Abstract
Objective
To perform a comprehensive assessment of maternal mortality in Argentina, the ultimate purpose being to strengthen the surveillance system and reorient reproductive health policies to prevent maternal deaths.
Methods
Our multicentre population-based study combining qualitative and quantitative methodologies included a descriptive analysis of under-registration and distribution of causes of death, a case–control study to identify risk factors in health-care delivery and verbal autopsies to analyse social determinants associated with maternal deaths.
Findings
A total of 121 maternal deaths occurred during 2002. The most common causes were abortion complications (27.4%), haemorrhage (22.1%), infection/sepsis (9.5%), hypertensive disorders (8.4%) and other causes (32.6%). Under-registration was 9.5% for maternal deaths (n = 95) and 15.4% for late maternal deaths (n = 26). The probability of dying was 10 times greater in the absence of essential obstetric care, active emergency care and qualified staff, and doubled with every 10-year increase in age. Other contributing factors included delays in recognizing “alarm signals”; reluctance in seeking care owing to desire to hide an induced abortion; delays in receiving timely treatment due to misdiagnosis or lack of supplies; and delays in referral/transportation in rural areas.
Conclusion
A combination of methodologies is required to improve research on and understanding of maternal mortality via the systematic collection of health surveillance data. There is an urgent need for a comprehensive intervention to address public health and human rights issues in maternal mortality, and our results contribute to the consensus-building necessary to improve the existing surveillance system and prevention strategies.
Résumé
bjectif
Evaluer de manière exhaustive la mortalité maternelle en Argentine, avec comme objectif final de renforcer le système de surveillance et de réorienter les politiques de santé génésique visant à prévenir les décès maternels.
Méthodes
Notre étude multicentrique en population, associant méthodes qualitatives et quantitatives, comprend une analyse descriptive du sous-enregistrement des décès maternels et de la distribution de leurs causes, une étude cas-témoins destinée à identifier les facteurs de risque dans la prestation des soins de santé, ainsi que des autopsies verbales, permettant d’analyser les déterminants sociaux liés aux décès maternels.
Résultats
Au total, 121 décès maternels sont intervenus au cours de l’année 2002. Ces décès étaient le plus souvent imputables à des complications d’avortement (27,4%), à des hémorragies (22,1%), à des infections ou à des accidents septiques (9,5%), à des troubles hypertensifs (8,4%) et à d’autres causes (32,6%). Le taux de sous-enregistrement s’élevait à 9,5% pour les décès maternels (n = 95) et à 15,4% pour les décès maternels tardifs (n = 26). La probabilité pour la mère de mourir était 10 fois plus élevée en l’absence de soins obstétricaux essentiels, de soins d’urgence actifs et de personnel qualifié, et multipliée par 2 pour chaque augmentation de 10 ans de l’âge maternel. Parmi les autres facteurs contribuant à la mortalité maternelle, figurent la reconnaissance tardive des « signes d’alerte » ; la réticence des femmes à solliciter des soins dans le cas d’un avortement induit qu’elles veulent cacher ; les retards dans l’administration d’un traitement (erreur diagnostique ou manque de fournitures) et, en zone rurale, les délais dans l’orientation vers un établissement spécialisé ou le transport.
Conclusion
L’association de plusieurs types de méthodes s’impose pour améliorer la recherche et les connaissances sur la mortalité maternelle à partir de données de surveillance sanitaire collectées de manière systématique. Il est urgent d’organiser une intervention de grande ampleur pour répondre aux problèmes liés à la mortalité maternelle qui relèvent de la santé publique et des droits de l’homme et nos résultats contribueront à l’établissement du consensus nécessaire pour améliorer les stratégies de prévention et le système de surveillance déjà en place.
Resumen
Objetivo
Realizar una evaluación integral de la mortalidad materna en la Argentina, con el objetivo último de fortalecer el sistema de vigilancia y reorientar las políticas de salud reproductiva para evitar las defunciones maternas.
Métodos
Nuestro estudio multicéntrico basado en la población, en el que se combinaron métodos cualitativos y cuantitativos, incluyó un análisis descriptivo del subregistro y la distribución de las causas de defunción, un estudio caso-control para identificar los factores de riesgo en la prestación de atención de salud y autopsias verbales para analizar los determinantes sociales asociados a la mortalidad materna.
Resultados
Durante 2002 se registraron en total 121 defunciones maternas. Las causas más comunes fueron complicaciones de abortos (27,4%), hemorragias (22,1%), infecciones/septicemia (9,5%), trastornos hipertensivos (8,4%) y otras causas (32,6%). El subregistro fue del 9,5% para las defunciones maternas (n = 95) y del 15,4% para las defunciones maternas tardías (n = 26). La probabilidad de morir fue diez veces mayor en ausencia de atención obstétrica esencial, guardia activa y personal calificado, y se duplicaba con cada aumento de 10 años de la edad. Otros factores contribuyentes fueron las demoras en el reconocimiento de las «señales de alarma»; la resistencia a buscar atención para ocultar un aborto provocado; los retrasos del inicio del tratamiento como consecuencia de un diagnóstico erróneo o de la falta de suministros; y los retrasos de la derivación y el transporte en las zonas rurales.
Conclusión
Se requiere una combinación de métodos para mejorar las investigaciones sobre la mortalidad materna y los conocimientos sobre la misma mediante la recopilación sistemática de datos de vigilancia sanitaria. Urge implementar una intervención integral que aborde los aspectos de la mortalidad materna relacionados con la salud pública y los derechos humanos. Nuestros resultados pueden ayudar a lograr el consenso necesario para mejorar el sistema de vigilancia y las estrategias de prevención actuales.
ملخص
الەدف
كان الەدف الأقصى من إجراء تقيـيم شمولي لوفيات الأمومة في الأرجنتين ەو تعزيز نظام الترصُّد وإعادة توجيە سياسات الصحة الإنجابية لتفادي موت الأمەات.
الطريقة
ضمت دراستنا المتعددة المراكز والمستندة على السكان طرائق كمية وأخرى كيفية، وشملت تحليلاً وصفياً لنقص التسجيل وتوزيع أسباب الوفيات، وەي دراسة للحالات والشواەد للتعرُّف على عوامل الاختطار في إيتاء الرعاية الصحية إلى جانب الصفة التشريحية اللفظية لتحليل المحدِّدات الاجتماعية التي رافقت موت الأمەات.
الموجودات
حدثت 121 وفاة بين الأمەات عام 2002. وكان أكثر الأسباب شيوعاً مضاعفات الإجەاض 27.4% والنزف 22.1% والعدوى والإنتان 9.5% واضطراب ارتفاع ضغط الدم 8.4% وأسباب أخرى 32.6%. وبلغ نقص التسجيل لوفيات الأمەات التي بلغ عددەا 95 نسبة 9.5% ووفيات الأمەات المتأخرة التي بلغ عددەا 26 نسبة 15.4%. وقد كان احتمال الموت أكثر بعشرة أضعاف عند غياب الرعاية التوليدية، وغياب الرعاية الإسعافية والعاملين المؤەلين، وقد تضاعف مع كل زيادة في العمر مقدارەا عشر سنوات. ومن العوامل الأخرى المساەمة في الوفيات التأخر في التعرُّف على (( العلامات المنذرة ))، ومقاومة التماس الرعاية بسبب الرغبة في إخفاء الإجەاض المحرَّض، والتأخُّر في تلقي المعالجة في موعدەا بسبب سوء التشخيص أو فقد الإمدادات، أو التأخُّر في الإحالة أو في النقل من المناطق الريفية.
الاستنتاج
لتحسين البحوث حول وفيات الأمەات وفەمەا عبر التجميع المنەجي لمعطيات الترصُّد الصحي لابد من اتباع منەجيات مشتركة. وتمس الحاجة إلى تدخل شمولي للتصدي لقضايا حقوق الإنسان والصحة العمومية المتعلقة بوفيات الأمەات، وتساەم النتائج التي حصلنا عليەا في بناء الإجماع الضروري لتحسين نظام الترصُّد الموجود حالياً واستـراتيجيات الوقاية.
Introduction
Maternal mortality is a human rights issue and an unequivocal expression of the economic, social and cultural disadvantages that women experience.1,2 Maternal mortality has been identified as a priority on health policy and research agendas for developing countries.3,4 Most maternal deaths occur in developing countries and a large proportion of these deaths are avoidable.5–9
In Argentina, the maternal mortality ratio (MMR) is lower than in countries classified as having high maternal mortality, but it is elevated when compared with other national indicators (low birth rate, high coverage of prenatal care and high percentage of institutional deliveries).10
The MMR in Argentina has remained steady during the last decade. In 2002, it was 46 per 100 000 live births, with remarkable differences between provinces: the MMR in the city of Buenos Aires was 14 per 100 000 live births, while in the province of Formosa it was 166 per 100 000 live births, almost 12 times higher.11 The causes were abortion complications (31%), other direct obstetric causes (53%) and indirect obstetric causes (16%).11 However, the accuracy of these statistics is uncertain, since the results of studies carried out in Argentina and a recent report by WHO estimated under-registration at 50%.12–14 The case of maternal mortality illustrates the presence of structural failures in the health-care system, quality of care and particularly the ability to manage obstetric emergencies and access health services. Argentina recently launched a Federal Health Plan that seeks to achieve a 20% reduction in the national MMR by 2007.15 Almost 25 years after the first Argentine study was carried out, research is needed to readdress the problem of maternal mortality, analyse the dynamics of social and health-services determinants, improve the monitoring process and formulate recommendations to reorient public health policies aimed at reducing maternal deaths.16
Methods
We performed a multicentre study in six Argentine provinces (Chaco, Formosa, Mendoza, San Juan, San Luis and Tucuman). Selection was based on these provinces’ MMR being higher than the national value, local political support and the presence of qualified researchers. The research was organized in three components: (1) a population-based study of under-registration of maternal mortality and distribution of causes; (2) a case–control study to evaluate risk factors associated with maternal deaths; and (3) verbal autopsies to determine the factors that impede timely and effective contact with health services.
Population-based study
A population-based study was conducted to determine the level of under-registration of maternal deaths, using a reproductive-age mortality survey (RAMOS) approach to study maternal deaths from 1 January to 31 December 2002.17–21 All death certificates of women aged 10–49 years and corresponding clinical records were reviewed based on definitions of the International Classification of Disease (ICD-10).22 All deaths (institutional and non-institutional) were included. The level of under-registration and the reclassification of causes were determined by comparing the causes recorded on the death certificate with the corresponding clinical record. In the case of non-institutional deaths, only the data from death certificates were considered.
Three classes of under-registration were estimated: maternal deaths (“death while pregnant or within 42 days of the termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and the site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes”22), late maternal deaths (“deaths from direct or indirect obstetric causes more than 42 days but less than one year after the termination of pregnancy”22) and total under-registration.
To ensure the validity of the study, field supervision complemented the data collection and analysis performed by local coding experts and obstetricians.
Case–control study
A paired case–control study was designed to evaluate risk factors associated with maternal deaths.23,24 Cases were women aged 10–49 years who had died from causes associated with pregnancy in public institutions during 2002; additional cases from 2001 were included to obtain the required sample size. Controls were surviving women admitted to public institutions with similar principal morbidity or co-morbidity and at the same stage of pregnancy (post-abortion, antepartum, intrapartum or postpartum). Maternal deaths in public institutions were selected since, historically, they represent 85% of all maternal deaths. Exclusion criteria were: late maternal deaths, deaths without corresponding clinical records and those attributable to rare causes, because of the difficulty in finding matched controls.
Risk factors were classified as hospital characteristics, delivery of care, characteristics of health-care providers and women’s biological and social profiles.
Prevalence data from the general population were used to calculate the study’s sample size and power.25 It was estimated that 85 pairs of cases and controls would be needed to obtain odds ratios (ORs) of at least 3 with a power of 80% and α = 0.05. The final sample consisted of 84 cases and 84 paired controls. The mean contribution of each province was 14 pairs (range, 8–20).
Sources of information used were death certificates, hospital discharge records, hospital statistics and clinical records.
Frequencies and means of the variables were calculated. For the univariate analysis, ORs and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated using the MacNemar test for paired data. For the multivariate model, conditional logistic regression for paired data was used.26 Adjusted ORs and 95% CI for institutional and biological variables were calculated and, after testing co-linearity and interaction, the variables included in the model were those showing a significance of P ≤ 0.1 without co-linearity. Finally, the model that proved to be the most stable with the best explanatory potential was selected.
Verbal autopsies
The verbal autopsy technique27–31 was used to reconstruct “the road to maternal death” and describe the dynamics of factors that impeded timely and efficient contact with the health system.32
The sample comprised 25 cases, 4 for each site (except San Luis, for which there were 5), stratified by cause of maternal death (complications of induced abortion, 11; other obstetric causes, 14). To ensure internal variability, the sample included at least one case per province with the following characteristics: adolescent, living in rural area and cared for at a private facility.
Field staff were trained and supervised, and data were analysed according to the “three delays” model: delay in the decision to seek care, delay in arrival at a health facility and delay in the provision of adequate care.33
Results
During 2002, 1516 women of reproductive age (10–49 years) died in the six provinces: 69% of these deaths were institutional and 31% non-institutional. Of the maternal deaths, most (85%) occurred in public hospitals. After reclassification, the number of confirmed maternal deaths increased from 108 to 121, but the ratio between maternal deaths and late maternal deaths remained constant (4:1). Levels of under-registration are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Estimates of under-registration of maternal deaths, by province (%).
| Indicatora | Province |
Total for provinces |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chaco | Formosa | Mendoza | San Juan | San Luis | Tucuman | (n / N)b | % | ||
| Maternal deaths | 0.0 | 13.6 | 0.0 | 11.1 | 14.3 | 21.0 | 9 / 95 | 9.5 | |
| Late maternal deaths | 18.2 | 16.7 | 50.0 | 0.0 | 50.0 | +300.0c | 4 / 26 | 15.4 | |
| Total maternal deaths | 6.9 | 14.3 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 22.2 | 10.0 | 13 / 121 | 10.8 | |
a The estimates of under-registration were determined by comparing the causes recorded on the death certificate with the corresponding clinical record. b n = number of cases of maternal death incorrectly registered, i.e. under-registration; N = overall cases of maternal death, late maternal death or total maternal deaths, as applicable. c The ‘+’ signifies over-registration of late maternal deaths.
The main causes of maternal death were abortion complications (27.4%), haemorrhage (22.1%), infection/sepsis (9.5%) and hypertensive disorders (8.4%). For late maternal deaths, hypertensive disorders and infections each accounted for 15% of the causes and the remaining 70% corresponded to other direct and indirect obstetric causes. The age distribution for confirmed maternal deaths was: 23% adolescents, 53.8% aged between 20 and 34 years, and 23% aged more than 35 years. With regard to stage of pregnancy, 26% of deaths occurred before 20 weeks of gestation, 25% within 7 days after delivery and 22% were late maternal deaths. Information on ethnicity could only be collected in Formosa, where the indigenous population comprises 7% of the total. Nevertheless, 36% of maternal deaths were of women from indigenous communities, which also had higher prevalence of late maternal deaths. The ratio of maternal deaths to late maternal deaths was 8:1 among non-indigenous women, and 1.5:1 among indigenous women in this province.
Risk factors associated with maternal deaths
Cases were 3 years older than controls; while 25% of the controls were aged 20 years or less, only 10% of the cases were in this age group (Table 2). No differences were found between cases and controls regarding educational level or marital status (Table 2). When pairing cases and controls by co-morbidity, the most common causes were the absence of co-morbidity or anaemia, followed by sepsis and hypertension. Differences in reproductive history were observed: there was a higher proportion of nulliparous women in the control group and many multiparous women among the cases. The distribution of causes among the 84 pairs of cases and controls was: abortion (49%), hypertension disorders (13%), postpartum haemorrhage (12%), antepartum haemorrhage (11%), sepsis (7%), indirect obstetric causes (7%) and haemorrhage during the first trimester (1%).
Table 2. Sociodemographic characteristics of cases and controls.
| Characteristic | Cases (n = 84) | Controls (n = 84) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 29.1 (8.0) | 25.8 (7.2) | 0.005 |
| Educational level (%) | 0.388 | ||
| < 7 years | 16.7 | 9.5 | |
| ≥ 7 years | 67.9 | 69.0 | |
| No data | 15.5 | 21.4 | |
| Marital status (%) | 0.67 | ||
| Married/in union | 50.6 | 52.4 | |
| Single/other | 33.7 | 36.6 | |
| No data | 15.7 | 11.0 | |
| Gravidity (%) | 0.021 | ||
| 0 | 12.3 | 29.3 | |
| 1–3 | 42.0 | 39.0 | |
| ≥ 4 | 45.7 | 31.7 | |
| Abortions (%) | 0.096 | ||
| 0 | 64.6 | 76.5 | |
| ≥ 1 | 35.4 | 23.5 | |
| Caesarean sections (%) | |||
| 0 | 68.8 | 78.8 | 0.349 |
| 1 | 13.8 | 10.0 | |
| ≥ 2 | 17.5 | 11.3 |
SD, standard deviation.
The statistically significant clinical factors associated with an increased risk of death are presented in Table 3. The absence of an obstetrics-gynaecology specialist on 24-hour active duty and the lack of essential obstetric care accounted for an eightfold increase in the risk of maternal death. The presence of a residency programme in obstetrics increased the availability of trained personnel; the risk of maternal death increased by 5.5 times in hospitals without residency programmes. Multiparity and age greater than 35 years also increased the risk of maternal death.
Table 3. Clinical and statistically significant risk factors for maternal death.
| Risk factor | Frequency |
OR | 95% CI | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | Controls | |||||
| Characteristics of hospital providing initial care | ||||||
| Availability of essential obstetric care: | 8.00 | 1.00–63.96 | 0.050 | |||
| No | 8 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 74 | 83 | ||||
| Number of deliveries/year: | 9.00 | 2.09–38.79 | 0.003 | |||
| < 1500 deliveries/year | 58 | 3 | ||||
| ≥ 1500 deliveries/year | 19 | 80 | ||||
| Obstetrics-gynaecology specialist on 24-hour active duty: | 8.00 | 1.84–34.79 | 0.006 | |||
| No | 18 | 4 | ||||
| Yes | 60 | 80 | ||||
| Characteristics of hospital where death or complications occurred | ||||||
| Availability of essential obstetric care: | 16.00 | 2.12–120.65 | 0.007 | |||
| No | 16 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 68 | 83 | ||||
| Number of deliveries/year: | 5.00 | 1.09–22.82 | 0.038 | |||
| < 1500 | 10 | 3 | ||||
| ≥ 1500 | 60 | 79 | ||||
| Obstetrics-gynaecology specialist on 24-hour active duty: | 22.00 | 2.96–163.21 | 0.003 | |||
| No | 25 | 4 | ||||
| Yes | 57 | 80 | ||||
| Delivery of care | ||||||
| Length of hospitalization (days): | 3.86 | 1.68–8.86 | 0.001 | |||
| > 5 | 56 | 31 | ||||
| 1–5 | 23 | 42 | ||||
| Characteristics of attending staff | ||||||
| Presence of residency programme: | 5.50 | 1.22–24.81 | 0.027 | |||
| No | 11 | 2 | ||||
| Yes | 73 | 82 | ||||
| Biological and social characteristics | ||||||
| Age > 19 years: | 4.67 | 1.34–16.24 | 0.015 | |||
| > 19 | 76 | 65 | ||||
| 15–19 | 8 | 19 | ||||
| Age ≥ 35 years: | 2.22 | 1.01–4.88 | 0.047 | |||
| ≥ 35 | 26 | 15 | ||||
| < 35 | 58 | 69 | ||||
| Previous gestations: | 2.18 | 1.07–4.45 | 0.032 | |||
| ≥ 4 | 38 | 23 | ||||
| 0–3 | 43 | 56 | ||||
CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio.
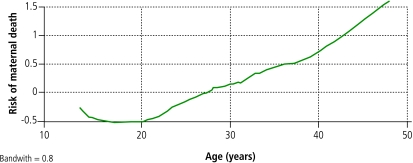
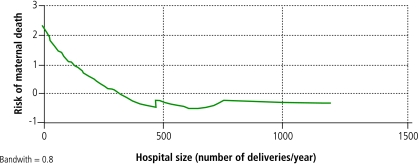
Age best represents the biological–social variables as a proxy of reproductive history: as age increases, so does parity. There was a linear relationship between age and the risk of maternal death (Fig. 1) except among adolescents; for those aged less than 15 years there was an inverse linear relationship. The odds of dying doubles with each decade: OR, 2.10 (95% CI, 1.25–3.52). Hospital size showed co-linearity with other variables that characterize hospital structure (availability of essential obstetric care, active emergency care and residency programmes) and the level of training of staff attending deliveries and providing post-abortion care (Table 4). Hospital size, as determined by the number of annual deliveries, showed an inverse linear relationship with mortality rates, with rates stabilizing for hospitals with greater than approximately 750–800 births (Fig. 2). Hospitals were classed as large or small (⩾ 1500 versus < 1500 deliveries/year, respectively). Conditioned logistic regression indicated that the probability of maternal death was nine times greater in small hospitals: OR, 9.00 (95% CI, 2.09–38.79).
Fig. 1.
Relationship between age and risk of maternal deatha
a The model chosen was the Lowess smoother logit transformed smooth model.
Table 4. Relationship between hospital size and other risk factors.
| Risk factor | Hospital size
(No. of deliveries per year) |
P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 1500
(n = 23) |
≥ 1500
(n = 138) |
|||||
| N | % | N | % | |||
| Absence of essential obstetric care | 5 | 21.7 | 0 | 0 | < 0.0001 | |
| Absence of residency programme | 12 | 52.2 | 0 | 0 | < 0.0001 | |
| Absence of on-call obstetrics-gynaecology specialist | 15 | 65.2 | 5 | 3.6 | < 0.0001 | |
Fig. 2.
Relationship between hospital size and risk of maternal deatha
a The model chosen was the Lowess smoother logit transformed smooth model.
The best explanatory multivariate model of maternal mortality included the biological characteristics of the woman and the characteristics of the institution providing obstetric care. In the final adjusted model, the probability of maternal death doubled for every 10-year increase in age and was 10 times higher in small hospitals. No confounding or interaction was found between age and hospital size.
Delays impeding timely and effective treatment
The results of verbal autopsies are reported as significant vignettes from a sample of testimonies obtained in the study.
The first type of delay was attributed to physical symptoms that were not recognized as “alarm signals”, fear of reporting an illegal abortion or lack of support from partners or from any other who could take care of the children. One mother said:
One of her [friends] blamed herself when my daughter died. She told me: “It is my fault because she had told me she could see pus drops coming out and it was so stupid of me not to tell her to go to the doctor.”
The second type of delay showed obstacles such as transportation difficulties and limited availability of nearby health services. According to a partner:
I told him: “I don’t have any way to take her,” and he [the community health agent] told me he would get me a bike. I couldn’t take her that afternoon. … Only the following day could we go to seek help, because I didn’t know what to do with my children.
The third type of delay resulted from errors in diagnosis and clinical decision-making, of lack of medical supplies and of staff proficiency in the management of obstetric emergencies. As one friend of a case said:
On Saturday, he was looking for blood donors. He found them among his group of friends. Since it was a weekend, they couldn’t draw blood because the appropriate blood bank staff was not available. The doctors told José to go to [another hospital], 9 kilometers’ distance from the city, to get some blood containers. They only gave him one, even though he told them he needed more.
Finally, delays in referrals and lack of coordination within the health-care network response were observed, as shown by this example given by a doctor:
Since contractions did not stop … I decided to refer the patient to a higher-complexity hospital at 10:40 am. The local ambulance had been out of work for one week; then I requested an ambulance from the reference hospital. It arrived at 2 pm and reached the reference hospital (120 km) after 5 pm. The road is in very bad shape.
Discussion and conclusions
This study selected Argentine provinces with a high MMR and analysed the factors that determine this problem’s scope and characteristics. Among the strengths of the methodology used are the combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches and the diversity of the dimensions analysed. The methodological strategy made it possible to address maternal deaths using a comprehensive theoretical framework that included users’ perception of the health-care system, quality and availability of health services, and the notification, coding and registration of maternal deaths.
Under-registration
International consensus holds that maternal deaths are usually under-registered.8,14,34 The estimated under-registration for this study was 9.5% for maternal deaths, 15.4% for late maternal deaths, and 10.8% for total maternal deaths, with great variability across provinces (Table 1).
A WHO publication estimates that MMRs in Argentina are actually double the official estimates for 2000, even though Argentina is considered to have a good registration system for cause of death.14 In deriving this estimate, an adjustment factor of 1.9 was used to calculate an MMR of 82 per 100 000 live births from the reported MMR of 43 per 100 000 live births, even though most other countries included in the same analysis subgroup had adjustment factors of 1.4–1.5. Our results do not support the WHO estimates, since the level of under-registration calculated is remarkably lower than that previously estimated by WHO and in previous studies.13,14,34,35
In the six provinces, the average proportion of deaths for which clinical records were found was 86% (range, 67.2–100%), thus suggesting that the estimate of under-registration might not be significantly biased by the proportion of clinical records found. However, 31% of the decedents were non-institutional and therefore did not have clinical records, indicating the need to explore maternal deaths within this population.
The research was based on data acquired in 2002 and was carried out during 2003 at the same time as an analysis performed by the Provincial Office of Health Statistics (OHS). This simultaneity, along with the deliberate strategy of collaborative work between the provincial research teams and OHS, could explain the low level of under-registration estimated. Moreover, efforts have been made by the OHS with the collaboration of United Nations agencies (Pan-American Health Organization/WHO, the United Nations Children’s Fund and the United Nations Population Fund) to improve the quality of the surveillance systems.
Causes
The results of this study revealed slight differences in the registration of all causes of death when compared with those published by the Ministry of Health for the same year. The numbers of cases of abortion complications, hypertensive disorders and infections were fewer than those reported by the Ministry of Health, while the numbers of cases of haemorrhage and other direct and indirect causes were higher. Differences between these numbers might be attributable to differences in the reclassification criteria used in this study after all clinical records had been analysed in depth.
The analysis of late maternal deaths is an original contribution of this study. This dimension is not yet well understood and needs greater recognition and evaluation. Ratios for late maternal mortality are lower in countries with high MMRs. As the quality of health services improves, total maternal mortality decreases while late maternal mortality rises. In developing countries, late maternal deaths account for 5–20% of all maternal deaths. In our study, late maternal deaths represented 21% of the total (n = 22). After reclassification, the relationship between maternal deaths and late maternal deaths remained unchanged (4:1).
Risk factors
The risk factors identified were biological and social variables, hospital structure, delivery of care and the qualifications of health-care providers33 according to the methodological approaches recommended in the literature.36,37
In the sample studied, abortion complications were over-represented as a cause of death when compared with the data from component I. The higher proportion of abortions may be attributable to the fact that only institutional deaths from the public sector were considered, or to the fact that the cases from 2001 that were included to reach the needed sample size had a higher proportion of abortion complications as cause of death (57.7% in 2001 versus 44.1% in 2002).
Of all the variables associated with maternal death, hospital size and age of the mother were selected to obtain a simple model summarizing the multiplicity of factors that influence the risk of maternal death. Apart from the methodological considerations of this selection, the number of hospital deliveries was highly correlated with other hospital-structure variables and the qualifications of the health-care providers. In addition, this variable could represent the ability of health services to adequately respond to obstetric emergencies, given its correlation with the availability of comprehensive obstetric care. Thus, hospital structure is the most important variable in determining the risk of maternal death. The availability of essential obstetric care, active emergency care and specialists played an important role in preventing these deaths. The presence of qualified professionals and appropriate supplies to provide emergency care is an efficient intervention to reduce maternal mortality, as the probability of maternal death increases ninefold in the absence of these conditions. Age was a significant variable, a proxy for reproductive history and a risk factor even in the presence of appropriate obstetric emergency care. The odds of maternal death double for every 10-year increase in age.
Social and cultural factors
Verbal autopsies showed that various social and cultural factors prevent timely and effective treatment. At the family level, the stigma of abortion and the concealment of abortive procedures within the family and community could explain a delay in seeking care.38 This situation contrasts with that of women who died from other obstetric causes, for whom the support of “significant others” made access to medical care possible without much delay. At the level of health services, women experienced misdiagnosis, inappropriate treatment and delays in referral. The lack of supplies together with the absence of skilled personnel caused delays in the adequate management of obstetric emergencies.
Recommendations
Considering the issues identified by the results of our study, we recommend a number of actions aimed at reducing maternal mortality:
Reorganization of the health-care network to promote timely referrals.
Improved availability of qualified professionals, facilities and medical supplies for essential and emergency obstetric care based on the best scientific evidence.5,29,35,36
Improvement in access to health services, especially in rural areas, with the involvement of health teams and communities.
Addressing the problem of complications associated with unsafe abortion, ensuring counselling and provision of post-abortion contraceptives and manual vacuum aspiration. Ultimately, the legalization of abortion would prevent women, especially those living in poverty, from undergoing dangerous and life-threatening abortion practices.
Strengthen the integration of health statistics departments and maternal–child health and epidemiology units to improve systems for the surveillance of maternal deaths.
In addition, the study had several beneficial effects that are worth mentioning. These include the dissemination of information, the promotion of public awareness on maternal mortality and the development of innovative responses by local governments through their political involvement.
The conventional scientific perspective tends to reduce health to illness, to individual cases and to empirically-tested phenomena – a typically determinist conception.39 For maternal mortality this is not the case: social determinants and human rights are the main influences to be accounted for. ■
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the relatives of the deceased women, members of the Maternal Mortality in Argentina Study Group (http://www.cedes.org/english/informacion/ci/publicaciones/index_2.html), and provincial-level research teams, departments of health statistics, maternal–child health programmes and hospital health statistics units, as well as: the Vigi+A Programme; the Latin American Center of Perinatology and Human Development; Virginia Camacho of PAHO; Henry Espinoza, Sofia Reynoso and Ana Langer of the Population Council; Daniel Ferrante, Eduardo Bergel, Luz Gibbons and Vilma Irazola of IECS; Élida Marconi of the health ministry’s statistics office; Alejandro Marzonetto; Juan Carlos O’Donnell of CONAPRIS/National Ministry of Health; Zulma Ortiz of the Center for Epidemiologic Research/National Academy of Medicine; and Melissa Rosenstein of the University of Pennsylvania and CEDES.
Footnotes
Funding: This research was supported by the Ministry of Health and Environment (CONAPRIS), Argentina; the Pan-American Health Organization, Argentina; and the United Nations Population Fund, Argentina.
Competing interests: None declared.
References
- 1.United Nations. The universal declaration of human rights. New York: United Nations; 1948. Available at: http://www.un.org/Overview/rights.html
- 2.Cook R, Dickens BM, Wilson A, Scarrow S. Advancing safe motherhood through human rights. Geneva: WHO; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Langer A, Espinoza H. [Unwanted pregnancy: impact on society and health in Latin America and the Caribbean]. In: [New challenges of political responsibility. Notebook of the Civil Society Forum of the Americas]. Buenos Aires: CEDES-FLACSO-CELS; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mahler H. The safe motherhood initiative: a call to action. Lancet. 1987;329:668–70. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(87)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ronsmans C, Graham WJ. Lancet Maternal Survival Series steering group. Maternal mortality: who, when, where, and why. Lancet. 2006;368:1189–200. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69380-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.[Regional Strategy for Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Reduction, 26th Pan-American Sanitary Conference, 54th Session of the Regional Committee, September 23-27, 2002, Washington, DC]. Washington: PAHO/WHO, (CSP26/SR/8).
- 7.Center for Population and Family Health. [Programme for the reduction of maternal mortality: options and proposals]. New York: School of Public Health, Columbia University; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Health Canada. Special report on maternal mortality and severe morbidity in Canada - enhanced surveillance. The path to prevention. Ottawa: Ministry of Public Works and Government Services; 2004. Available at: http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/rhs-ssg/srmm-rsmm/index.html
- 9.The 10/90 report on health research 2003–2004. Geneva: Global Forum for Health Research; 2004. Available at: http://www.globalforumhealth.org/ Site/002__What%20we%20do/005__Publications/001__10%2090%20reports.php
- 10.The world health report 2005 - make every mother and child count. Geneva: WHO; 2005. Available at: http://www.who.int/whr/2005/en/ [DOI] [PubMed]
- 11.[Vital statistics 2002]. Buenos Aires: Ministry of Health; 2003.
- 12.Althabe O, Vinacur P, Althabe F. [Remarks and technical notes]. In: Althabe O, Vinacur P, Althabe F, eds. [Maternal mortality in Argentina]. Buenos Aires: Ministry of Health; 1987. [Google Scholar]
- 13.INAPSA. [Study of maternal mortality in Mendoza Province. Years 1993-1994-1995]. Buenos Aires: Ministry of Health; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 14.AbouZahr C, Wardlaw T. Maternal mortality in 2000: estimates developed by WHO, UNICEF and UNFPA. United Nations Children’s Fund; 2003. Available at: http://www.childinfo.org/maternal_mortality_in_2000.pdf
- 15.Federal Health Plan Buenos Aires: Ministry of Health; 2004. Available at: http://www.msal.gov.ar/htm/site/institucional_planfederal.asp
- 16.Department of Health, Economy and Society, CEDES. [Sexual and reproductive health and rights, 2000–2003, a period of advances and setbacks]. In: Center for Legal and Social Studies (CELS), [Human rights in Argentina. 2002–2003 report]. Buenos Aires: CELS; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stanton C, Hobcraft J, Hill K, Kodjogbe N, Mapeta WT, Munene F, et al. Every death counts: measurement of maternal mortality via census. Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79:657–64. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hill K, AbouZahr C, Wardlaw T. Estimates of maternal mortality for 1995. Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79:182–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Betrán AP, Wojdyla D, Posner SF, Metin Gülmezoglu A. National estimates for maternal mortality: an analysis based on the WHO systematic review of maternal mortality and morbidity. BMC Public Health. 2005;5:131. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-5-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Valongueiro S, Ludermir AB, Gominho LAF. Cad Saude Publica. 2003;19(Suppl. 2):S293–301. doi: 10.1590/s0102-311x2003000800011. [Evaluation of procedures for identifying maternal deaths] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Laurenti R, Mello-Jorge MHP, Gotlieb SL. Cad Saude Publica. 2000;16:23–30. doi: 10.1590/s0102-311x2000000100003. [Reflections on the measurement of maternal mortality] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.International classification of diseases and related health problems - 10th revision. Geneva: WHO; 1992.
- 23.Schlesselman J. Case-control studies: design, conduct and analysis. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1982. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hennekens CH, Buring JE. Chapter II. Types of epidemiologic studies: case–control studies. In: Mayrent SL, ed. Epidemiology in medicine, 1st ed. Boston: Little, Brown; 1987. p. 132-45. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Villar J, Ba’aqeel H, Piaggio G, Lumbiganon P, Belizan J, Farnot U, et al. WHO Antenatal Care Trial Research Group. WHO antenatal care randomised trial for the evaluation of a new model of routine antenatal care. Lancet. 2001;357:1551–64. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04722-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lachin J. Biostatistical methods. The assessment of relative risks. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chandramohan D, Rodrigues LC, Maude GH, Hayes RJ. The validity of verbal autopsies for assessing the causes of institutional maternal death. Stud Fam Plann. 1998;29:414–22. doi: 10.2307/172253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gajalakshmi V, Peto R, Kanaka S, Balasubramanian S. Verbal autopsy of 48,000 adult deaths attributable to medical causes in Chennai, India. BMC Public Health. 2002;16:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-2-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kane T, el-Kady AA, Saleh S, Hage M, Stanback J, Potter L. Maternal mortality in Giza, Egypt: magnitude, causes and prevention. Stud Fam Plann. 1992;23:45–57. doi: 10.2307/1966827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Langer A, Hernández B, García C, Saldaña G. Identifying interventions to prevent maternal mortality in Mexico: a verbal autopsy study. In: Berer M, Sundari Ravindran TK, eds. Safe motherhood initiatives: critical issues. Reprod Health Matters 1999;127-136. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sloan NL, Langer A, Hernandez B, Romero M, Winikoff B. The etiology of maternal mortality in developing countries: what do verbal autopsies tell us? Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79:805–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fathalla M. The long road to maternal death. People. 1987;14:8–9. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Maine D, Murat A, Ward V, Kamara A. The three delays model. In: The design and evaluation of maternal mortality programs. New York: Center for Population and Family Health, Columbia University. 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 34.[Maternal mortality in selected areas, Series 8, Data analysis]. Buenos Aires: Ministry of Health, National Program of Health Statistics; 1985.
- 35.[Study of maternal mortality. Analysis of under-registration of maternal deaths in the federal capital (1985)]. Buenos Aires: Health Department, Maternal and Child Health Program; 1989.
- 36.Hernández B, Langer A, Romero M, Chirinos J. Salud Publica Mex. 1994;36:521–8. [Factors associated with hospital maternal death in the state of Morelos, Mexico] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Garenne M, Mbaye K, Bah MD, Correa P. Risk factors for maternal mortality: a case–control study in Dakar hospitals (Senegal). Afr J Reprod Health. 1997;1:14–24. doi: 10.2307/3583271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ramos S, Romero M. On how a restrictive legal context affects the quality of care of induced abortions. Gynaecol Forum. 1999;4:18–20. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Breilh J. [Critical epidemiology. Emancipating science and intercultures],1st ed. Buenos Aires: Lugar Editorial; 2003. [Google Scholar]