Abstract
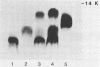
The lipopolysaccharides (LPS) of Chlamydia trachomatis, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. anitratus, and Re mutants of Salmonella sp. were shown to share related immunodeterminants , as demonstrated by double immunodiffusion and immunoblotting from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels. The cross-reactive material in the extracellular slime of A. calcoaceticus var. anitratus was shown to be released LPS. The Acinetobacter LPS was found to separate in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis into three fractions. The cross-reactive component was the fraction migrating fastest, at a rate identical to Re-type LPS of Salmonella sp. The Acinetobacter LPS could be used as antigen in complement fixation assays performed on paired sera of patients with chlamydial pneumonia; it gave results identical to those of the chlamydial complement fixation glycolipid antigen conventionally used in such assays in 9 of 10 patients.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Jennings H. J., Kenny C. P. Structural elucidation of the 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid containing meningococcal 29-e capsular polysaccharide antigen using carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):645–651. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Brunner H. Serological cross-reactions between Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and chlamydiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):819–822. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.819-822.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Galanos C. Isolation, purification, and chemical analysis of the lipopolysaccharide and lipid A of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus NCTC 10305. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(2):233–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H., Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Differential determination of the 3-Deoxy-D-mannooctulosonic acid residues in lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella minnesota rough mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon D., Szabó L. The synthesis of 3-deoxy-5-O-methyloctulosonic acid and its behaviour in the Warren reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 18;29(1):184–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhir S. P., Hakomori S., Kenny G. E., Grayston J. T. Immunochemical studies on chlamydial group antigen (presence of a 2-keto-3-deoxycarbohydrate as immunodominant group). J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):116–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann K., Jann B. The K antigens of Escherichia coli. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:53–79. doi: 10.1159/000407421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxén H., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane protein (porin) preparations in experimental murine salmonellosis: effect of lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.328-332.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Risse H. J., Ruschmann E., Schlecht S., Schmidt G., Schulte-Holthausen H., Wheat R., Westphal O., Schlosshardt J. Structural relationship of Salmonella O and R antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):349–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHIESEN M., VOLKERT M. An ornithosis related antigen from a coccoid bacterium. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1956;39(2):117–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1956.tb03383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nakae T. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;20:163–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Leinonen M., Saikku P., Mäkelä P. H. The genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia: resemblance to the lipopolysaccharide of enteric bacteria. Science. 1983 Jun 17;220(4603):1279–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.6344216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIMIZU Y., BANKOWSKI R. A. THE NATURE OF THE CROSS REACTIONS BETWEEN A BACTERIUM OF THE GENUS HERELLEA AND THE ORNITHOSIS VIRUS IN COMPLEMENT FIXATION. Am J Vet Res. 1963 Nov;24:1283–1290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Meyer K. F. Lymphogranuloma venereum. II. Characterization of some recently isolated strains. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):636–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.636-638.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Nurminen M., Mäkelä P. H. Mutants defective in the 33K outer membrane protein of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):376–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.376-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain S. M., Fesik S. W., Armitage I. M. Characterization of lipopolysaccharide from a heptoseless mutant of Escherichia coli by carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2906–2910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKERT M., CHRISTENSEN P. M. Two ornithosis complement-fixing antigens from infected yolk sacs. I. The phosphatide antigen, the virus antigen and methods for their preparation. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;37(2):211–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Broady K. W., Lüderitz O., Rietschel E. T. The chemical structure of lipid A. Demonstration of amide-linked 3-acyloxyacyl residues in Salmonella minnesota Re lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]