Abstract
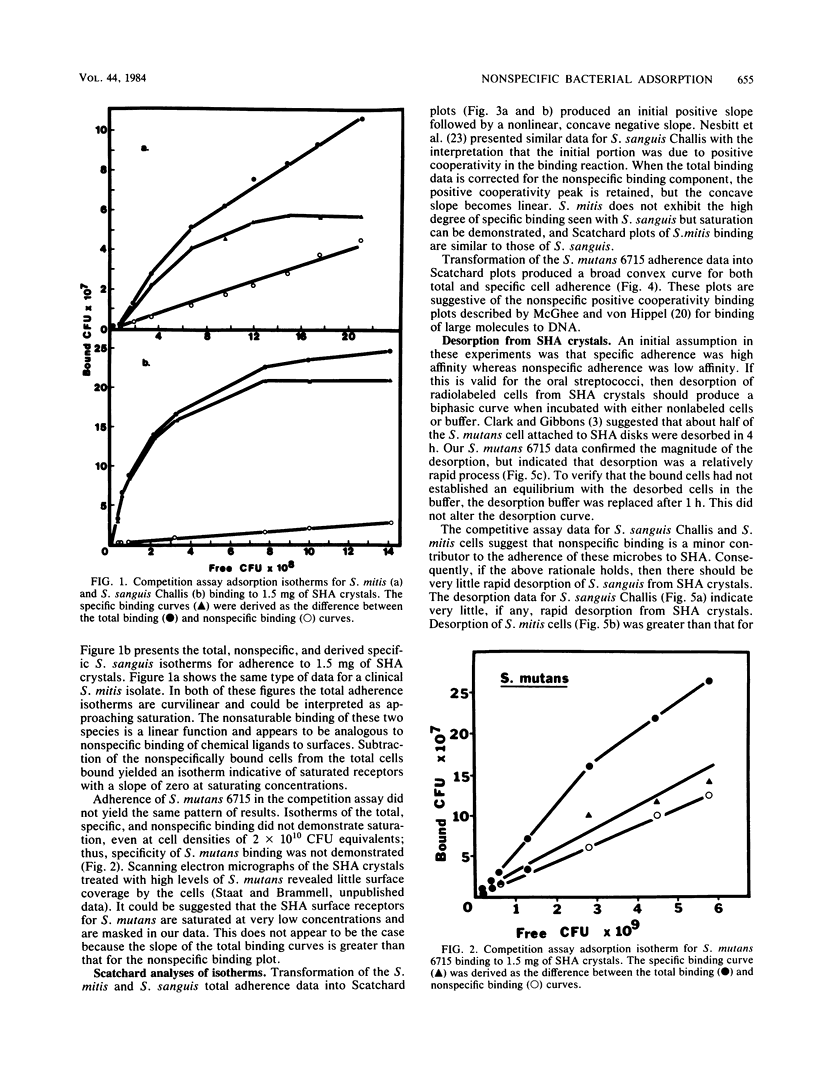
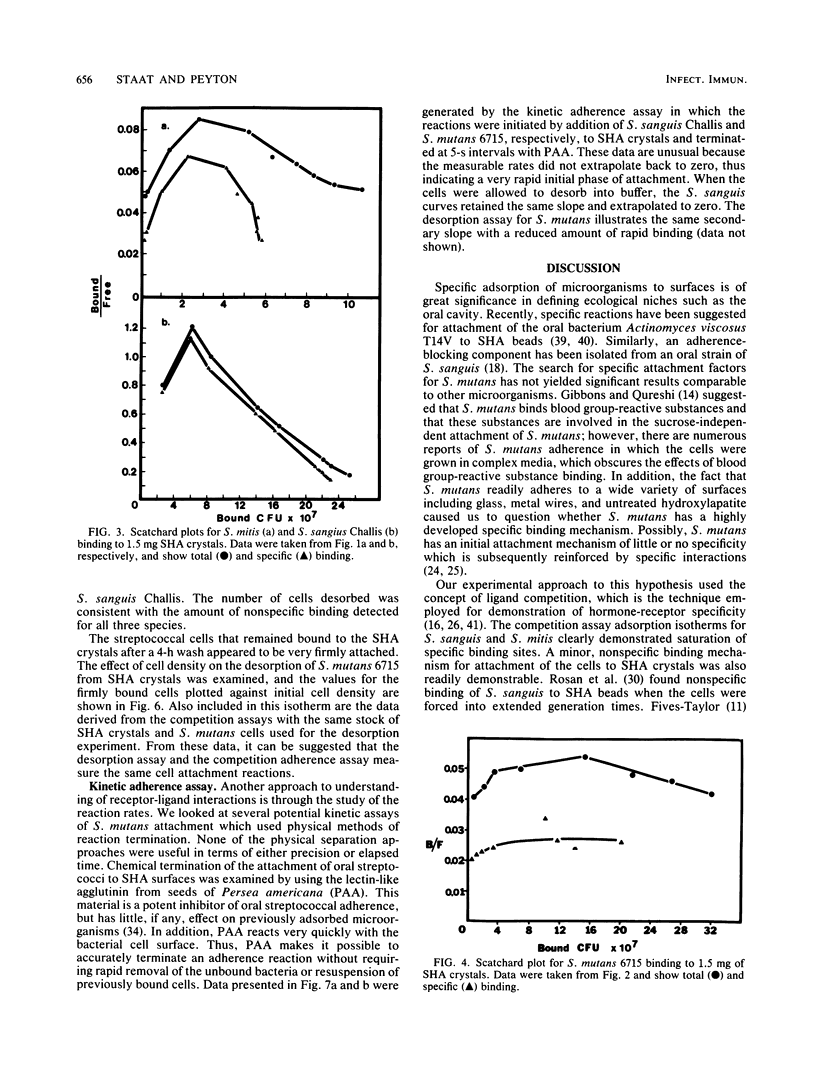
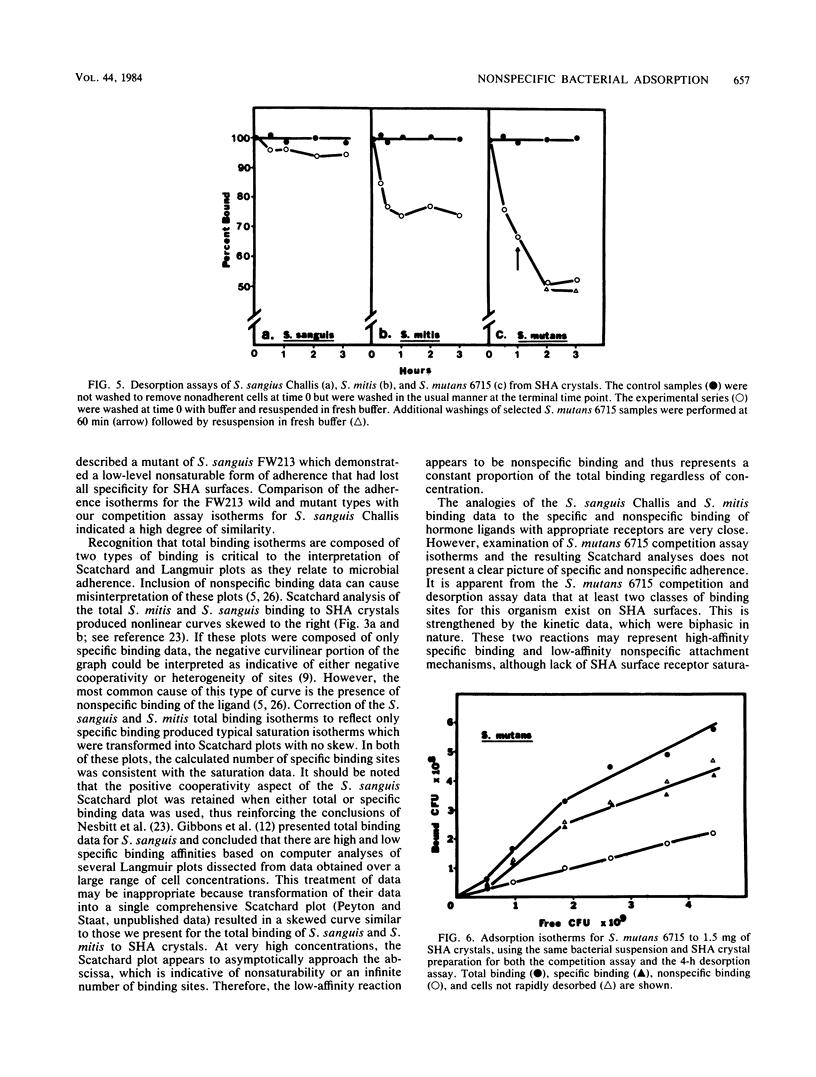
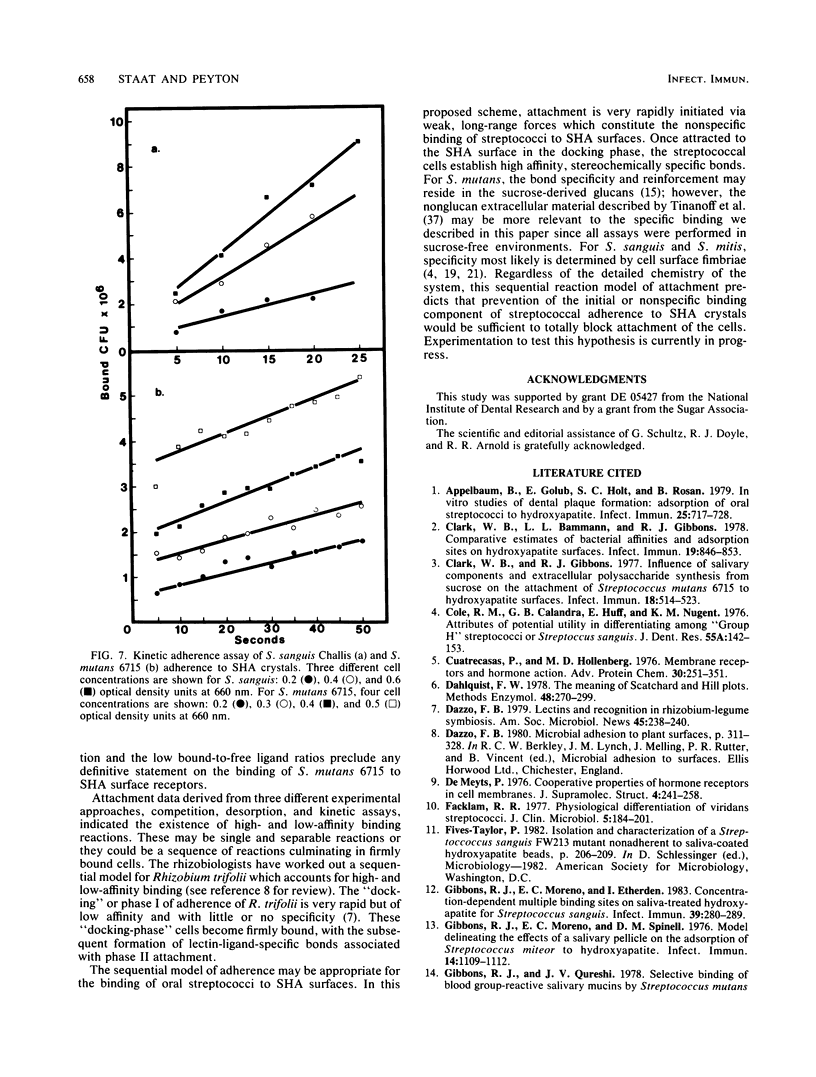
It is proposed that binding of oral streptococci to saliva-coated hydroxylapatite (SHA) surfaces is a multifactorial process involving both specific and nonspecific receptors. In this context, specific binding is described as a high-affinity, saturable interaction between the cell and binding surface. Conversely, nonspecific binding is considered to be a nonsaturable, generalized, low-affinity reaction. Experimental differentiation of specific binding from nonspecific binding was achieved with a competition assay which utilized a large excess of nonradiolabeled bacteria to compete with the 3H-labeled cells for attachment to receptors on 1.5 mg of SHA crystals. Competition assays of Streptococcus sanguis and Streptococcus mitis adhesion clearly demonstrated that the total binding isotherm was composed of a saturable specific binding reaction and a minor nonspecific binding component. This was further substantiated by analysis of nonlinear Scatchard plots of the total binding data. The competition data for Streptococcus mutans binding indicated that ca. 50% of the S. mutans binding appeared to be specific, although saturation of the SHA surfaces with bacterial cells could not be demonstrated. Experiments measuring desorption of radiolabeled cells from SHA crystals into buffer showed that ca. 50% of the bound S. mutans cells were removed after 4 h, whereas less than 5% of the S. sanguis cells were eluted from the SHA surfaces. The kinetics of attachment were studied by using an extract of Persea americana as a noncompetitive inhibitor of adherence. The total cell binding data for these experiments suggested a very rapid binding reaction followed by a slower rate of attachment. It was concluded from these three different experimental approaches that adherence of selected oral streptococci to SHA surfaces involves specific, high-affinity and nonspecific, low-affinity binding reactions. The concept is developed that in vitro streptococcal attachment to SHA can be described as a two-reaction process in which the low-affinity interaction of the cell with the SHA surface precedes the establishment of the stronger, specific bonds needed for the maintenance of streptococci in the oral cavity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum B., Golub E., Holt S. C., Rosan B. In vitro studies of dental plaque formation: adsorption of oral streptococci to hydroxyaptite. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):717–728. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.717-728.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Bammann L. L., Gibbons R. J. Comparative estimates of bacterial affinities and adsorption sites on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):846–853. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.846-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Gibbons R. J. Influence of salivary components and extracellular polysaccharide synthesis from sucrose on the attachment of Streptococcus mutans 6715 to hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):514–523. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.514-523.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Hollenberg M. D. Membrane receptors and hormone action. Adv Protein Chem. 1976;30:251–451. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist F. W. The meaning of Scatchard and Hill plots. Methods Enzymol. 1978;48:270–299. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)48015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P. Cooperative properties of hormone receptors in cell membranes. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(2):241–258. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. Physiological differentiation of viridans streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):184–201. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.184-201.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Moreno E. C., Etherden I. Concentration-dependent multiple binding sites on saliva-treated hydroxyapatite for Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):280–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.280-289.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Moreno E. C., Spinell D. M. Model delineating the effects of a salivary pellicle on the adsorption of Streptococcus miteor onto hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1109–1112. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1109-1112.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Qureshi J. V. Selective binding of blood group-reactive salivary mucins by Streptococcus mutans and other oral organisms. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.665-671.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H., Ingersoll L. Molecular basis for the different sucrose-dependent adherence properties of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):330–337. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.330-337.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G. Isolation of a protein-containing cell surface component from Streptococcus sanguis which affects its adherence to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.428-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Proportional distribution and relative adherence of Streptococcus miteor (mitis) on various surfaces in the human oral cavity. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):852–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.852-859.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., von Hippel P. H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Reynolds H. S., Genco R. J. Characterization of tufted streptococci isolated from the "corn cob" configuration of human dental plaque. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):235–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.235-245.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G., Staat R. H., Arnold R. R. Positive coooperativity in the binding of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):157–165. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.157-165.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J., Jontell M., Krasse B. Effect of macromolecules on adherence of Streptococcus mutans. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;Suppl 24:173–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik D., Kraus F. W., Henshaw L. C. In vitro attachment of streptococci to the tooth surface. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):794–800. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.794-800.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D. Mathematics of hormone-receptor interaction. I. Basic principles. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1973;36(0):289–326. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3237-4_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Appelbaum B., Campbell L. K., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Chemostat studies of the effect of environmental control on Streptococcus sanguis adherence to hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.64-70.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rölla G., Iversen O. J., Bonesvoll P. Lipoteichoic acid - the key to the adhesiveness of sucrose grown Streptococcus mutans. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:607–617. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rölla G., Robrish S. A., Bowen W. H. Interaction of hydroxyapatite and protein-coated hydroxyapatite with Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Oct;85B(5):341–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg I. H. Scatchard plots. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):312–313. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4530.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shklair I. L., Keene H. J. A biochemical scheme for the separation of the five varieties of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Nov;19(11):1079–1081. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staat R. H., Doyle R. J., Langley S. D., Suddick R. P. Modification of in vitro adherence of Streptococcus mutans by plant lectins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:639–647. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staat R. H., Langley S. D., Doyle R. J. Streptococcus mutans adherence: presumptive evidence for protein-mediated attachment followed by glucan-dependent cellular accumulation. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):675–681. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.675-681.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terleckyj B., Willett N. P., Shockman G. D. Growth of several cariogenic strains of oral streptococci in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):649–655. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.649-655.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinanoff N., Tanzer J. M., Freedman M. L. In vitro colonization of Streptococcus mutans on enamel. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1010-1019.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R. A., Gollan J. L., Ockner R. K. Scatchard plots. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):313–313. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4530.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. T., Clark W. B., Birdsell D. C. Adherence of Actinomyces viscosus T14V and T14AV to hydroxyapatite surfaces in vitro and human teeth in vivo. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1066–1074. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1066-1074.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. T., Clark W. B. Fibril-mediated adherence of Actinomyces viscosus to saliva-treated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):577–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.577-584.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


