Abstract
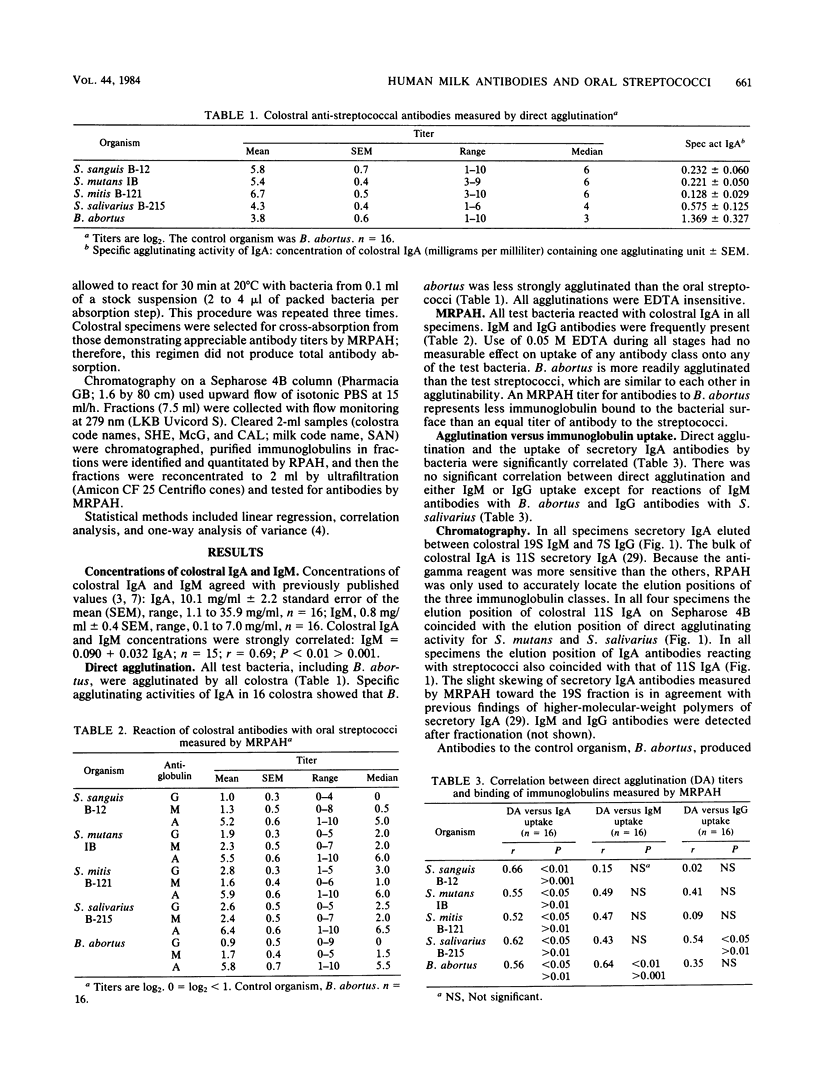
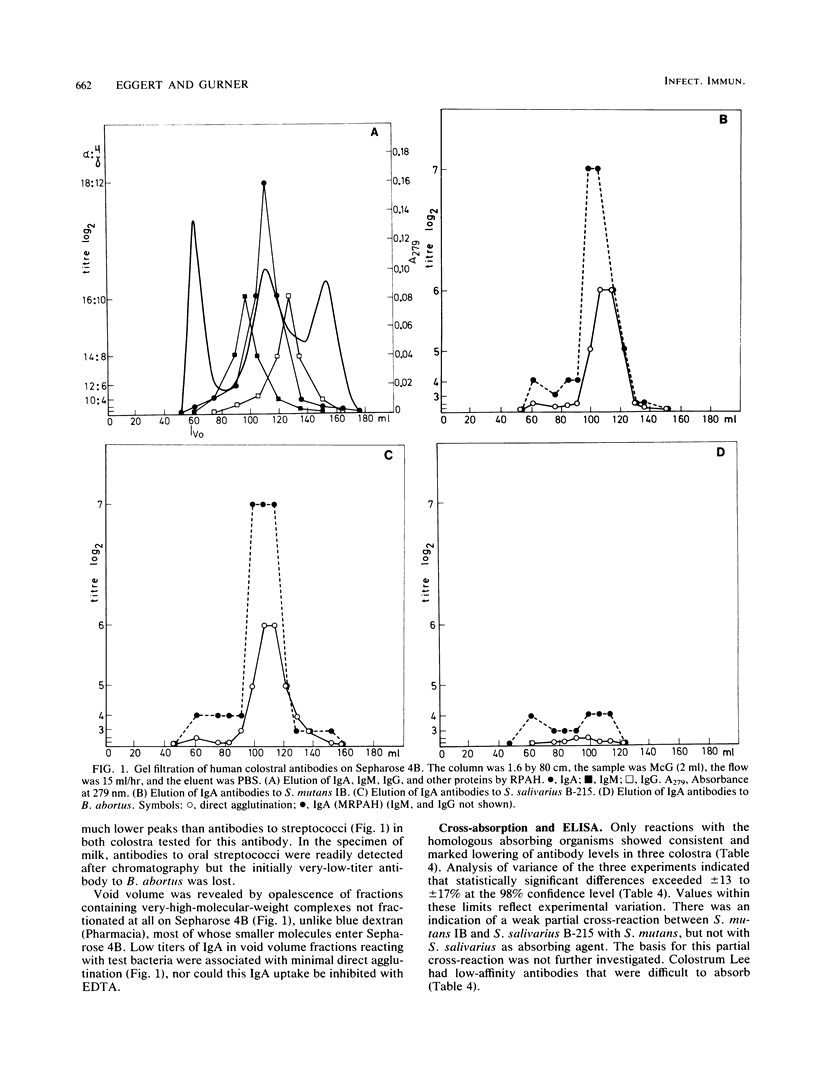
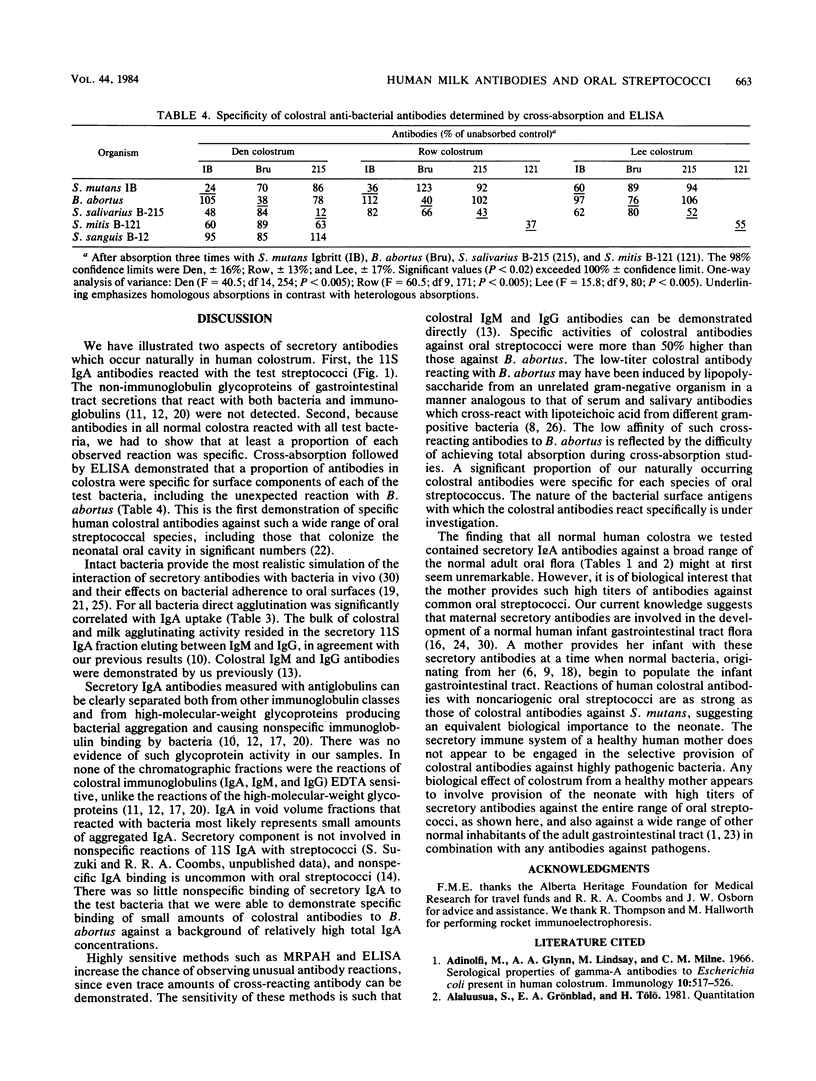
Colostrum or early breast milk or both from each of 16 healthy women contained agglutinating antibodies for all normal streptococcal inhabitants of the human oral cavity (S. mutans, S. sanguis, S. mitis, and S. salivarius), including those which colonize the neonatal oral cavity in significant numbers. Agglutination correlated with the amount of immunoglobulin A (IgA) binding to bacterial surfaces as measured by mixed reverse passive antiglobulin hemagglutination. Surprisingly, colostral IgA agglutinated our control organism, Brucella abortus. Low levels of colostral or milk IgM and IgG antibodies also reacted with all of the test bacteria. Absorption studies with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay showed that a proportion of antibodies in colostrum and early milk is specific for each of the different oral streptococci. Fractionation on Sepharose 4B indicated that 11S secretory IgA is the predominant form of colostral and milk antibody for all of the test bacteria, including B. abortus. No evidence was found that reactions other than antigen-antibody reactions resulted in binding of colostral immunoglobulins by any of the test bacteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi M., Glynn A. A., Lindsay M., Milne C. M. Serological properties of gamma-A antibodies to Escherichia coli present in human colostrum. Immunology. 1966 Jun;10(6):517–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammann A. J., Stiehm E. R. Immune globulin levels in colostrum and breast milk, and serum from formula- and breast-fed newborns. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Aug-Sep;122(4):1098–1100. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. R., Mestecky J., McGhee J. R. Naturally occurring secretory immunoglobulin A antibodies to Streptococcus mutans in human colostrum and saliva. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):355–362. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.355-362.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz R. J., Jordan H. V., White G. The early establishment of Streptococcus mutans in the mouths of infants. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Mar;20(3):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Fjellanger I., Gjeruldsen S. T. Human secretory immunoglobulins. I. Salivary secretions from individuals with normal or low levels of serum immunoglobulins. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1970;12:3–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Carlén A., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Examination of parotid saliva for antibodies reacting with Streptococcus mutans, lipoteichoic acid and peptidoglycan by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1979 Jun;87C(3):251–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Grahnén H., Jonsson G., Wikner S. Establishment of Streptococcus sanguis in the mouths of infants. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Dec;15(12):1143–1148. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggert F. M. Bacterial aggregating and conglutinin-like factors in human saliva and amniotic fluid: investigations of molecular size [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Feb;7(1):193–194. doi: 10.1042/bst0070193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggert F. M., Edebo L. B., Gurner B. W., Coombs R. R. A simplified procedure for measuring the class of anti-bacterial antibodies by mixed reverse passive antiglobulin haemagglutination (MRPAH). J Immunol Methods. 1979;26(2):125–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggert F. M. The nature of secretory agglutinins and aggregating factors. I. Secretory conglutinin-like factor, secretory bacterial aggregating factors and secretory IgA antibody in human saliva and amniotic fluid. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;61(2):192–202. doi: 10.1159/000232433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggert F. M. The nature of secretory agglutinins and aggregating factors. IV. Complexing between non-mucin glycoproteins, immunoglobulins and mucins in human saliva and amniotic fluid. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980;62(1):46–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson D., Bratthall D., Björck L., Myhre E., Kronvall G. Interactions between human serum proteins and oral streptococci reveal occurrence of receptors for aggregated beta 2-microglobulin. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):279–283. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.279-283.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freimer E. H., Raeder R., Feinstein A., Herbert J., Gurner B. W., Coombs R. R. Detection of protein A-like substances on haemolytic streptococci prior to use in mixed reverse passive antiglobulin haemagglutination (MRPAH). J Immunol Methods. 1979;31(3-4):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I., Gibbons R. J., Spinell D. M. Characteristics of some high molecular weight constituents with bacterial aggregating activity from whole saliva and dental plaque. Caries Res. 1971;5(2):111–123. doi: 10.1159/000259739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelstrup J., Richmond S., West C., Gibbons R. J. Fingerprinting human oral streptococci by bacteriocin production and sensitivity. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Dec;15(12):1109–1116. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Roland K., Mestecky J. Interference of secretory immunoglobulin A with sorption of oral bacteria to hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):942–951. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.942-951.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thomson R. A. Immunoconglutinins in human saliva--a group of unusual IgA antibodies. Immunology. 1970 Feb;18(2):157–169. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G., Germaine G. R. Effect of bacterial aggregation on the adherence of oral streptococci to hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):935–941. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.935-941.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY C., SNYDER M. L., PARKER R. B. THE INDIGENOUS ORAL FLORA OF MAN. I. THE NEWBORN TO THE 1-YEAR-OLD INFANT. Arch Oral Biol. 1965 Jan-Feb;10:61–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(65)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland D. B., Samson R. R., Parkin D. M., Shearman D. J. Bacterial agglutination studies with secretory IgA prepared from human gastrointestinal secretions and colostrum. Gut. 1972 Jun;13(6):450–458. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.6.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy L. K., Bhogal B. S., Mackenzie T. Duration of anti-adhesive and bactericidal activities of milk from vaccinated sows on Escherichia coli O149 in the digestive tract of piglets during the nursing period. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Nov;27(3):289–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Malamud D., Appelbaum B., Golub E. Characteristic differences between saliva-dependent aggregation and adhesion of streptococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):86–90. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.86-90.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Beighton D. Specificity of natural antibodies reactive with Streptococcus mutans in monkeys. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):741–744. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.741-744.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. L., Merrett T. G., Ishizaka K., Thornley M. J., Coombs R. R. Comparison of reverse passive antiglobulin haemagglutination with double antibody radioimmunoassay for estimation of total human serum IgE. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 May;48(2):417–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T. B., Jr, TAN E. M., SOLOMON A., PRENDERGAST R. A. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IMMUNE SYSTEM COMMON TO CERTAIN EXTERNAL SECRETIONS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:101–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatevossian A., Newbrun E. Electrophoretic and immunoelectrophoretic studies of proteins in the aqueous phase of human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(4):275–280. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


