Abstract
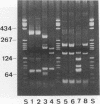
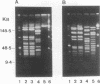
Rochalimaea quintana was isolated from the blood of a French human immunodeficiency virus-infected patient with bacillary angiomatosis. The isolate showed the typical growth characteristics of Rochalimaea species and was inert when typical biochemical testing was used. The purpose of the present work was to characterize and compare this new isolate with reference strains of R. quintana, Rochalimaea vinsonii, and Rochalimaea henselae by using immunofluorescence, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), Western blot (immunoblot), restriction fragment length polymorphism-PCR of the citrate synthase gene, 16S rRNA gene sequencing, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. SDS-PAGE, Western blot, restriction fragment length polymorphism-PCR with TaqI enzyme, and 16S rRNA gene sequencing could differentiate the three Rochalimaea species and allowed characterization of the French isolate as R. quintana. However, identification of the Rochalimaea isolate to the species level was more easily obtained by immunofluorescence with specific murine antisera. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis allowed differentiation of the French R. quintana isolate from R. quintana Fuller and may serve as an epidemiological tool.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birren B. W., Lai E., Clark S. M., Hood L., Simon M. I. Optimized conditions for pulsed field gel electrophoretic separations of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7563–7582. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., O'Connor S. P., Winkler H. H., Steigerwalt A. G. Proposals to unify the genera Bartonella and Rochalimaea, with descriptions of Bartonella quintana comb. nov., Bartonella vinsonii comb. nov., Bartonella henselae comb. nov., and Bartonella elizabethae comb. nov., and to remove the family Bartonellaceae from the order Rickettsiales. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;43(4):777–786. doi: 10.1099/00207713-43-4-777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. S., Worthington M. G., Brenner D. J., Moss C. W., Hollis D. G., Weyant R. S., Steigerwalt A. G., Weaver R. E., Daneshvar M. I., O'Connor S. P. Rochalimaea elizabethae sp. nov. isolated from a patient with endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):872–881. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.872-881.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drancourt M., Raoult D. Proposed tests for the routine identification of Rochalimaea species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Sep;12(9):710–713. doi: 10.1007/BF02009387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embley T. M. The linear PCR reaction: a simple and robust method for sequencing amplified rRNA genes. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1991 Sep;13(3):171–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1991.tb00600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J. Intracerebral bacillary angiomatosis in HIV. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Nov 1;117(9):795–795. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-9-795_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. Fast and sensitive multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Apr;5(2):151–153. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler J. E., Quinn F. D., Berger T. G., LeBoit P. E., Tappero J. W. Isolation of Rochalimaea species from cutaneous and osseous lesions of bacillary angiomatosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 3;327(23):1625–1631. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212033272303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey D., Dolan M. J., Moss C. W., Garcia M., Hollis D. G., Wegner S., Morgan G., Almeida R., Leong D., Greisen K. S. Relapsing illness due to Rochalimaea henselae in immunocompetent hosts: implication for therapy and new epidemiological associations. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;14(3):683–688. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.3.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marullo S., Jaccard A., Roulot D., Mainguene C., Clauvel J. P. Identification of the Rochalimaea henselae 16S rRNA sequence in the liver of a French patient with bacillary peliosis hepatis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1462–1462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1462-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matar G. M., Swaminathan B., Hunter S. B., Slater L. N., Welch D. F. Polymerase chain reaction-based restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of a fragment of the ribosomal operon from Rochalimaea species for subtyping. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1730–1734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1730-1734.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurin M., Raoult D. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Rochalimaea quintana, Rochalimaea vinsonii, and the newly recognized Rochalimaea henselae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 Oct;32(4):587–594. doi: 10.1093/jac/32.4.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrell B. R., Weiss E., Dasch G. A. Morphological and cell association characteristics of Rochalimaea quintana: comparison of the Vole and Fuller strains. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.633-640.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik M., Schwartzman W. A., Barka N. E., Peter J. B. Possible role of Rochalimaea henselae in pathogenesis of AIDS encephalopathy. Lancet. 1992 Oct 17;340(8825):971–971. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92855-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkocha L. A., Geaghan S. M., Yen T. S., Nishimura S. L., Chan S. P., Garcia-Kennedy R., Honda G., Stoloff A. C., Klein H. Z., Goldman R. L. Clinical and pathological features of bacillary peliosis hepatis in association with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1581–1586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Anderson B. E., Clarridge J. E., 3rd, Rodriguez-Barradas M. C., Jones D. C., Carr J. H. Characterization of a novel Rochalimaea species, R. henselae sp. nov., isolated from blood of a febrile, human immunodeficiency virus-positive patient. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.265-274.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A. Isolation of Rochalimaea species. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 13;328(19):1422–1423. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305133281912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Loutit J. S., Schmidt T. M., Falkow S., Tompkins L. S. The agent of bacillary angiomatosis. An approach to the identification of uncultured pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1573–1580. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman W. A., Nesbit C. A., Baron E. J. Development and evaluation of a blood-free medium for determining growth curves and optimizing growth of Rochalimaea henselae. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1882–1885. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1882-1885.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater L. N., Coody D. W., Woolridge L. K., Welch D. F. Murine antibody responses distinguish Rochalimaea henselae from Rochalimaea quintana. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1722–1727. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1722-1727.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater L. N., Welch D. F., Hensel D., Coody D. W. A newly recognized fastidious gram-negative pathogen as a cause of fever and bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 6;323(23):1587–1593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012063232303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spach D. H., Callis K. P., Paauw D. S., Houze Y. B., Schoenknecht F. D., Welch D. F., Rosen H., Brenner D. J. Endocarditis caused by Rochalimaea quintana in a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):692–694. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.692-694.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spach D. H., Panther L. A., Thorning D. R., Dunn J. E., Plorde J. J., Miller R. A. Intracerebral bacillary angiomatosis in a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Ann Intern Med. 1992 May 1;116(9):740–742. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-9-740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch D. F., Pickett D. A., Slater L. N., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J. Rochalimaea henselae sp. nov., a cause of septicemia, bacillary angiomatosis, and parenchymal bacillary peliosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):275–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.275-280.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Williamson L. R., Winkler H. H., Krause D. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Rickettsia prowazekii citrate synthase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3564-3572.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lamballerie X., Zandotti C., Vignoli C., Bollet C., de Micco P. A one-step microbial DNA extraction method using "Chelex 100" suitable for gene amplification. Res Microbiol. 1992 Oct;143(8):785–790. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90107-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]