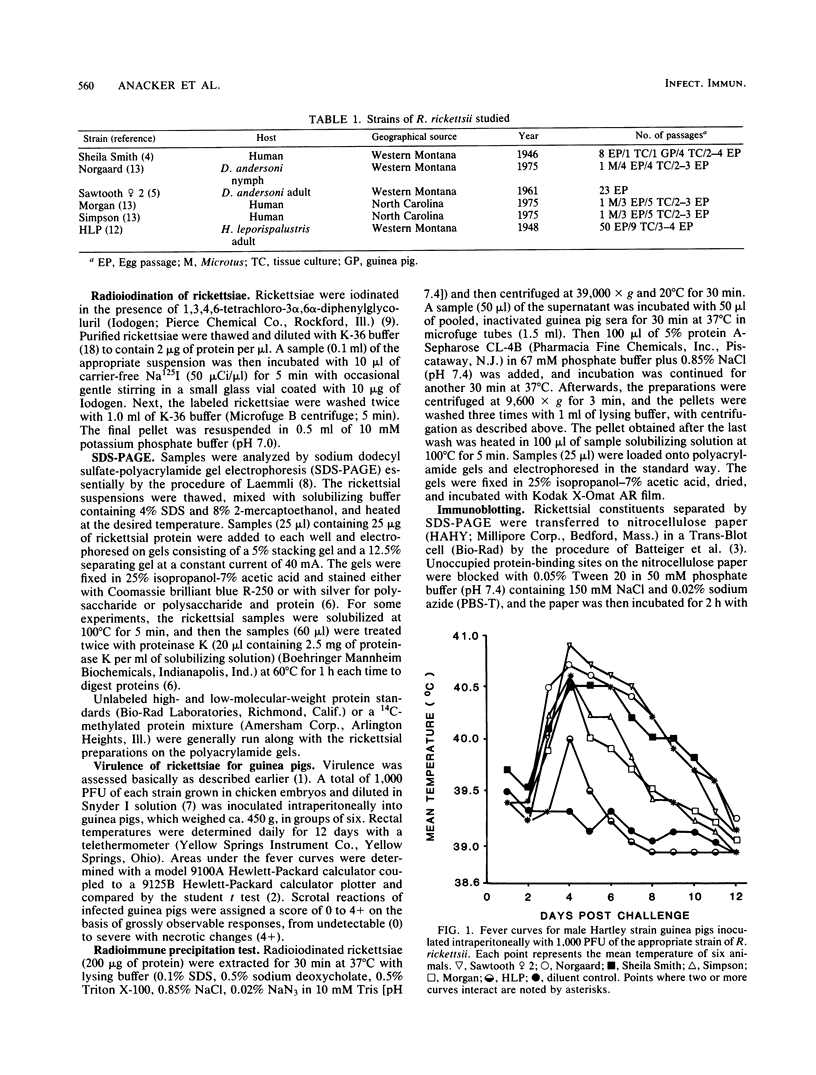
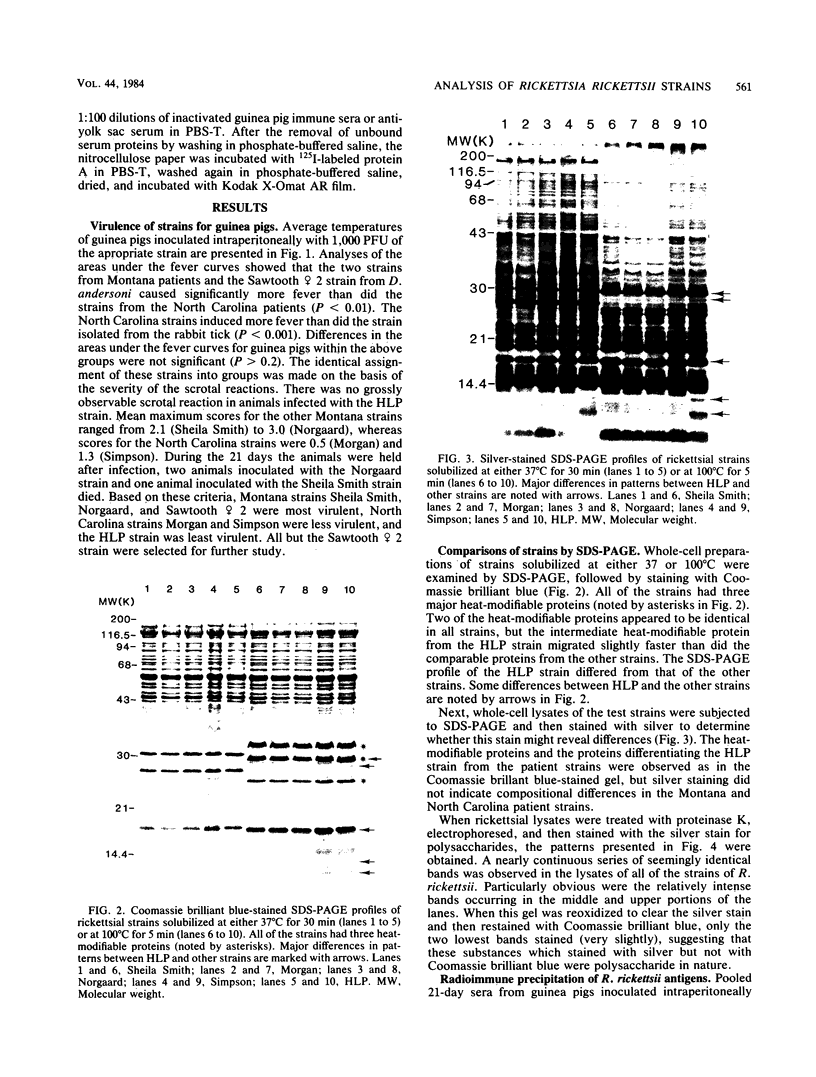
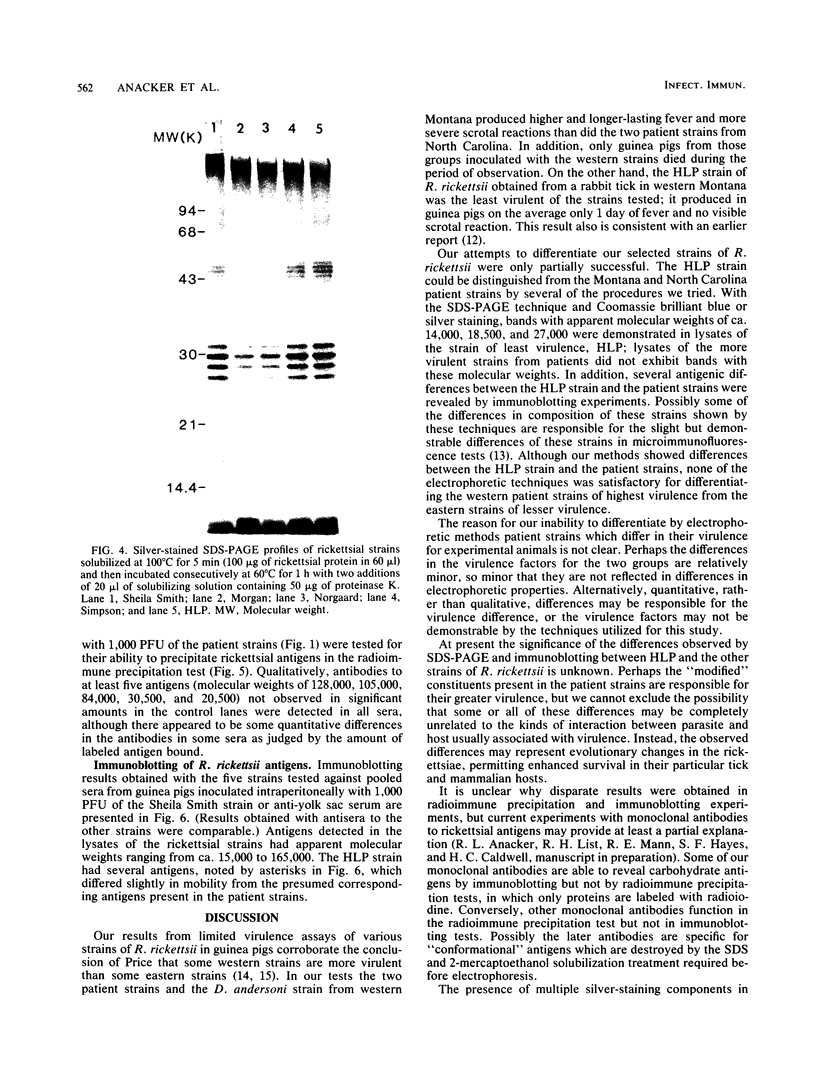
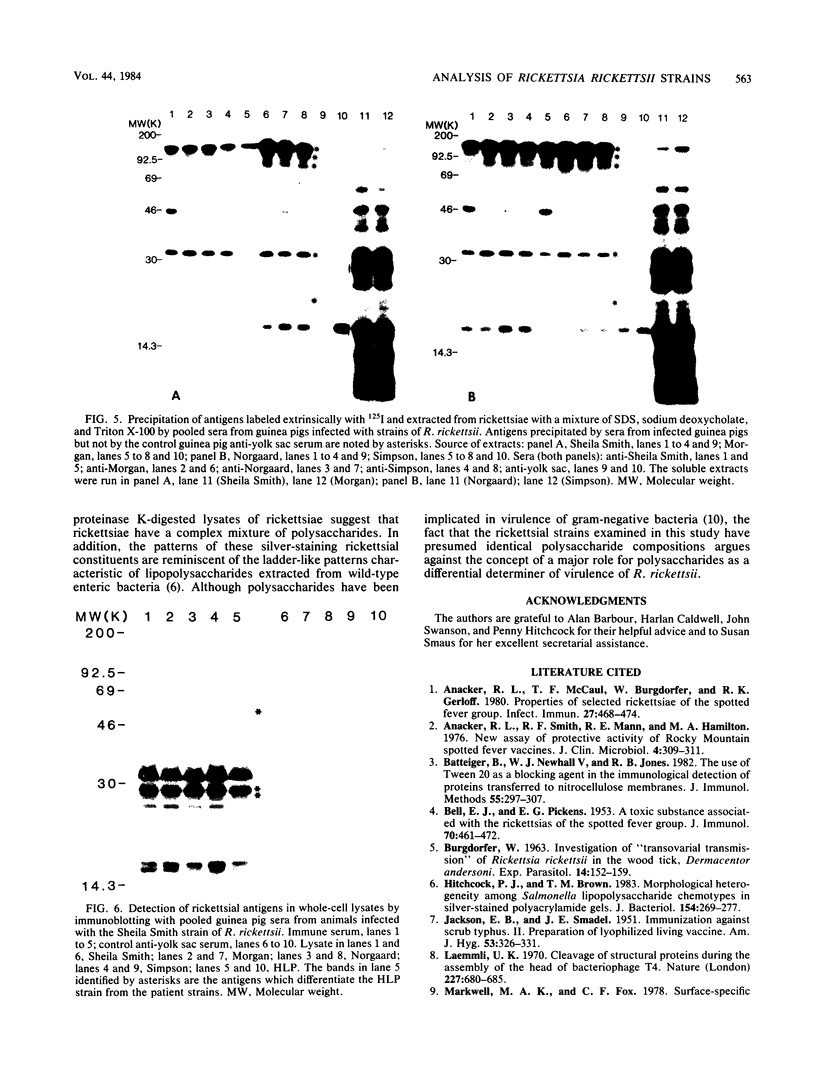
Six strains of Rickettsia rickettsii from Montana and North Carolina were examined in an effort to identify rickettsial constituents associated with virulence. Fever responses, scrotal reactions, and mortalities of male guinea pigs inoculated intraperitoneally with 1,000 PFU of rickettsial strains revealed that the two Montana patient strains ( Sheila Smith and Norgaard ) and one Montana strain ( Sawtooth female 2) from the wood tick, Dermacentor andersoni, could be placed in the group of highest virulence, the two North Carolina strains (Morgan and Simpson) in the group of lesser virulence, and the Montana strain (HLP) from the rabbit tick, Haemaphysalis leporispalustris , in the group of lowest virulence. The HLP strain was differentiated from the other strains by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by staining with Coomassie brilliant blue or with silver. The patient strains could not be differentiated from each other by these procedures. All of the strains apparently had three heat-modifiable proteins. Analysis of proteinase K-digested rickettsial lysates by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis suggested that the strains had a complex mixture of polysaccharides. These putative polysaccharides probably were not related to the differences in virulence of the strains, since the patterns for all of the strains were identical. At least five antigens (molecular weights of 128,000, 105,000, 84,000, 30,500, and 20,500) were demonstrated by radioimmune precipitation tests employing extracts from radioiodine-labeled rickettsiae and antibodies from infected guinea pigs. With these same sera a minimum of 14 antigens was detected in these strains by an immunoblotting procedure. The apparent molecular weights of several of the HLP antigens differed from those of the presumed corresponding antigens of the other strains. The electrophoretic techniques utilized in this study were not sufficiently sensitive to demonstrate compositional differences in the patient strains which differed in their virulence for guinea pigs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., McCaul T. F., Burgdorfer W., Gerloff R. K. Properties of selected rickettsiae of the spotted fever group. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):468–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.468-474.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anacker R. L., Smith R. F., Mann R. E., Hamilton M. A. New assay of protective activity of Rocky Mountain spotted fever vaccines. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Sep;4(3):309–311. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.3.309-311.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. J., PICKENS E. G. A toxic substance associated with the rickettsias of the spotted fever group. J Immunol. 1953 May;70(5):461–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Tyrrell D. A., Head B., Rees R. J. Inhibition of haemaggregation by lepromin and other mycobacterial substances. Nature. 1967 Dec 9;216(5119):1019–1020. doi: 10.1038/2161019a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON E. B., SMADEL J. E. Immunization against scrub typhus. II. Preparation of lyophilized living vaccine. Am J Hyg. 1951 May;53(3):326–331. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F. Virulence factors of the bacterial cell surface. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):630–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER R. R., PICKENS E. G., LACKMAN D. B., BELLE E. J., THRAIKILL F. B. Isolation and characterization of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Rickettsiae from the rabbit tick Haemaphysalis leporis-palustris Packard. Public Health Rep. 1951 Apr 13;66(15):455–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE W. H. The epidemiology of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. I. The characterization of strain virulence of Rickettsia rickettsii. Am J Hyg. 1953 Sep;58(2):248–268. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Burgdorfer W., Gerloff R. K., Hughes L. E., Bell E. J. Serologic typing of rickettsiae of the spotted fever group by microimmunofluorescence. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1961–1968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOENNER H. G., LACKMAN D. B., BELL E. J. Factors affecting the growth of rickettsias of the spotted fever group in fertile hens' eggs. J Infect Dis. 1962 Mar-Apr;110:121–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.2.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Coolbaugh J. C., Williams J. C. Separation of viable Rickettsia typhi from yolk sac and L cell host components by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):456–463. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.456-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]