Abstract
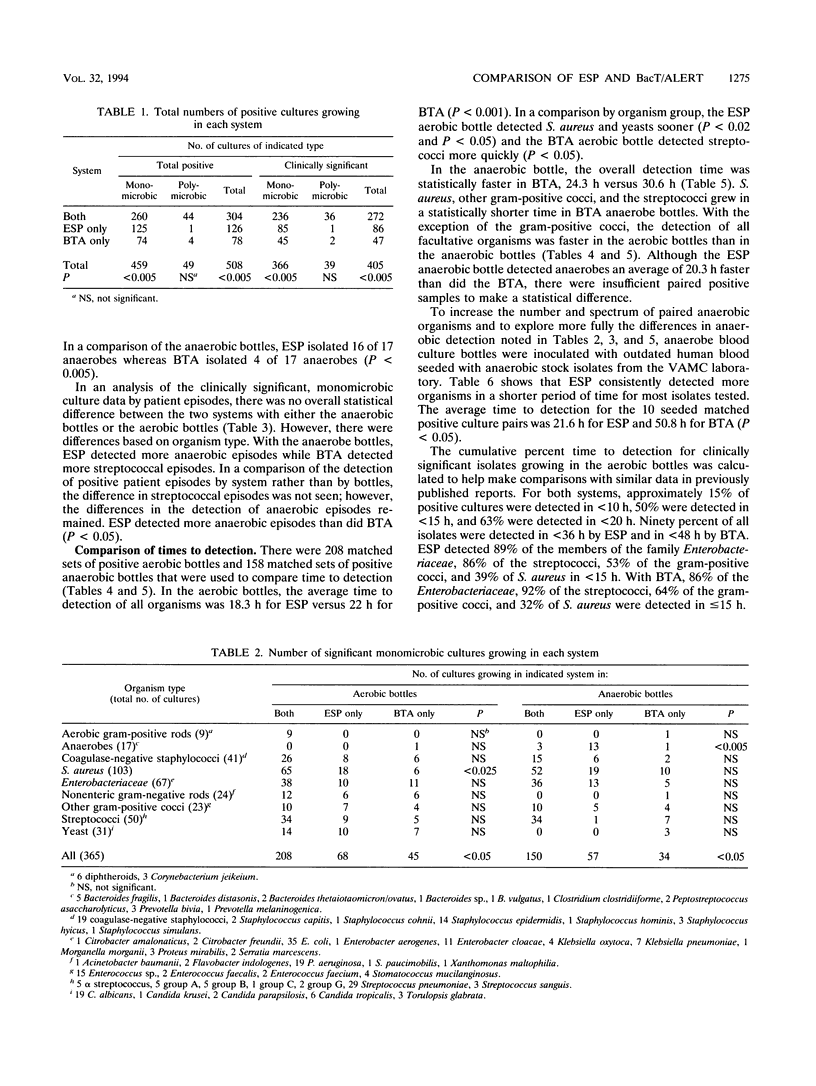
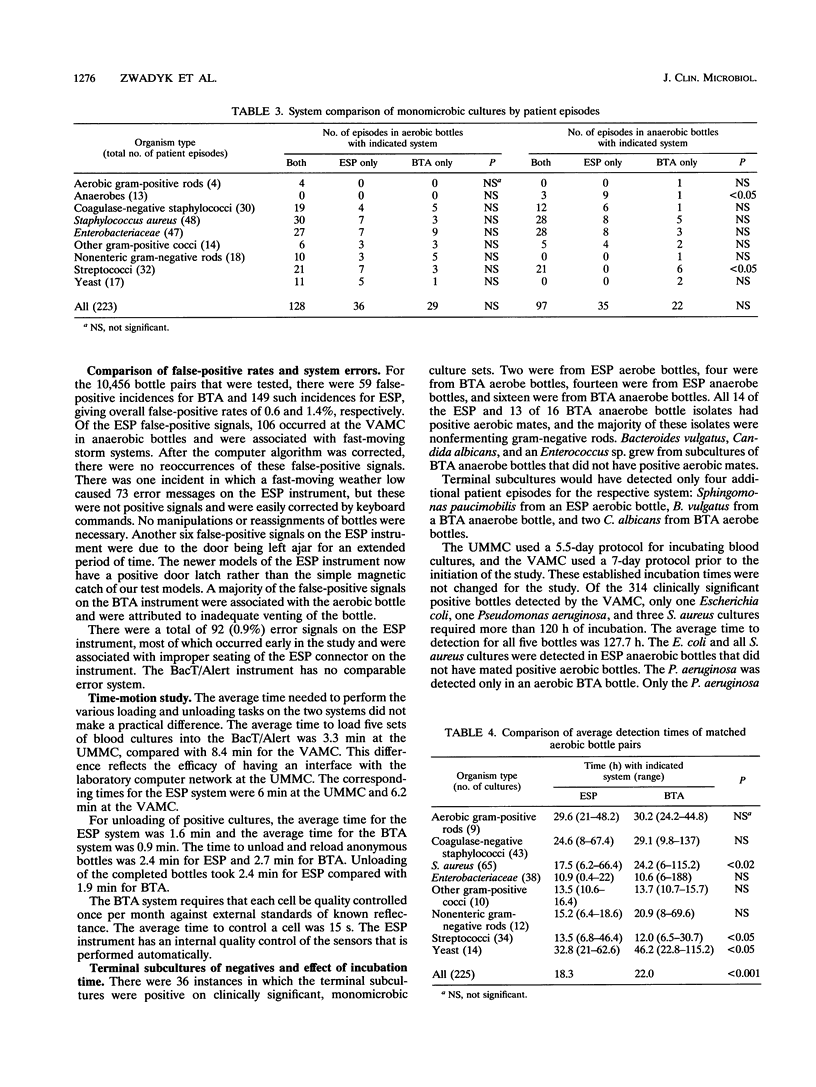
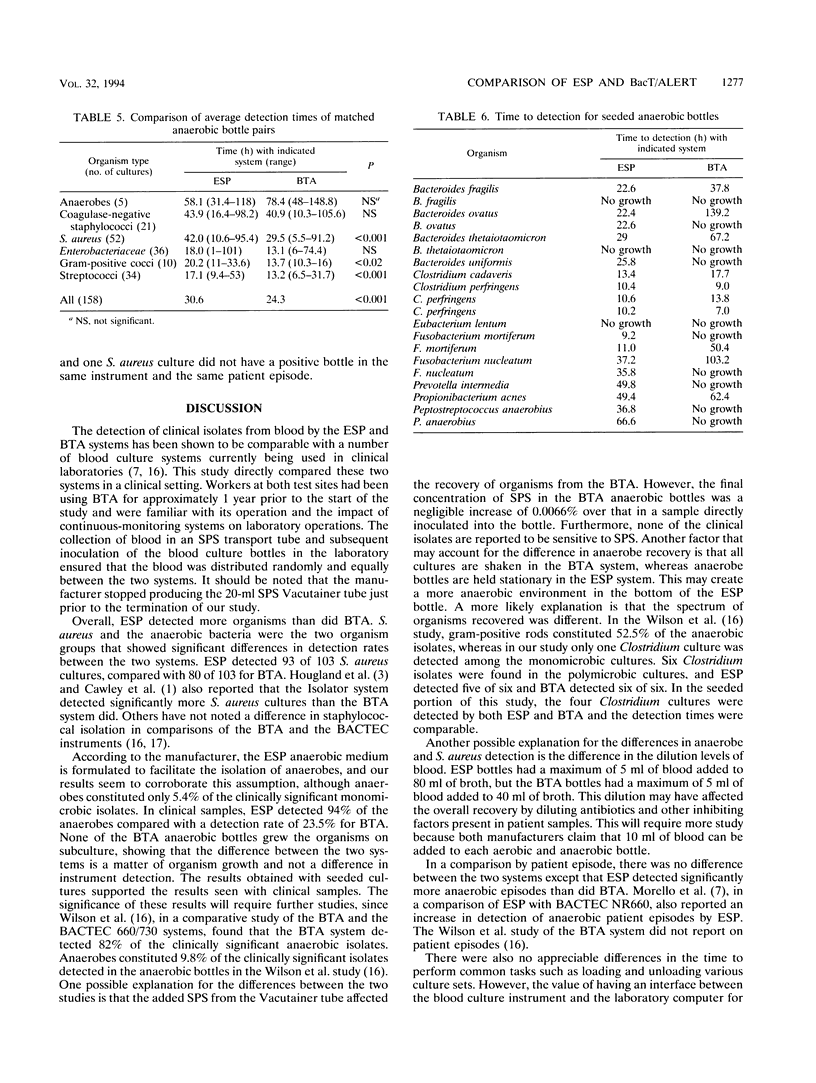
The Difco ESP and Organon Teknika BacT/Alert (BTA) systems were evaluated in a clinical study of 5,421 aerobic and 5,035 anaerobic blood cultures. Of 405 clinically significant positive cultures evaluated, 272 grew in both systems, 86 grew in ESP only, and 47 grew in BTA only (P < 0.005). Of 320 organisms detected in aerobic bottles, 208 grew in both systems, 68 grew in ESP only and 45 grew in BTA only (P < 0.05), with Staphylococcus aureus the only organism showing a statistically significant difference. The ESP anaerobic bottle also detected more anaerobes (16 of 17 versus 4 of 17, P < 0.005) and more organisms overall (57 versus 34, P < 0.05). However, with the exception of patients with anaerobic bacteremia (12 of 13 for ESP and 4 of 13 for BTA, P < 0.05), there was no statistical difference in the detection of patient episodes. Average detection time of matched aerobic bottles was 18.3 h for ESP and 22.0 h for BTA (P < 0.001). For matched pairs of anaerobic bottles, the average detection time was faster in the BTA bottles (P < 0.001), because of the growth of facultative organisms. To explore the differences in anaerobic detection more fully, 20 sets of anaerobic bottles were seeded with 12 anaerobic species mixed with human blood. ESP grew more organisms (17 of 20 versus 10 of 20, P < 0.025), and the average time to detection for the 10 paired positive cultures was 21.6 h for ESP and 50.8 h for BTA (P < 0.05). Times for loading and unloading bottles were similar for both systems.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hardy D. J., Hulbert B. B., Migneault P. C. Time to detection of positive BacT/Alert blood cultures and lack of need for routine subculture of 5- to 7-day negative cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2743–2745. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2743-2745.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisher K. K., Whyburn D. R., Koepnick F. E. Comparison of the BacT/Alert pediatric blood culture system, Pedi-BacT, with conventional culture using the 20-milliliter Becton-Dickinson supplemented peptone broth tube. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):793–797. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.793-797.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morello J. A., Leitch C., Nitz S., Dyke J. W., Andruszewski M., Maier G., Landau W., Beard M. A. Detection of bacteremia by Difco ESP blood culture system. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Mar;32(3):811–818. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.3.811-818.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe T. C., Wilson M. L., Turner J. E., DiGuiseppi J. L., Willert M., Mirrett S., Reller L. B. BacT/Alert: an automated colorimetric microbial detection system. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1608–1612. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1608-1612.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasilauskas B., Gay R., Zwadyk P., Pfaller M., Koontz F. Multicenter comparison of MicroScan and BACTEC blood culture systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2355–2358. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2355-2358.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. L., Mirrett S., Reller L. B., Weinstein M. P., Reimer L. G. Recovery of clinically important microorganisms from the BacT/Alert blood culture system does not require testing for seven days. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;16(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(93)90127-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. L., Weinstein M. P., Reimer L. G., Mirrett S., Reller L. B. Controlled comparison of the BacT/Alert and BACTEC 660/730 nonradiometric blood culture systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):323–329. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.323-329.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


