Abstract
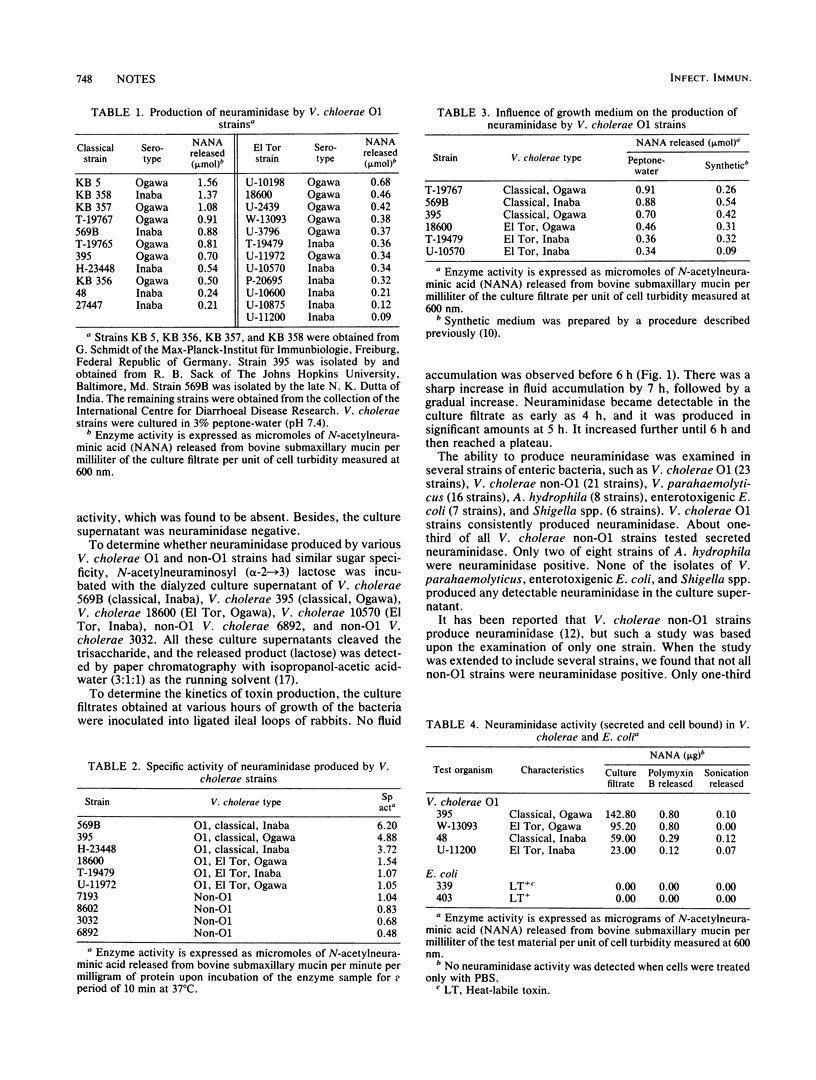
Vibrio cholerae O1 strains belonging to both biotypes (classical and El Tor) and both serotypes (Ogawa and Inaba) produced neuraminidase which was released rather than cell bound. Classical strains made more neuraminidase than did El Tor strains. About one-third of V. cholerae non-O1 strains and one-fourth of Aeromonas hydrophila strains were neuraminidase positive. Strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Shigella spp. did not produce detectable neuraminidase.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., FRENCH E. L., LIND P. E. Purification and properties of neuraminidase from Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Mar;24:409–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE S. N., CHATTERJE D. N. An experimental study of the mechanism of action of Vibriod cholerae on the intestinal mucous membrane. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):559–562. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Shigella dysenteriae 1 cytotoxin: periplasmic protein releasable by polymyxin B and osmotic shock. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):270–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.270-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R. Viral and bacterial neuraminidases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;59:35–74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65444-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Polymyxin B-Induced Release of Low-Molecular-Weight, Heat-Labile Enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1010–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1010-1017.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. Composition and immunochemical properties of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):382–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.382-389.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levner M. H., Urbano C., Rubin B. A. Lincomycin increases synthetic rate and periplasmic pool size for cholera toxin. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):441–447. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.441-447.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H. E. Occurrence of neuraminidase and acylneuraminate pyruvate lyase in a strain of vibrio falling into Heiberg's group II isolated from a patient with diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):430–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.430-433.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHRIVASTAVA D. L. ENZYMES IN VIBRIO CHOLERAE. Indian J Med Res. 1964 Aug;52:801–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinnaka Y., Carpenter C. C., Jr An enterotoxin produced by noncholera vibrios. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1972 Dec;131(6):403–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


