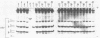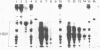Abstract
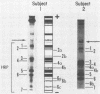
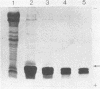
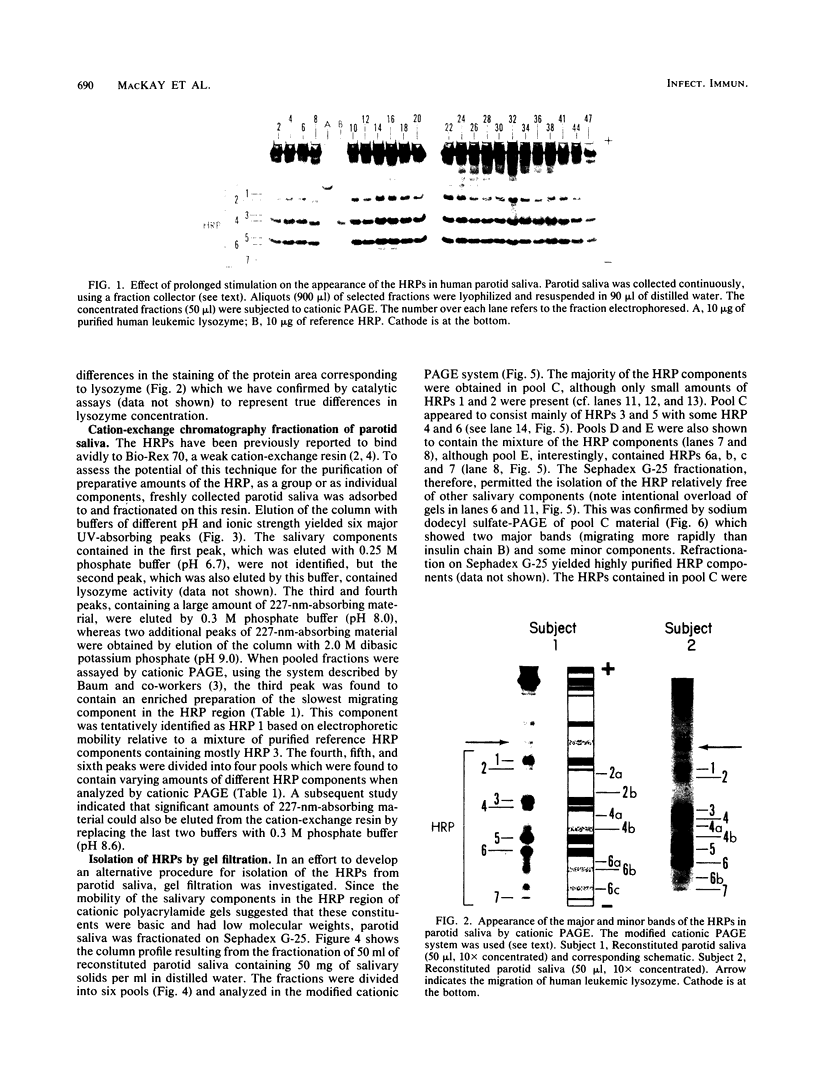
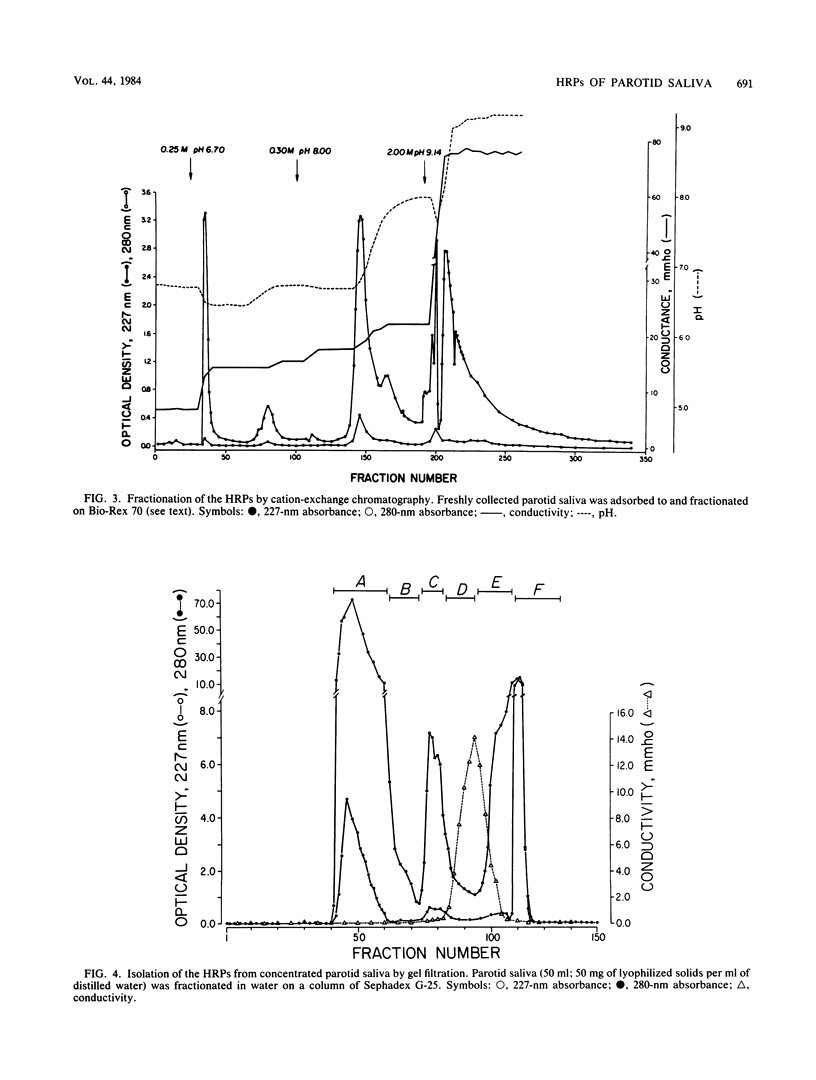
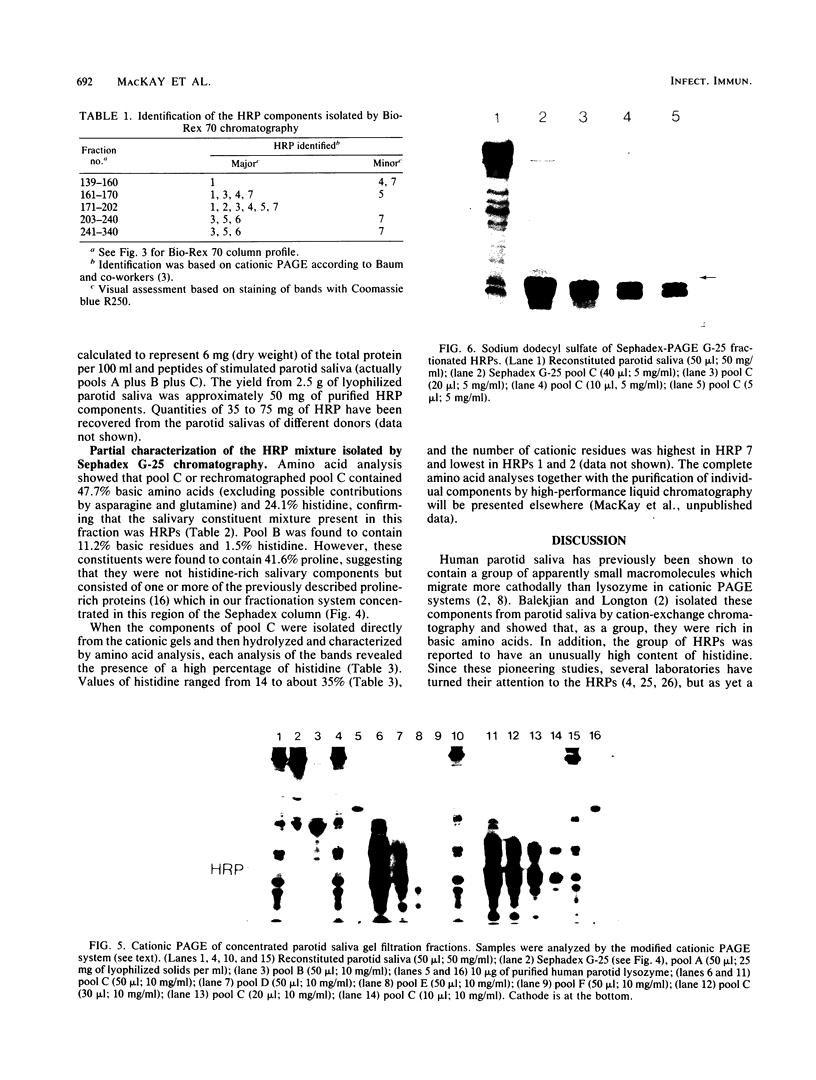
Freshly collected parotid saliva collected from human donors were shown by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to continuously secrete a group of low-molecular-weight cationic polypeptides. Up to 14 bands could be identified by Coomassie blue staining, and all bands migrated more rapidly than purified human leukemic lysozyme in cationic polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. These peptides could be isolated as a group relatively free of other salivary components and recovered in high yields from concentrated parotid saliva by Sephadex G-25 chromatography. In sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis, the histidine-rich polypeptide bands appeared as just two bands migrating at the tracking dye and ahead of insulin chain B. Amino acid analysis of the mixture revealed an average content of at least 48% cationic residues, of which half were histidine. When stained bands were eluted from electrophoretic gels, hydrolyzed, and subjected to amino acid analyses, they were found to be enriched in histidine. There was also a correlation of the electrophoretic mobility with the content of basic amino acids. Sephadex G-25 chromatography is a convenient, simple method for preparing milligram quantities of the histidine-rich polypeptides for chemical and biochemical studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azen E. A. Genetic protein polymorphisms in human saliva: an interpretive review. Biochem Genet. 1978 Feb;16(1-2):79–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00484386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balekjian A. Y., Longton R. W. Histones isolated from human parotid fluid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):676–682. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum B. J., Bird J. L., Longton R. W. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of human salivary histidine-rich-polypeptides. J Dent Res. 1977 Sep;56(9):1115–1118. doi: 10.1177/00220345770560091801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A., Connell G. E. Purification and partial characterization of four proteins from human parotid saliva. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):455–464. doi: 10.1042/bj1230455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. Salivary proline-rich proteins. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Jun 11;45(2):83–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00223503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. The binding of calcium to a salivary phosphoprotein, protein C, and comparison with calcium binding to protein A, a related salivary phosphoprotein. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):241–245. doi: 10.1042/bj1630241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla C. A., Stringham R. M., Jr Electrophoresis of human salivary secretions at acid pH. J Chromatogr. 1970 Jul 29;50(2):345–348. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)97959-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. R., Gracy R. W. Extraction of proteins and peptides from Coomassie Blue-stained sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 15;96(2):352–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90592-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I. Fractionation of human parotid salivary proteins and the isolation of an histidine-rich acidic peptide which shows high affinity for hydroxyapatite surfaces. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Sep;20(9):553–558. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. I. The isolation from human parotid saliva of a tyrosine-rich acidic peptide which exhibits high affinity for hydroxyapatite surfaces. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Dec;18(12):1531–1541. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isemura S., Saitoh E., Sanada K. The amino acid sequence of a salivary proline-rich peptide, P-C, and its relation to a salivary proline-rich phosphoprotein, protein C. J Biochem. 1980 Apr;87(4):1071–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman D. L., Keller P. J. The basic proline-rich proteins in human parotid saliva from a single subject. Arch Oral Biol. 1979;24(4):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(79)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu S., Ikeda K., Hamaguchi K., Miwa S., Nakashima K. Binding of N-acetyl-chitotriose to human lysozyme. J Biochem. 1975 Aug;78(2):327–333. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Ellison S. A., Bahl O. P. The isolation from human parotid saliva and partial characterization of the protein core of a major parotid glycoprotein. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Jul;18(7):827–837. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. J., Weill J. C., Ellison S. A. The isolation and analysis of a glycoprotein from parotid saliva. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 12;188(1):165–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Keller P. J. The isolation of some basic proline-rich proteins from human parotid saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1977;22(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(77)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay B. J., Denepitiya L., Iacono V. J., Krost S. B., Pollock J. J. Growth-inhibitory and bactericidal effects of human parotid salivary histidine-rich polypeptides on Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):695–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.695-701.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay B. J., Iacono V. J., Zuckerman J. M., Osserman E. F., Pollock J. J. Quantitative recovery, selective removal and one-step purification of human parotid and leukemic lysozymes by immunoadsorption. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):93–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim F. G., Hay D. I., Franzblau C. Proline-rich proteins from human parotid saliva. I. Isolation and partial characterization. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov;10(23):4233–4238. doi: 10.1021/bi00799a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters E. H., Azen E. A. Isolation and partial characterization of human parotid basic proteins. Biochem Genet. 1977 Oct;15(9-10):925–946. doi: 10.1007/BF00483989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters E. H., Goodfriend T., Azen E. A. Human Pb, human post-Pb, and nonhuman primate Pb proteins: immunological and biochemical relationships. Biochem Genet. 1977 Oct;15(9-10):947–962. doi: 10.1007/BF00483990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. J., Denepitiya L., MacKay B. J., Iacono V. J. Fungistatic and fungicidal activity of human parotid salivary histidine-rich polypeptides on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):702–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.702-707.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner A. H., Nemes P., Bucholtz C. The use of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G250 perchloric acid solution for staining in electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 Apr;64(2):509–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90461-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger D. H., Hay D. I. Complete covalent structure of statherin, a tyrosine-rich acidic peptide which inhibits calcium phosphate precipitation from human parotid saliva. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1689–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. S., Bennick A. The primary structure of a salivary calcium-binding proline-rich phosphoprotein (protein C), a possible precursor of a related salivary protein A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5943–5948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. S., Hofmann T., Bennick A. The complete primary structure of a proline-rich phosphoprotein from human saliva. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4800–4808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]