Abstract
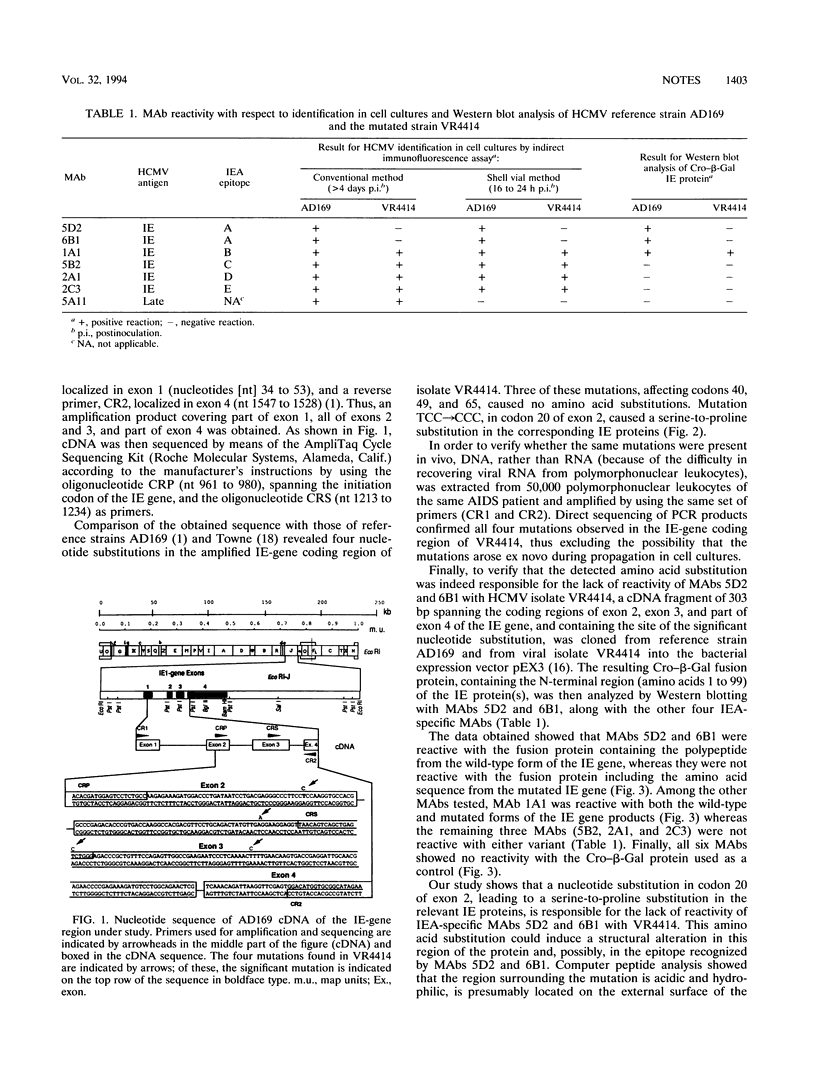
In an AIDS patient with a disseminated human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection, presence of HCMV in blood was repeatedly excluded by the shell vial culture method with the HCMV immediate-early (IE) antigen-specific monoclonal antibody (MAb) 5D2 currently employed for rapid HCMV identification, whereas it was repeatedly confirmed by all other assays (conventional virus isolation from blood, antigenemia, and DNAemia). Sequence analysis of the HCMV strain revealed a point mutation in exon 2 of the IE gene, which led to a serine-to-proline substitution at position 20 of the corresponding protein. Cloning and expression of a region of the IE gene containing the mutation showed that this was responsible for the lack of reactivity of MAb 5D2. A pool of IE antigen-reactive MAbs instead of a single MAb must be used for rapid HCMV identification to detect all viral strains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akrigg A., Wilkinson G. W., Oram J. D. The structure of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1985 Mar;2(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. W., Scott K. M. Rapid quantitation of cytomegalovirus and assay of neutralizing antibody by using monoclonal antibody to the major immediate-early viral protein. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):504–507. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.504-507.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L. Cytomegalovirus infection in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):449–456. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Baldanti F., Sarasini A., Furione M., Percivalle E., Revello M. G., Zipeto D., Zella D. Effect of foscarnet induction treatment on quantitation of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) DNA in peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes and aqueous humor of AIDS patients with HCMV retinitis. The Italian Foscarnet Study Group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Jan;38(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Revello M. G., Percivalle E., Morini F. Comparison of different immunostaining techniques and monoclonal antibodies to the lower matrix phosphoprotein (pp65) for optimal quantitation of human cytomegalovirus antigenemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1232–1237. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1232-1237.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Revello M. G., Percivalle E., Zavattoni M., Parea M., Battaglia M. Quantification of human cytomegalovirus viremia by using monoclonal antibodies to different viral proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2681-2688.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Zipeto D., Percivalle E., Parea M., Revello M. G., Maccario R., Peri G., Milanesi G. Human cytomegalovirus infection of the major leukocyte subpopulations and evidence for initial viral replication in polymorphonuclear leukocytes from viremic patients. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1236–1244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleaves C. A., Smith T. F., Shuster E. A., Pearson G. R. Rapid detection of cytomegalovirus in MRC-5 cells inoculated with urine specimens by using low-speed centrifugation and monoclonal antibody to an early antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):917–919. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.917-919.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazeron M. C., Jahn G., Plachter B. Monoclonal antibody E-13 (M-810) to human cytomegalovirus recognizes an epitope encoded by exon 2 of the major immediate early gene. J Gen Virol. 1992 Oct;73(Pt 10):2699–2703. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-10-2699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plachter B., Britt W., Vornhagen R., Stamminger T., Jahn G. Analysis of proteins encoded by IE regions 1 and 2 of human cytomegalovirus using monoclonal antibodies generated against recombinant antigens. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):642–652. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popow-Kraupp T., Kunz C. Detection of cytomegalovirus in clinical specimens by virus isolation and by a monoclonal antibody against the early nuclear antigen. J Med Virol. 1988 Mar;24(3):275–282. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890240305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. P., Schrier R. D., Oldstone M. B. Cytomegalovirus infects human lymphocytes and monocytes: virus expression is restricted to immediate-early gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6134–6138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster E. A., Beneke J. S., Tegtmeier G. E., Pearson G. R., Gleaves C. A., Wold A. D., Smith T. F. Monoclonal antibody for rapid laboratory detection of cytomegalovirus infections: characterization and diagnostic application. Mayo Clin Proc. 1985 Sep;60(9):577–585. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60979-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Stinski M. F. Autoregulation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):676–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.676-682.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.665-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]