Abstract
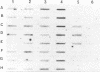
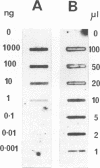
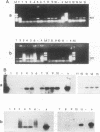
A molecular method for the detection of Pseudomonas pseudomallei was developed on the basis of the differences in the 23S rRNA sequences of related species of the genus Pseudomonas. An 18-base oligonucleotide probe, designed following partial sequencing of 23s ribosomal DNA (rDNA), was used for the identification and detection of P. pseudomallei either by hybridization or by direct PCR. Optimal detection was obtained by hybridization of the probe with PCR-amplified rDNA rather than with total genomic DNA or colony blots. One nanogram of template DNA amplified in a PCR mixture containing 14% glycerol could be detected in slot blots hybridized with the digoxigenin-labelled probe and the lumigen PPD detection system. Amplified rDNA sequences from 41 P. pseudomallei strains of various origins hybridized with the probe. The probe also hybridized with three Pseudomonas mallei reference strains under conditions of high stringency but failed to hybridize with amplified rDNA sequences from other closely related Pseudomonas spp. PCR with a conserved primer and the 18-base oligonucleotide probe (direct PCR) specifically amplified P. pseudomallei and P. mallei. By using these methods, approximately 10(4) P. pseudomallei cells per ml could be detected in artificially inoculated blood samples and in blood dried on filter paper following Chelex extraction. The detection limit in blood was increased to 10(2) cells per ml by concentration of bacteria from 0.5 ml of blood or by a 24-h blood culture enrichment prior to PCR. Approximately 10(3) cells per ml were detected in seeded sputum samples. The detection times by direct PCR and indirect PCR and then probe hybridization were approximately 5 h and 24 h, respectively. These results indicate that amplification of conserved rDNA sequences by PCR directly or by hybridization with a probe to PCR fragments offers promise for the detection of P. pseudomallei and P. mallei.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashdown L. R. An improved screening technique for isolation of Pseudomonas pseudomallei from clinical specimens. Pathology. 1979 Apr;11(2):293–297. doi: 10.3109/00313027909061954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashdown L. R., Clarke S. G. Evaluation of Culture Techniques for Isolation of Pseudomonas pseudomallei from Soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):4011–4015. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.4011-4015.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashdown L. R. Rapid differentiation of Pseudomonas pseudomallei from Pseudomonas cepacia. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1992 May;14(5):203–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1992.tb00685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bej A. K., Steffan R. J., DiCesare J., Haff L., Atlas R. M. Detection of coliform bacteria in water by polymerase chain reaction and gene probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):307–314. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.307-314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck G. E., O'Hara L. C., Summersgill J. T. Rapid, simple method for treating clinical specimens containing Mycobacterium tuberculosis to remove DNA for polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1331–1334. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1331-1334.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaowagul W., White N. J., Dance D. A., Wattanagoon Y., Naigowit P., Davis T. M., Looareesuwan S., Pitakwatchara N. Melioidosis: a major cause of community-acquired septicemia in northeastern Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):890–899. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dance D. A. Melioidosis: the tip of the iceberg? Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dance D. A. Pseudomonas pseudomallei: danger in the paddy fields. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Jan-Feb;85(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90134-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN M., MOODY M. D., THOMASON B. M. Staining bacterial smears with fluorescent antibody. I. General methods for Malleomyces pseudomallei. J Bacteriol. 1956 Sep;72(3):357–361. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.3.357-361.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höpfl P., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H., Larsen N. The 23S ribosomal RNA higher-order structure of Pseudomonas cepacia and other prokaryotes. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 6;185(2):355–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. S., Uldum S. A., Søndergård-Andersen J., Vuust J., Lind K. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of Mycoplasma genitalium in clinical samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):46–50. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.46-50.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kain K. C., Lanar D. E. Determination of genetic variation within Plasmodium falciparum by using enzymatically amplified DNA from filter paper disks impregnated with whole blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1171–1174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1171-1174.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin P. A., Szotyori Z., Fromholc C., Almond N. Avoidance of PCR false positives [corrected]. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):201–201. doi: 10.1038/344201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leelarasamee A., Bovornkitti S. Melioidosis: review and update. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):413–425. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. E., Desmarchelier P. M. Molecular typing of Pseudomonas pseudomallei: restriction fragment length polymorphisms of rRNA genes. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):533–539. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.533-539.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy D. C., Nauman R. K., Paxton H. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1089–1093. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1089-1093.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morotomi M., Hoshina S., Green P., Neu H. C., LoGerfo P., Watanabe I., Mutai M., Weinstein I. B. Oligonucleotide probe for detection and identification of Campylobacter pylori. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2652–2655. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2652-2655.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph K. M., Parkinson A. J., Black C. M., Mayer L. W. Evaluation of polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Oct;31(10):2661–2666. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.10.2661-2666.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos A. R., De Miranda A. B., Sarno E. N., Suffys P. N., Degrave W. M. Use of PCR-mediated amplification of Mycobacterium leprae DNA in different types of clinical samples for the diagnosis of leprosy. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Oct;39(4):298–304. doi: 10.1099/00222615-39-4-298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toschka H. Y., Höpfl P., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7182–7182. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthiekanun V., Dance D., Chaowagul W., Suputtamongkol Y., Wattanagoon Y., White N. Blood culture techniques for the diagnosis of melioidosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;9(9):654–658. doi: 10.1007/BF01964266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabuuchi E., Kosako Y., Oyaizu H., Yano I., Hotta H., Hashimoto Y., Ezaki T., Arakawa M. Proposal of Burkholderia gen. nov. and transfer of seven species of the genus Pseudomonas homology group II to the new genus, with the type species Burkholderia cepacia (Palleroni and Holmes 1981) comb. nov. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(12):1251–1275. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb02129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lamballerie X., Zandotti C., Vignoli C., Bollet C., de Micco P. A one-step microbial DNA extraction method using "Chelex 100" suitable for gene amplification. Res Microbiol. 1992 Oct;143(8):785–790. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90107-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]