Abstract
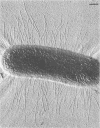
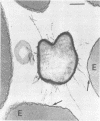
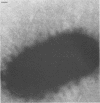
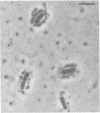
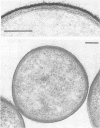
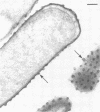
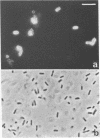
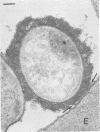
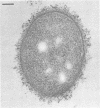
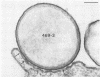
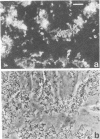
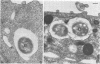
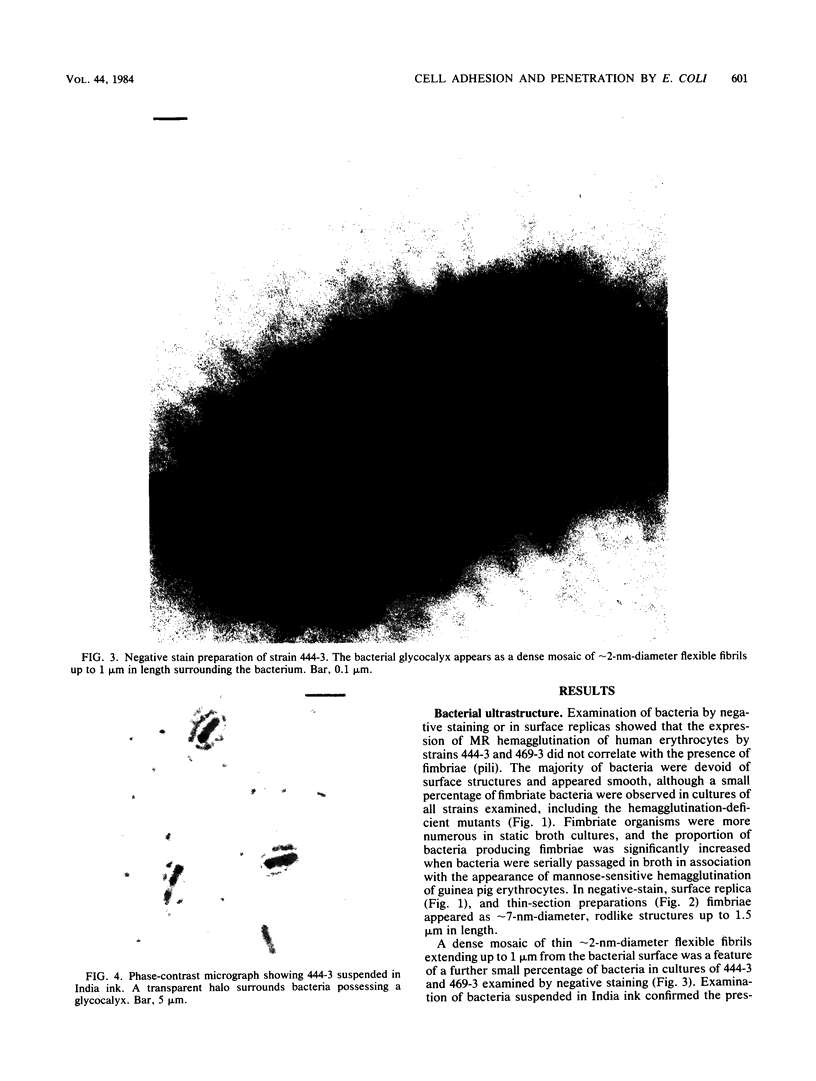
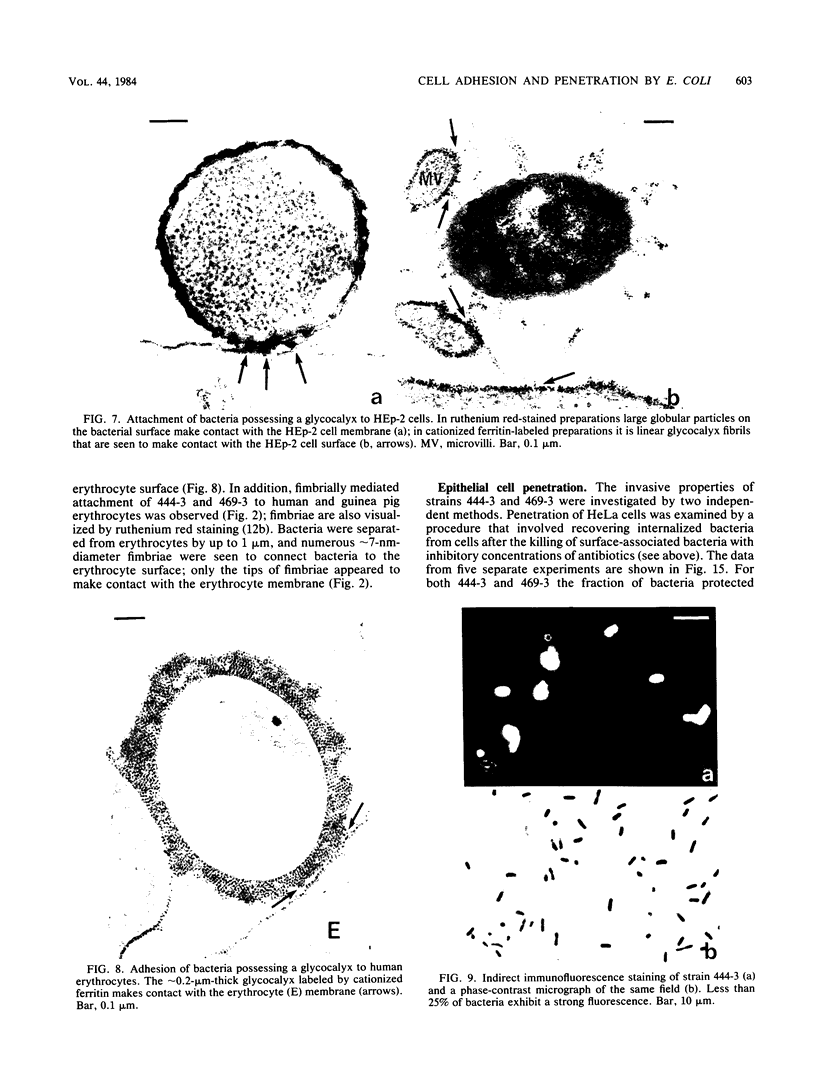
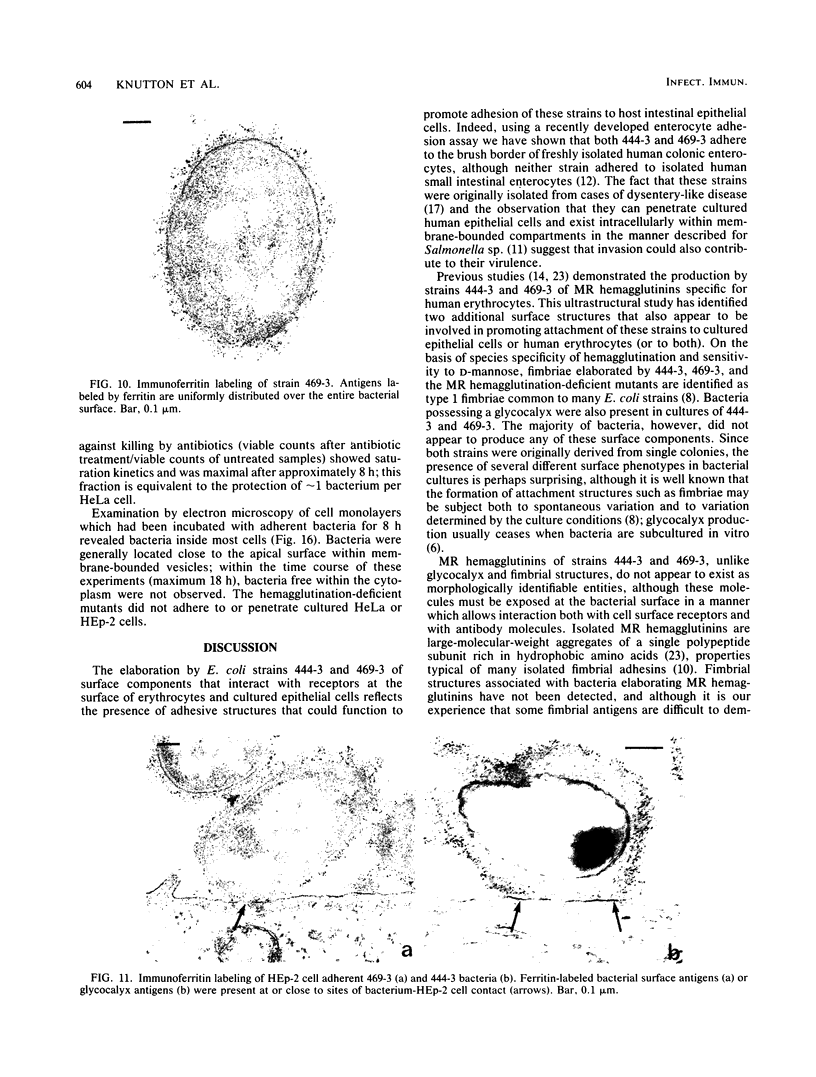
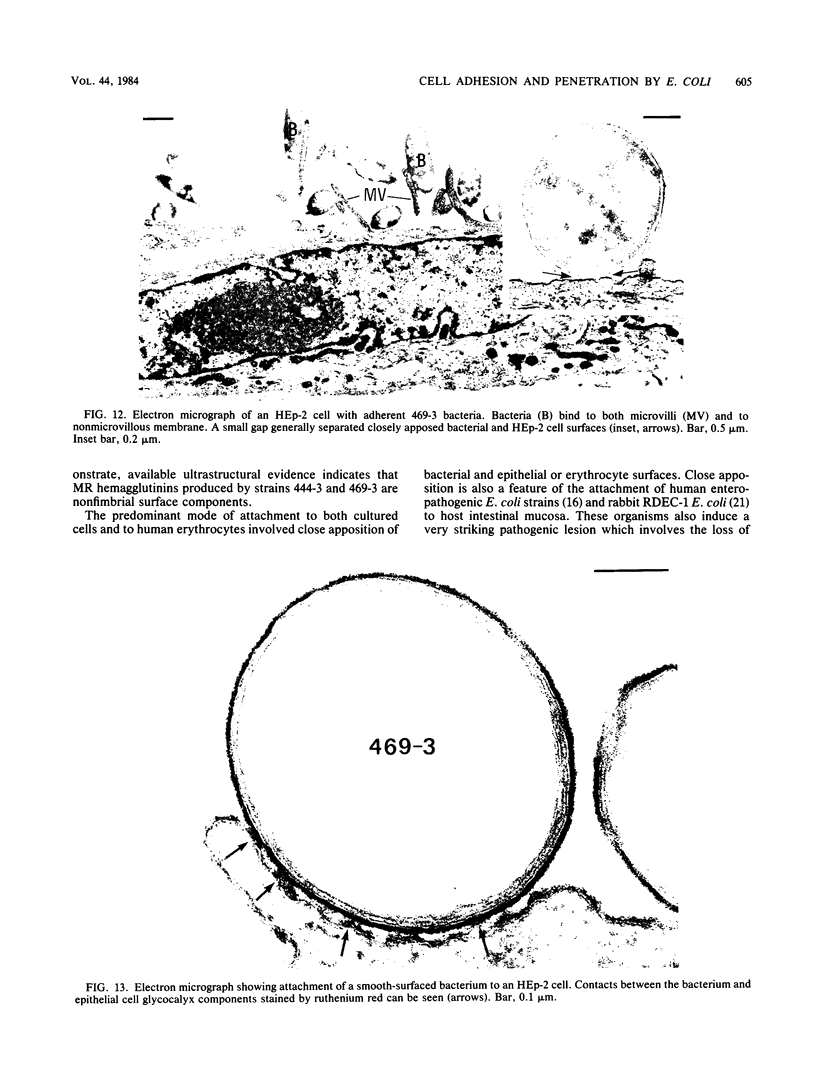
The adherence of invasive Escherichia coli strains 444-3 and 469-3 to human erythrocytes and to cultured HeLa and HEp-2 cells has been examined by electron microscopy. Bacteria elaborating type 1 fimbriae, glycocalyces , and nonfimbrial mannose-resistant hemagglutinins specific for human erythrocytes were identified in cultures of both strains, and each of these different bacterial surface components appeared to be involved in attachment of 444-3 and 469-3 to cultured epithelial cells or human erythrocytes (or to both). Both strains, which were isolated from infants with dysentery-like illness, penetrated cultured epithelial cells and existed within membrane-bounded intracellular vesicles. Mutants of 444-3 and 469-3 selected for deficiency in mannose-resistant hemagglutination did not adhere to or penetrate cultured cells. These ultrastructural studies demonstrate the complexity of the bacterial surface and show that E. coli strains 444-3 and 469-3 can elaborate several different adhesions , each of which could function to promote attachment to host intestinal epithelial cells. Mucosal invasion may also be an important virulence property of these strains.
Full text
PDF


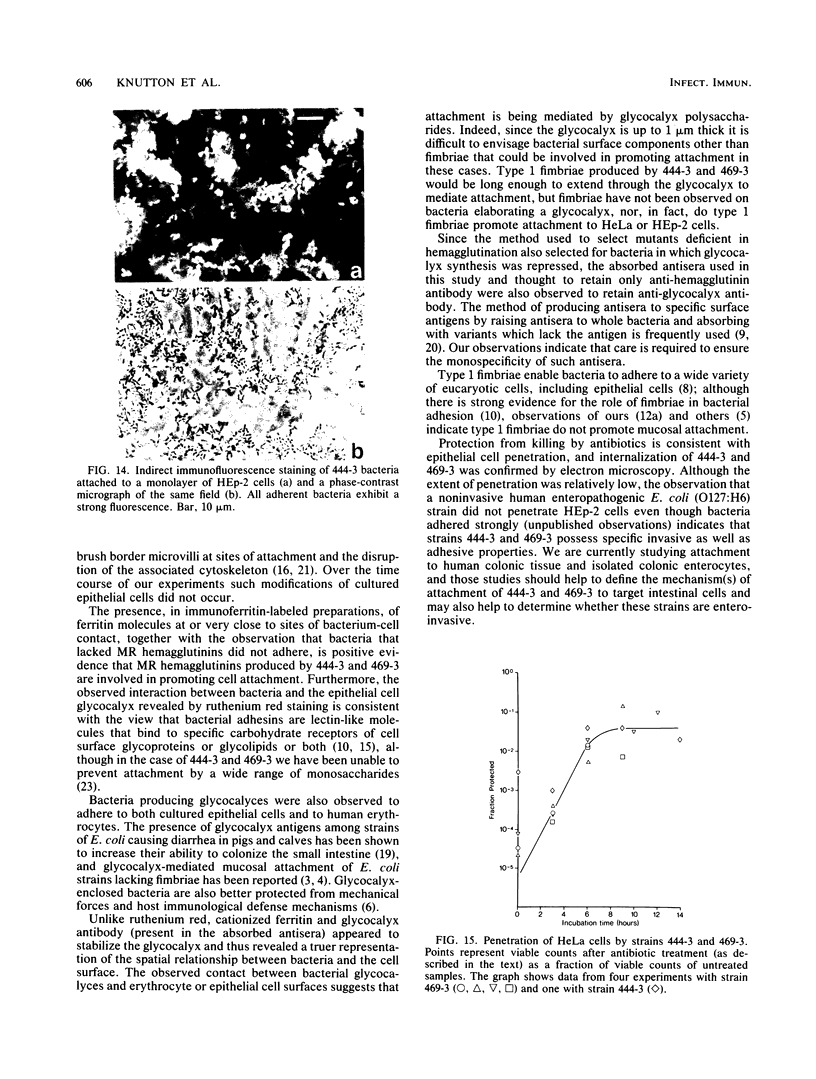
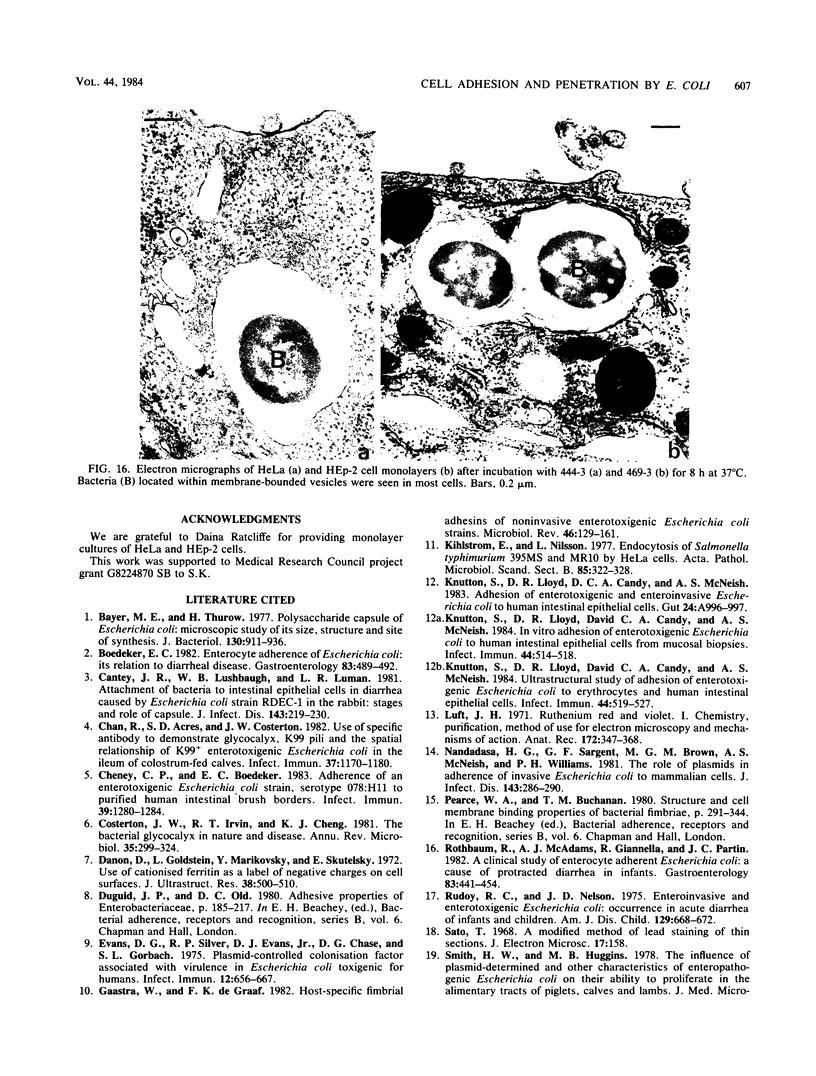

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E., Thurow H. Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli: microscope study of its size, structure, and sites of synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):911–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.911-936.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boedeker E. C. Enterocyte adherence of Escherichia coli: its relation to diarrheal disease. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):489–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B., Inman L. R. Attachment of bacteria to intestinal epithelial cells in diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 in the rabbit: stages and role of capsule. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):219–230. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R., Acres S. D., Costerton J. W. Use of specific antibody to demonstrate glycocalyx, K99 pili, and the spatial relationships of K99+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in the ileum of colostrum-fed calves. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1170–1180. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1170-1180.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Boedeker E. C. Adherence of an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain, serotype O78:H11, to purified human intestinal brush borders. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1280–1284. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1280-1284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:299–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon D., Goldstein L., Marikovsky Y., Skutelsky E. Use of cationized ferritin as a label of negative charges on cell surfaces. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Mar;38(5):500–510. doi: 10.1016/0022-5320(72)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Nilsson L. Endocytosis of Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR10 by HeLa cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):322–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., Candy D. C., McNeish A. S. In vitro adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal epithelial cells from mucosal biopsies. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):514–518. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.514-518.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., Candy D. C., McNeish A. S. Ultrastructural study of adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to erythrocytes and human intestinal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.519-527.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandadasa H. G., Sargent G. F., Brown M. G., McNeish A. S., Williams P. H. The role of plasmids in adherence of invasive Escherichia coli to mammalian cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):286–290. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudoy R. C. Enteroinvasive and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Occurrence in acute diarrhea of infants and children. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jun;129(6):668–672. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120430008004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T. A modified method for lead staining of thin sections. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1968;17(2):158–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J. Two mannose-resistant haemagglutinins on enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of serotype O6:K15:H16 or H-isolated from travellers' and infantile diarrhoea. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2081–2096. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Inman L. R., O'Hanley P. D., Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of Escherichia coli O15 (RDEC-1) enteric infection in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):686–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.686-694.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]