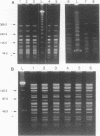
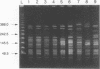
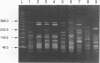
Abstract
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) was performed on 180 isolates of Vibrio cholerae serogroup O1 representing 6 different multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MEE) types and 27 rRNA restriction fragment length polymorphism types (ribotypes). Isolates were digested with the restriction enzyme NotI and were separated into 63 patterns on the basis of differences in band arrangements. In general, strains which were different by MEE or ribotyping also had different PGFE patterns. PFGE identified individual strains within a single MEE type or ribotype; isolates with one PFGE pattern were less frequently distinguished by ribotyping. All V. cholerae O1 isolates tested from the Latin American epidemic were indistinguishable by their MEE, ribotype, or PFGE patterns. PFGE could further distinguish strains of this same ribotype isolated in Africa, Europe, the South Pacific, or Southeast Asia. Although both MEE and PFGE could identify the strain from the Latin American epidemic, PFGE was more rapid and less labor intensive. PFGE also distinguished nontoxigenic isolates endemic to the U.S. Gulf Coast from unrelated nontoxigenic isolates. In the present study PFGE was more discriminating than other previously described subtyping assays for V. cholerae O1 and appears to be a useful epidemiologic tool.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida R. J., Cameron D. N., Cook W. L., Wachsmuth I. K. Vibriophage VcA-3 as an epidemic strain marker for the U.S. Gulf Coast Vibrio cholerae O1 clone. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):300–304. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.300-304.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbeit R. D., Arthur M., Dunn R., Kim C., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Resolution of recent evolutionary divergence among Escherichia coli from related lineages: the application of pulsed field electrophoresis to molecular epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):230–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. J., Blake P. A. Epidemiological usefulness of changes in hemolytic activity of Vibrio cholerae biotype El Tor during the seventh pandemic. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):126–129. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.126-129.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Allegra D. T., Snyder J. D., Barrett T. J., McFarland L., Caraway C. T., Feeley J. C., Craig J. P., Lee J. V., Puhr N. D. Cholera--a possible endemic focus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 7;302(6):305–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002073020601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A. Epidemiology of cholera in the Americas. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1993 Sep;22(3):639–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F., Evins G. M., Cook W. L., Almeida R., Hargrett-Bean N., Wachsmuth K. Genetic diversity among toxigenic and nontoxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 isolated from the Western Hemisphere. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Aug;107(1):225–233. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. L., Wachsmuth K., Johnson S. R., Birkness K. A., Samadi A. R. Persistence of plasmids, cholera toxin genes, and prophage DNA in classical Vibrio cholerae O1. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):222–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.222-226.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePaola A., Capers G. M., Motes M. L., Olsvik O., Fields P. I., Wells J., Wachsmuth I. K., Cebula T. A., Koch W. H., Khambaty F. Isolation of Latin American epidemic strain of Vibrio cholerae O1 from US Gulf Coast. Lancet. 1992 Mar 7;339(8793):624–624. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90917-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmarchelier P. M., Senn C. R. A molecular epidemiological study of Vibrio cholerae in Australia. Med J Aust. 1989 Jun 5;150(11):631–634. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1989.tb136726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothues D., Tümmler B. New approaches in genome analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: application to the analysis of Pseudomonas species. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2763–2776. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Bradford H. B., Roberts N. C., Falkow S. Molecular epidemiology of Vibrio cholerae in the U.S. Gulf Coast. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):129–134. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.129-134.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klontz K. C., Tauxe R. V., Cook W. L., Riley W. H., Wachsmuth I. K. Cholera after the consumption of raw oysters. A case report. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Dec;107(6):846–848. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-6-846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy S. A., McPhearson R. M., Guarino A. M., Gaines J. L. Toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 and cargo ships entering Gulf of Mexico. Lancet. 1992 Mar 7;339(8793):624–625. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90918-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic T., Bopp C., Olsvik O., Wachsmuth K. Epidemiologic application of a standardized ribotype scheme for Vibrio cholerae O1. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2474–2482. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2474-2482.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroeher U. H., Karageorgos L. E., Morona R., Manning P. A. Serotype conversion in Vibrio cholerae O1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2566–2570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauxe R. V., Blake P. A. Epidemic cholera in Latin America. JAMA. 1992 Mar 11;267(10):1388–1390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. L., Tuttle J., Pramukul T., O'Brien K., Barrett T. J., Jolbitado B., Lim Y. L., Vugia D., Morris J. G., Jr, Tauxe R. V. An outbreak of cholera in Maryland associated with imported commercial frozen fresh coconut milk. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1330–1335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth I. K., Bopp C. A., Fields P. I., Carrillo C. Difference between toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 from South America and US gulf coast. Lancet. 1991 May 4;337(8749):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91744-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth I. K., Evins G. M., Fields P. I., Olsvik O., Popovic T., Bopp C. A., Wells J. G., Carrillo C., Blake P. A. The molecular epidemiology of cholera in Latin America. J Infect Dis. 1993 Mar;167(3):621–626. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.3.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan W., Chang N., Taylor D. E. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli genomic DNA and its epidemiologic application. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1068–1072. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Mazurek G. H., Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., Pang Y., Murphy D. T., Wallace R. J., Jr DNA polymorphisms in strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: a tool for epidemiology. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1551-1556.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]