Abstract
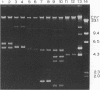
A set of 103 epidemiologically well-defined Acinetobacter baumannii isolates obtained from nine hospital outbreaks and 21 unrelated strains were characterized by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) of total genomic DNA digested with ApaI. Among outbreak strains, eight different patterns and five possible variants were identified by PFGE. Results were compared with those from traditional typing methods such as plasmid profile analysis, antimicrobial susceptibility, and biotyping. Plasmid analysis revealed six different and two related patterns; one outbreak strain lacked plasmids. A total of 16 of the 21 unrelated strains harbored plasmids and exhibited unique patterns. Epidemiologically unrelated strains were placed into only two biotypes and had similar antimicrobial susceptibility patterns but were clearly distinguished by PFGE. PFGE of A. baumannii chromosomal DNA yielded reproducible and easily readable results and showed excellent discriminatory power. However, plasmid profile analysis may provide a cost-effective first step in epidemiological typing of A. baumannii isolates obtained from well-defined hospital outbreaks.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allardet-Servent A., Bouziges N., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bourg G., Gouby A., Ramuz M. Use of low-frequency-cleavage restriction endonucleases for DNA analysis in epidemiological investigations of nosocomial bacterial infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2057–2061. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2057-2061.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P. Isolation of Acinetobacter from soil and water. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):39–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.39-42.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck-Sagué C. M., Jarvis W. R., Brook J. H., Culver D. H., Potts A., Gay E., Shotts B. W., Hill B., Anderson R. L., Weinstein M. P. Epidemic bacteremia due to Acinetobacter baumannii in five intensive care units. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Oct;132(4):723–733. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P. J., Grimont P. A. Identification and biotyping of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Sep-Oct;138(5):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P. J., Jeanjean S., Vieu J. F., Dijkshoorn L. Species, biotype, and bacteriophage type determinations compared with cell envelope protein profiles for typing Acinetobacter strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.170-176.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cefai C., Richards J., Gould F. K., McPeake P. An outbreak of Acinetobacter respiratory tract infection resulting from incomplete disinfection of ventilatory equipment. J Hosp Infect. 1990 Feb;15(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(90)90128-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkshoorn L., Aucken H. M., Gerner-Smidt P., Kaufmann M. E., Ursing J., Pitt T. L. Correlation of typing methods for Acinetobacter isolates from hospital outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):702–705. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.702-705.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagon J. Y., Chastre J., Hance A. J., Montravers P., Novara A., Gibert C. Nosocomial pneumonia in ventilated patients: a cohort study evaluating attributable mortality and hospital stay. Am J Med. 1993 Mar;94(3):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerner-Smidt P. Ribotyping of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter baumannii complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2680–2685. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2680-2685.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Moellering R. C., Jr, Kunz L. J. Infections with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus (Herellea vaginicola): clinical and laboratory studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1977 Mar;56(2):79–97. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197703000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouby A., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bouziges N., Bourg G., Mesnard R., Bouvet P. J. Use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for investigation of hospital outbreaks of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1588–1591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1588-1591.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gräser Y., Klare I., Halle E., Gantenberg R., Buchholz P., Jacobi H. D., Presber W., Schönian G. Epidemiological study of an Acinetobacter baumannii outbreak by using polymerase chain reaction fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2417–2420. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2417-2420.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartstein A. I., Morthland V. H., Rourke J. W., Jr, Freeman J., Garber S., Sykes R., Rashad A. L. Plasmid DNA fingerprinting of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus subspecies anitratus from intubated and mechanically ventilated patients. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1990 Oct;11(10):531–538. doi: 10.1086/646087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly-Guillou M. L., Bergogne-Berezin E., Vieu J. F. A study of the relationships between antibiotic resistance phenotypes, phage-typing and biotyping of 117 clinical isolates of Acinetobacter spp. J Hosp Infect. 1990 Jul;16(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(90)90048-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropec A., Hübner J., Daschner F. D. Comparison of three typing methods in hospital outbreaks of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus infection. J Hosp Infect. 1993 Feb;23(2):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(93)90017-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslow J. N., Mulligan M. E., Arbeit R. D. Molecular epidemiology: application of contemporary techniques to the typing of microorganisms. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;17(2):153–164. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. E., Vecchio J., Pantelick E. L., Farrel P., Mazon D., Zervos M. J., Hierholzer W. J., Jr Association of contaminated gloves with transmission of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. anitratus in an intensive care unit. Am J Med. 1991 Nov;91(5):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal S., Tager I. B. Prevalence of gram-negative rods in the normal pharyngeal flora. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Sep;83(3):355–357. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata H., Fujita K., Maruyama S., Kakehashi H., Mori Y., Yoshioka H. Acinetobacter calcoaceticus biovar anitratus septicaemia in a neonatal intensive care unit: epidemiology and control. J Hosp Infect. 1989 Jul;14(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(89)90129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H., Baginski R., Schulze A., Pulverer G. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):750–753. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H., Baginski R., Schulze A., Pulverer G. The distribution of Acinetobacter species in clinical culture materials. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Nov;279(4):544–552. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H., Baginski R. The clinical significance of Acinetobacter baumannii in blood cultures. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jul;277(2):210–218. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80615-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert H., Schulze A., Baginski R., Pulverer G. Plasmid DNA fingerprinting of Acinetobacter species other than Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Jan;32(1):82–86. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.1.82-86.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherertz R. J., Sullivan M. L. An outbreak of infections with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus in burn patients: contamination of patients' mattresses. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):252–258. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins L. S. The use of molecular methods in infectious diseases. N Engl J Med. 1992 Oct 29;327(18):1290–1297. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199210293271808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Acinetobacter baumannii serotyping for delineation of outbreaks of nosocomial cross-infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2713–2716. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2713-2716.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]