Abstract
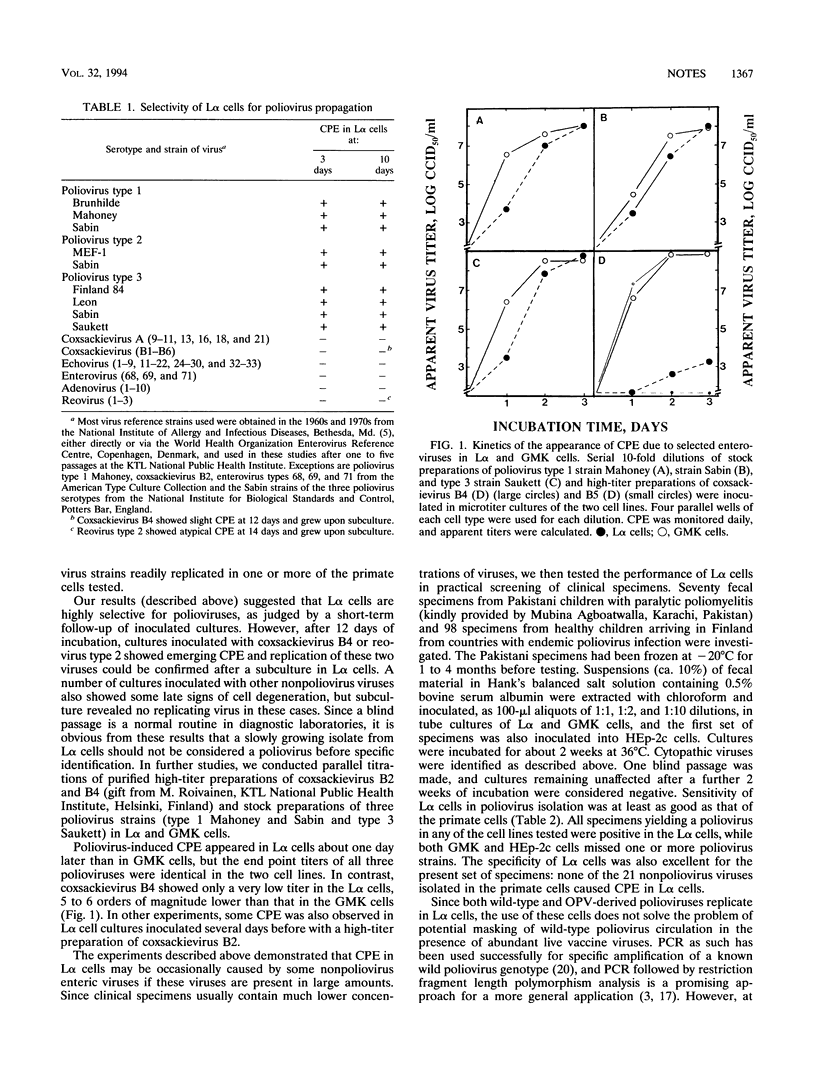
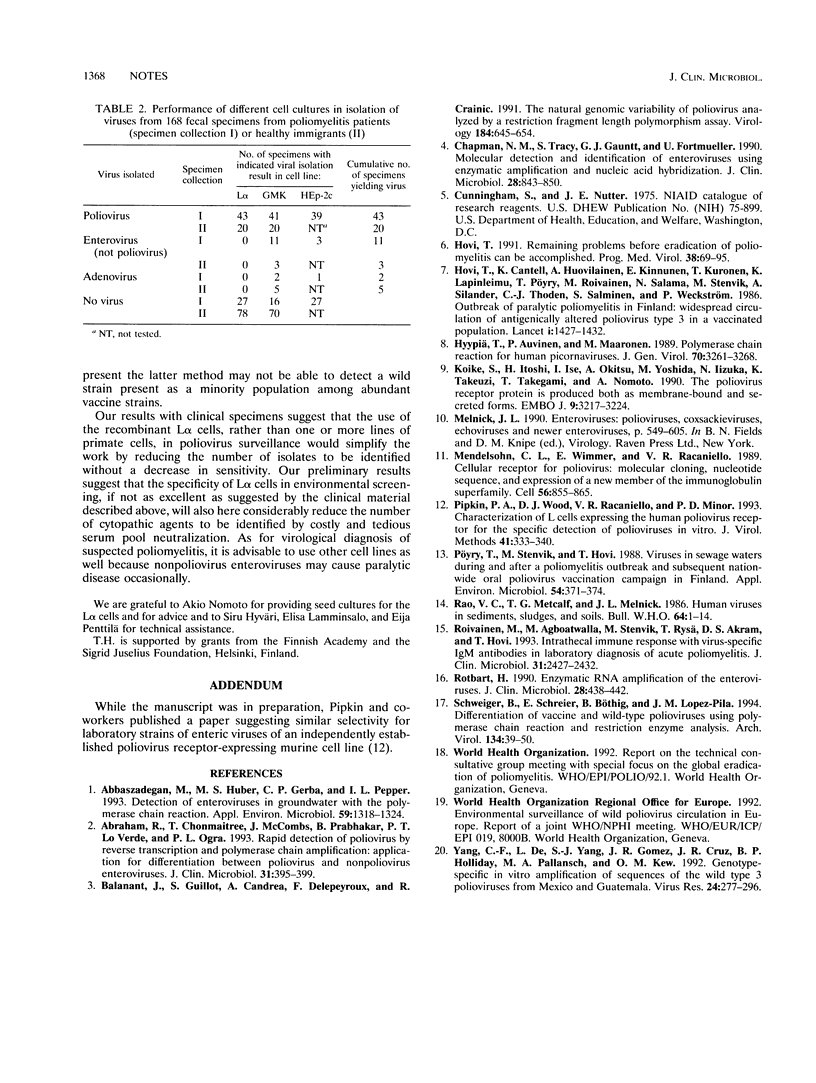
Sixty-eight laboratory strains representing 49 enterovirus, 10 adenovirus, and 3 reovirus serotypes were inoculated in a recombinant murine cell line expressing the human poliovirus receptor gene (L alpha cells). Only polioviruses caused cytopathic effect over a 10-day period. Likewise, only polioviruses were isolated, by use of L alpha cells, from 168 fecal specimens from children from developing countries. These results suggest that the recombinant L alpha cells can be used for selective isolation of poliovirus from clinical specimens.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbaszadegan M., Huber M. S., Gerba C. P., Pepper I. L. Detection of enteroviruses in groundwater with the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1318–1324. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1318-1324.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham R., Chonmaitree T., McCombs J., Prabhakar B., Lo Verde P. T., Ogra P. L. Rapid detection of poliovirus by reverse transcription and polymerase chain amplification: application for differentiation between poliovirus and nonpoliovirus enteroviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):395–399. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.395-399.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balanant J., Guillot S., Candrea A., Delpeyroux F., Crainic R. The natural genomic variability of poliovirus analyzed by a restriction fragment length polymorphism assay. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):645–654. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90434-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman N. M., Tracy S., Gauntt C. J., Fortmueller U. Molecular detection and identification of enteroviruses using enzymatic amplification and nucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.843-850.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T., Cantell K., Huovilainen A., Kinnunen E., Kuronen T., Lapinleimu K., Pöyry T., Roivainen M., Salama N., Stenvik M. Outbreak of paralytic poliomyelitis in Finland: widespread circulation of antigenically altered poliovirus type 3 in a vaccinated population. Lancet. 1986 Jun 21;1(8495):1427–1432. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91566-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T. Remaining problems before eradication of poliomyelitis can be accomplished. Prog Med Virol. 1991;38:69–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Auvinen P., Maaronen M. Polymerase chain reaction for human picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3261–3268. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Horie H., Ise I., Okitsu A., Yoshida M., Iizuka N., Takeuchi K., Takegami T., Nomoto A. The poliovirus receptor protein is produced both as membrane-bound and secreted forms. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3217–3224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipkin P. A., Wood D. J., Racaniello V. R., Minor P. D. Characterisation of L cells expressing the human poliovirus receptor for the specific detection of polioviruses in vitro. J Virol Methods. 1993 Mar;41(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(93)90022-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöyry T., Stenvik M., Hovi T. Viruses in sewage waters during and after a poliomyelitis outbreak and subsequent nationwide oral poliovirus vaccination campaign in Finland. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):371–374. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.371-374.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. C., Metcalf T. G., Melnick J. L. Human viruses in sediments, sludges, and soils. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64(1):1–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roivainen M., Agboatwalla M., Stenvik M., Rysä T., Akram D. S., Hovi T. Intrathecal immune response and virus-specific immunoglobulin M antibodies in laboratory diagnosis of acute poliomyelitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2427–2432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2427-2432.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotbart H. A. Enzymatic RNA amplification of the enteroviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):438–442. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.438-442.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger B., Schreier E., Böthig B., López-Pila J. M. Differentiation of vaccine and wild-type polioviruses using polymerase chain reaction and restriction enzyme analysis. Arch Virol. 1994;134(1-2):39–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01379105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. F., De L., Yang S. J., Ruiz Gómez J., Cruz J. R., Holloway B. P., Pallansch M. A., Kew O. M. Genotype-specific in vitro amplification of sequences of the wild type 3 polioviruses from Mexico and Guatemala. Virus Res. 1992 Aug;24(3):277–296. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90124-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


