Abstract
Mutations in MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2), cause the neurodevelopmental disorder Rett syndrome (RTT). Although MECP2 mutations are rare in idiopathic autism, reduced MeCP2 levels are common in autism cortex. MeCP2 is critical for postnatal neuronal maturation and a modulator of activity-dependent genes such as Bdnf (brain-derived neurotropic factor) and JUNB. The activity-dependent early growth response gene 2 (EGR2), required for both early hindbrain development and mature neuronal function, has predicted binding sites in the promoters of several neurologically relevant genes including MECP2. Conversely, MeCP2 family members MBD1, MBD2 and MBD4 bind a methylated CpG island in an enhancer region located in EGR2 intron 1. This study was designed to test the hypothesis that MECP2 and EGR2 regulate each other’s expression during neuronal maturation in postnatal brain development. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis showed EGR2 binding to the MECP2 promoter and MeCP2 binding to the enhancer region in EGR2 intron 1. Reduction in EGR2 and MeCP2 levels in cultured human neuroblastoma cells by RNA interference reciprocally reduced expression of both EGR2 and MECP2 and their protein products. Consistent with a role of MeCP2 in enhancing EGR2, Mecp2-deficient mouse cortex samples showed significantly reduced EGR2 by quantitative immunofluorescence. Furthermore, MeCP2 and EGR2 show coordinately increased levels during postnatal development of both mouse and human cortex. In contrast to age-matched Controls, RTT and autism postmortem cortex samples showed significant reduction in EGR2. Together, these data support a role of dysregulation of an activity-dependent EGR2/MeCP2 pathway in RTT and autism.
INTRODUCTION
Rett syndrome (RTT) and autism fall within the five pervasive developmental disorders (PDDs) described in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (1). Clinical features of RTT include autistic features, mental retardation, postural hypotonia, difficulties in locomotion, loss of purposeful hand use, stereotyped hand movements, progressive scoliosis, seizures, and autonomic nervous system disturbances (2–4). RTT patients also suffer from respiratory abnormalities including hyperventilation, breath-holding, apnea and air swallowing as well as feeding problems characterized by poor tongue mobility and difficulties in swallowing of food (5,6).
RTT is an X-linked dominant PDD caused by mutations in methyl CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2) (7). MeCP2, which binds methylated CpGs, is a chromatin-associated protein (8) which can both activate and repress transcription (9,10). Required for maturation of neurons, MeCP2 is developmentally regulated in both human and mouse (11–13). Although MECP2 mutations cause RTT in females, milder mutations and duplications of MECP2 have been found in males with mental retardation (14,15). Reduced MeCP2 expression in brain has been observed in 79% of autism cortex samples (16) and functional variants of the MECP2 gene may confer autism vulnerability (17). A hypomorphic allele of Mecp2 in a transgenic mouse model also shows abnormal social behavior (18,19) further implicating reduced MeCP2 expression in autistic behavior.
The maturation of neuronal networks involves translation of sensory experience into synaptic connectivity mediated by activity-dependent gene transcription (20–22). Many of the characteristics of the RTT phenotype involve defects in the processes which rely upon this activity-dependent maturation program including dendritic branching, synaptic plasticity, memory and learning and inhibitory circuits (22). Activity-dependent gene cascades underlying these processes are often triggered by neuronal activity followed by calcium influx and a related protein phosphorylation event (23).
Immediate early genes (IEGs), a class of activity-dependent genes, are rapidly and transiently induced by neuronal activation and other cellular or extra-cellular stimuli without the necessity for de novo protein synthesis (24,25). IEGs can be classified into two categories, ‘effector IEGs’ such as brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) which play a direct functional role at the synapse and ‘regulatory IEGs’ which for the most part consist of inducible transcription factors including c-Fos, JunB, and the EGR family (26,27).
There is some evidence that activity-dependent gene expression pathways are disrupted in RTT. Several IEGs have been identified as actual or potential MeCP2 targets including JUNB (9), EGR1 (28), and Bdnf (21,22,29). Recently it was shown that MeCP2 binds the JUNB promoter when the gene is transcriptionally active (9). In Zhou et al. (22), activity-dependent phosphorylation of MeCP2 at serine 421 correlated with the transcriptional induction of Bdnf. Interestingly, double mutants of Bdnf and Mecp2 have a more severe RTT phenotype while overexpression of Bdnf in Mecp2-deficient mice extends life and improves motor deficits (30). It was shown in 2006 that both embryonic and adulthood ablation of Bdnf reduced transcription of Egr2 (early growth response gene 2) and its sister gene, Egr1 (31).
EGR2 encodes a zinc finger transcription factor observed in both the somata and dendrites of central neurons (32). EGR2 plays an important role in the transient formation of hindbrain developmental compartments or rhombomeres and is also an important factor in peripheral myelination, maintenance of synaptic plasticity and long-term potentiation (33–37). Recently, EGR2 was described as the most downregulated gene in lymphoblastoid cell lines from five monozygotic twin sets discordant with respect to severity of autism and/or language impairment suggesting that EGR2 might play a role in the development of autism (38). To further study the role of MeCP2 in IEG regulation, we investigated EGR2/EGR2 as a potential target and transcriptional regulator of MeCP2. Here we show the reciprocal binding and co-regulation of MeCP2 and EGR2 and demonstrate that EGR2 is significantly reduced in Mecp2-deficient mouse as well as human RTT and autism brain.
RESULTS
ChIP reveals reciprocal binding of MeCP2 to the EGR2 intron and EGR2 to the MECP2 promoter
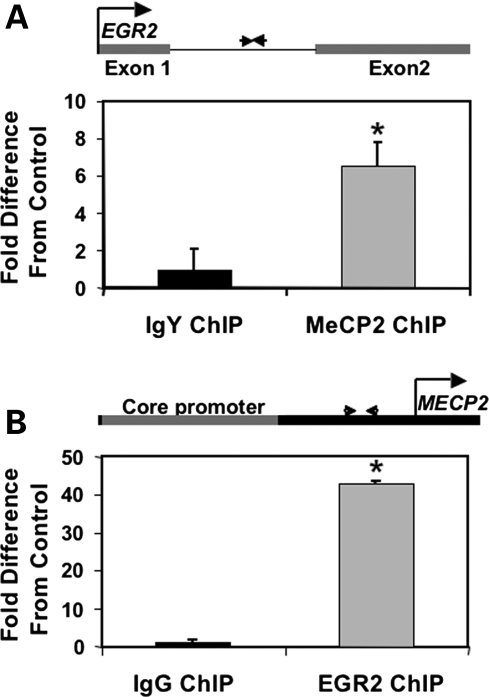
Since an intronic sequence of EGR2 has previously been shown to be a binding site for MBDs (methyl-binding domains) 1, 2 and 4 (39), this region was further explored as a potential regulatory target for MeCP2. Because of a suggested role of MeCP2 in the matrix attachment of chromatin loop structures (40) a bioinformatics search for matrix attachment regions (MARs) (41) was conducted using MAR-Wiz, identifying a 900 bp region within the EGR2 intron (EGR2 contains only one intron) with strong binding potential (Supplementary Material, Fig. S1). To directly test whether MeCP2 bound to this EGR2 regulatory sequence in neuronal cells, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with MeCP2-specific antibodies was conducted on chromatin from 48 h PMA(phorbol ester)-stimulated SH-SH5Y neuroblastoma cells, a system previously demonstrated to show increased MeCP2 levels (42). Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) using primers designed to the EGR2 intron showed significant enrichment of MeCP2 ChIP fragments at this site compared with a Control ChIP experiment using a non-specific antibody in the place of the anti-MeCP2 antibody. (Fig. 1A).
Figure 1.
(A) ChIP using anti-MeCP2 or non-specific IgY was performed on chromatin from PMA-stimulated human neuroblastoma cells in two separate experiments. qPCR was performed using primers designed to a DNA sequence in the EGR2 intron which contains a putative MAR and CpGs in the vicinity of A/T runs (diagrammed above). MeCP2 ChIP was significantly enriched compared with the IgY Control ChIP normalized to one (*P < 0.03 by Wilcoxon). Results are the mean ± SEM of six replicates. (B) ChIP was performed using anti-EGR2 or non-specific IgG and primers were designed to a region between the MECP2 core promoter and transcriptional start site which contained a predicted EGR2-binding site (diagrammed above). EGR2 ChIP was significantly enriched compared with the RIgG Control ChIP normalized to 1 (*P < 0.02 by Wilcoxon). Results are the mean ± SEM of seven replicates. Both the experimental and the Control ChIP experiments were normalized to input.
The MECP2 promoter sequence was examined for potential EGR2-binding sites using TESS (transcriptional element search string) (43). A highly conserved site located between the core promoter (44) and the transcriptional start site of MECP2 (Supplementary Material, Figs S2 and S3) was tested for enrichment of EGR2 binding by ChIP (Fig. 1B). EGR2 binding to the MECP2 promoter also revealed significant enrichment compared with the non-specific IgG Control by ChIP (Fig. 1B). Positive Controls for known MeCP2 and EGR2-binding sites, SNRPN (45) and MBP (myelin basic protein) (46) respectively, showed expected enrichment compared with the appropriate non-specific antibody Controls (Supplementary Material, Fig. S4).
Reciprocal siRNA knockdown of EGR2 and MECP2
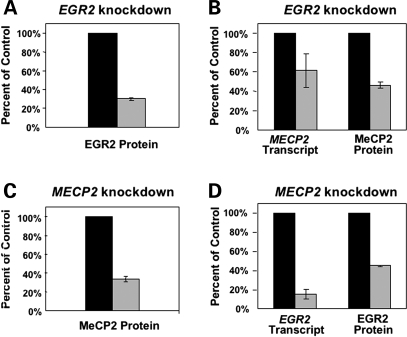
MeCP2 expression increases during maturation of neurons, a process that can be modeled by stimulation of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells with PMA. Both MECP2 and EGR2 protein showed ∼2-fold upregulation within 20 h of PMA treatment for EGR2 and 68 h after PMA treatment for MeCP2 when measured by immunofluorescence and laser scanning cytometry (LSC) (Supplementary Material, Fig. S5). To test a potential co-regulatory relationship between EGR2 and MECP2, siRNAs specifically targeting MECP2 and EGR2 were transfected into SH-SY5Y cells, revealing a pattern of reciprocal knockdown. Transfection with EGR2 siRNA resulted not only in reduction in EGR2 protein and EGR2 transcript as measured by immunofluorescence and LSC or qPCR, respectively (Fig. 2A and Supplementary Material, Fig. S6A), but also a significant reduction in MeCP2 protein and MECP2 transcript compared with Controls, measured by LSC and qPCR (Fig. 2B and Supplementary Material, Fig. S6B). Conversely, transfection with MECP2 siRNA resulted not only in reduction in MeCP2 protein and MECP2 transcript (Fig. 2A and Supplementary Material, Fig. S6C) but also a significant reduction in EGR2 protein and EGR2 transcript compared with Controls, measured by LSC and qPCR (Fig. 2D and Supplementary Material, Fig. S6D). Reciprocal knockdowns were also observed in cells which were transfected with siRNA but not stimulated with PMA (data not shown).
Figure 2.
Reciprocal siRNA transfections were performed on SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells then stimulated 4 h later with PMA. 48 and 72 h post-transfection EGR2 and MeCP2 protein levels were quantified by immunofluorescence and LSC. Results are shown for the optimal timepoint of knockdown for EGR2 (48 h) and MeCP2 (72 h), but all timepoints were assayed for transcript levels for MECP2 and EGR2 (Supplementary Material, Fig. S6) and protein levels showed similar results at both timepoints (data not shown). All results are shown as the mean ± SEM of three replicates with the mean Control normalized to 100%. (A) SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with EGR2 siRNA (light gray bars) or Control (black bars) and show reduced EGR2. (B) Cells transfected as in ‘A’ were also tested for MECP2 transcript by qPCR and MeCP2 protein by LSC. (C) SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with MECP2 siRNA (light gray bars) or Control (black bars), showing specific knockdown of MeCP2 levels. (D) Cells transfected as in ‘C’ showed reduced EGR2 transcript by qPCR and EGR2 protein by LSC.
Developmental expression profile of MeCP2 and EGR2
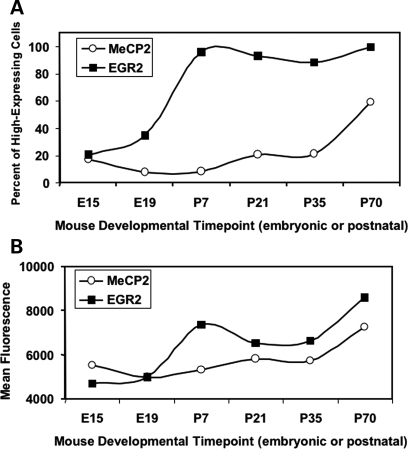
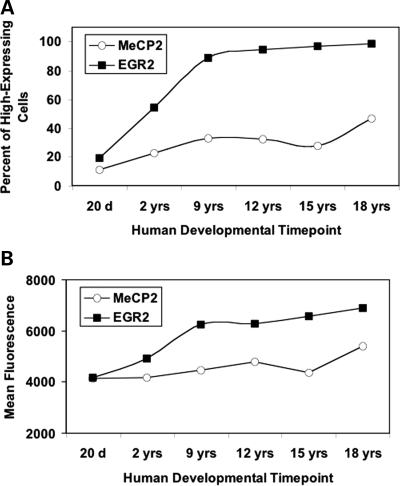
A mouse tissue array containing cores of cortical tissue from wild-type C57BL/6J mice at a variety of prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal timepoints, was immunofluorescently stained for MeCP2 and EGR2 protein and fluorescence was quantified to determine the developmental ontogeny of MeCP2 and EGR2 in mouse cortex. This analysis revealed a rise in the percentage of cells with high EGR2, beginning at embryonic (E19) and reaching a plateau at postnatal day 7 (P7) for EGR2 and a more gradual rise from 1 to 10 weeks of age for MeCP2 (Fig. 3A). The overall levels of both EGR2 and MeCP2 showed gradual, coordinated increases in postnatal brain with age (Fig. 3B). MeCP2 and EGR2 were colocalized in neurons, but EGR2 staining was both nuclear and cytoplasmic, as has been previously reported (32).
Figure 3.
LSC analysis of immunofluorescence for MeCP2 and EGR2 on a mouse developmental tissue microarray. Expression patterns in the mouse cortex show increasing levels of both MeCP2 and EGR2 during development. (A) In order to determine the percent of high-expressing cells in the mouse cortex, cell populations with high and low EGR2 or MeCP2 protein levels were differentiated by gating an LSC histogram for the youngest cerebral cortex postmortem sample (E15) at the right half-maximum. (B) Mean MeCP2 or EGR2 protein in the mouse cortex was determined by measuring the mean fluorescence value (mean maximum pixel) for all cortical cells at each developmental timepoint.
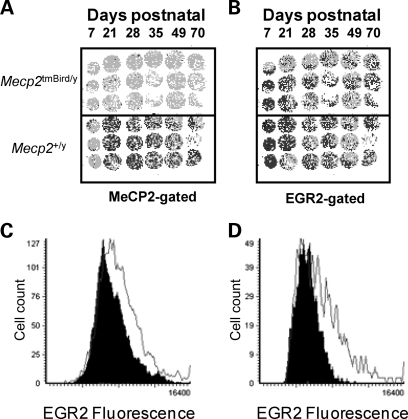
In order to further test the hypothesis that EGR2 might be involved in regulatory pathways relevant to RTT, a tissue microarray containing triplicate 600 μm cores of cortical tissue from a mouse model of RTT (Mecp2tm1Bird/y) and wild-type C57BL/6J littermate Controls for six age-matched timepoints (P7, P28, P35, P49, P56 and P70) was immunofluorescently stained for MeCP2 and EGR2 and analyzed by LSC (Fig. 4). Analysis of the array showed significantly decreased EGR2 expression in Mecp2tm1Bird/y cortical cells for all mutant cortical core samples compared with all wild-type core samples at all timepoints (P < 0.00005, Fig. 4C). Reductions in EGR2 were most apparent in Mecp2-deficient cortical cells at the P28 timepoint (Fig. 4D). Furthermore, follow-up staining of sagittal brain sections from P28 wild-type (C57BL/6J) and Mecp2-null (Mecp2tm1Bird/y) mice confirmed significantly decreased EGR2 in multiple areas of the brain, including medulla, cerebellum and pons (Supplementary Material, Fig. S7).
Figure 4.
EGR2 Expression is dysregulated in Mecp2tm1Bird/y mouse cortical cells. Four replicate tissue microarrays containing triplicate cores from wild-type male or Mecp2 tm1Bird/y mouse cortex at six postnatal timepoints (P7, P28, P35, P49, P56 and P70) were stained using antibodies recognizing EGR2 and MeCP2. The arrays were gated for MeCP2 expression (A) or EGR2 expression (B). Individual cells (pixels) colored darkly represent high MeCP2 or EGR2 staining, defined as the right half-maximum of the histogram. (C) In a representative histogram, decreased EGR2 was detected by immunofluorescence and LSC in the Mecp2tm1Bird/y cortical cells for the group of six Mecp2tm1Bird/y mice in the array (black histogram) compared with all six Controls grouped (white histogram) (P < 0.00005 by χ2). (D) Differences were most apparent at P28 in wild-type male cortical cells (white histogram) compared with Mecp2 tm1Bird/y cortical cells (black histogram) (P < 0.0001 by χ2).
EGR2 increases developmentally in postnatal human cortex and is downregulated in RTT and autism cortex
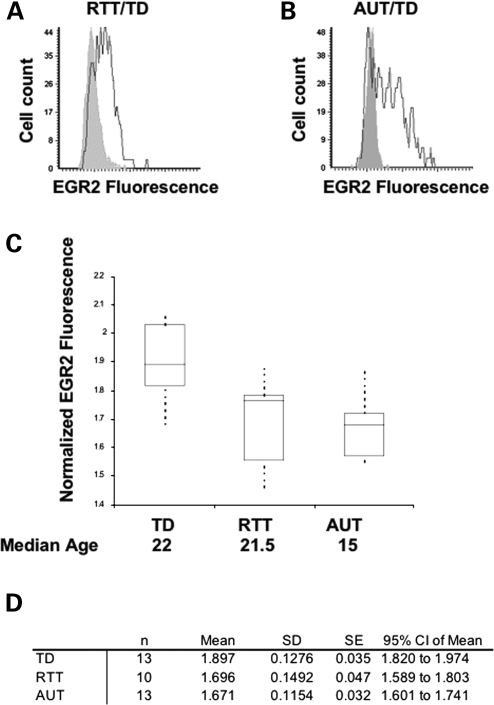
To test the hypothesis that EGR2 expression is dysregulated in human RTT and autism brain, LSC analysis of EGR2 and MeCP2 immunofluorescence on a human tissue microarray containing triplicate cortical samples from individuals with RTT, autism or other neurodevelopmental disorders was examined and compared with age-matched typically developing Controls. Similar to mouse cortex, EGR2 immunofluorescence colocalized with MeCP2 staining in human cortical neurons (Supplementary Material, Fig. S8). Analysis of human developmental EGR2 expression showed that, as in the mouse, MeCP2 and EGR2 are developmentally increased over postnatal lifespan in typically developed (TD) cortex (Fig. 5). More specifically, a steady increase in the number of EGR2-high cells from the age of 20 days to 18 years was observed (Fig. 5A). Group comparison of TD, RTT and autism samples (RTT/TD and AUT/TD) spanning childhood to adult years showed a statistically significant downregulation of EGR2 in RTT (P < 0.005 by t-test) and AUT brain (P < 0.00005 by t-test) (Supplementary Material, Table S1). A comparison of each individual RTT or AUT sample to its three closest age-matched TD Control samples also showed that EGR2 was dysregulated in a subset of samples, with a statistically significant downregulation of EGR2 observed in both RTT and AUT brain (Supplementary Material, Table S1). A non-parametric analysis similarly demonstrated statistically significant EGR2 downregulation in RTT and AUT brain as the means were outside a 95% confidence interval (Fig. 6D). As previously observed (16,47) MeCP2 was also significantly reduced in autism brain (Supplementary Material, Table S1).
Figure 5.
LSC analysis of MeCP2 and EGR2 immunofluorescence on a human tissue microarray. Human cortical cells (Brodmann Area 9) show increasing levels of both MeCP2 and EGR2 during development. (A) In order to determine the percent of high-expressing cells in the human cortex, cell populations with high and low MeCP2 or EGR2 protein levels were differentiated as in the mouse cortex. The high- and low-expressing cell populations were gated on the right-half maximum of the histogram for the youngest age and this gate was used for all subsequent ages. (B) Mean MeCP2 or EGR2 protein expression in the human cortex was determined by measuring the mean fluorescence value (mean maximum pixel) at each age examined.
Figure 6.
Immunohistochemical analysis by LSC of a human postmortem brain cortical array including samples from TD, RTT and autism brain. EGR2 was significantly lower in both RTT and autism brain samples. (A) Representative histogram showing higher EGR2 expression (dark histogram) in TD cortex compared with EGR2 expression in RTT cortex (light histogram). (B) Representative histogram showing higher EGR2 expression (dark histogram) in TD cortex compared with EGR2 expression in autism cortex (light histogram). (C) Boxplot of EGR2 fluorescence (maximum pixel) normalized to housekeeping Control (Histone H1) with comparisons made between Control (n = 13), RTT (n = 10) and autism (n = 13). Boxplot of EGR2 in TD, RTT and autism cortex. (D) Statistical analysis showed non-overlapping 95% confidence intervals for the TD, RTT and autism samples and downregulation of EGR2 in RTT and autism brain (see Supplementary Material, Table S1 for additional analyses).
DISCUSSION
In this study, we have used a candidate approach for activity-dependent early activation transcription to identify a new MeCP2 target gene, EGR2. As an IEG, EGR2 is increased rapidly in response to neuronal activity. Here we show evidence that EGR2 positively regulates MECP2 by binding to its promoter, and in turn, MeCP2 binds to an enhancer of EGR2, further upregulating expression of both genes in a positive feedback loop for increased neuronal maturation. In vivo we have established that developmental upregulation of EGR2 parallels the developmental ontogeny of MeCP2 and that EGR2 is dysregulated in an animal model of RTT as well as in human RTT and MeCP2-deficient autism brain.
The EGR genes have recently been implicated in a number of neuropsychiatric or neurodevelopmental conditions including schizophrenia (48,49) depression (50), dysregulated stress response (49,51), aggression (49) and autism (38). EGR2 may play a novel role in cognitive functions associated with attention, an executive function with which autistic individuals often experience difficulty (37,52,53). Our results are consistent with a role of EGR2 in autism spectrum and neurodevelopmental disorders.
The EGR family of transcription factors are able to mediate, amplify or modulate the impact of downstream gene expression patterns. EGR family genes are responsive to both cellular and environmental stimuli such as triazole (54), progesterone (55), stress (56), seizures (57) and valproic acid (58). Interestingly, perinatal exposure to valproic acid is a known risk factor for autism (59–62). EGR2 is involved in brain development (63–65), myelination and routing of axons (66,67). Our results provide a role of EGR2 in MeCP2 regulation and suggest that the postnatal developmental ontogenies of EGR2 and MeCP2 are interrelated. One alternative explanation for the reciprocal regulation of MeCP2 and EGR2 in siRNA experiments could be simply a delay of maturational differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells with either factor acting through an indirect versus direct pathway. However, the observation of direct binding of MeCP2 to EGR2 and EGR2 to MECP2 by ChIP in the same cell line supports a model of direct interactions in addition to indirect pathways such as the Mecp2/Bdnf/Egr2 pathway previously described (31).
Since EGR2 is a regulator of many neurologically relevant genes, disruption of normal EGR2 expression has the potential to influence many downstream targets. Previously identified neurologically relevant EGR2 targets include EGR2 itself; the NAB genes whose protein products interact with EGR2 to repress gene expression; inhibition of differentiation genes, ID2 and ID4, as well as a number of HOX genes (68–71). Interestingly, ID2 and ID3 are also targets of MeCP2 (72) and homozygous mutations in HOXA1 were observed in familial pedigrees with autism (73), further implicating these regulatory pathways in autism spectrum disorders. More recently, homozygosity mapping of multiple recessive autism pedigrees revealed that a number of genes regulated by neuronal activity may be implicated in autism (74).
Although MeCP2 was once predicted to be solely a transcriptional repressor of genes with methylated CpG island promoters, more recent genomic analyses have established that the primary function of MeCP2 is not the silencing of methylated promoters (9,10). To the contrary, the majority of MeCP2-bound promoters are actively expressed (9) and more transcripts are upregulated by increasing Mecp2 genetic dosage than downregulated (10). Interestingly, genomic ChIP analyses showed that the majority of the intragenic MeCP2-binding sites were intronic (9). In the context of EGR2 regulation this is not surprising, as earlier researchers demonstrated that other members of the MBD family-bound methylated CpGs within the EGR2 intron examined here (39). These results are also consistent with regulation of GABRB3, where MeCP2 binds to an intronic methylated sequence and promotes rather than represses expression (75).
As a result of our study, we propose that EGR2 and MeCP2 have the ability to facilitate each other’s postnatal developmental expression. At critical developmental stages, intra- or extra-cellular stimuli induce expression of EGR2 or MeCP2 each of which can bind the appropriate site, near the MECP2 core promoter in the case of EGR2, or the EGR2 intron in the case of MeCP2, enhancing the expression of its regulatory partner in a positive feedback loop. This positive feedback mechanism may serve to fine-tune the genomic response to a variety of environmental stimuli.
Dysregulation of this feedback system may play a role in the defects associated with autism spectrum disorders, with loss or reduction in functional MeCP2 decreasing the responsiveness of EGR family members and other IEGs to stimuli which induce the maturation of neuronal networks in typical cortical development. Our human brain analyses support the hypothesis that RTT and autism are disorders of stalled or arrested maturational brain development (76,77) as EGR2 levels in adult RTT and autism brain are lower than expected for their age. These results also suggest the possibility that increasing neuronal stimuli postnatally may partially improve the maturational defects of RTT and autism. In support of this premise, recent studies showed environmental enrichment could ameliorate motor coordination deficits in a mouse model of RTT (78,79) and evidence suggests that early behavioral interventions have a positive effect on autism outcomes (80). A number of clinical trials involving autistic patients are examining the effects of aripiprazole (Abilify®, Bristol-Myers Squibb), an atypical antipsychotic which may upregulate EGR2 (81, http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=autism+aripiprazole). Further examination of EGR2 and other IEGs in relation to autism spectrum disorders, including RTT, should be undertaken as part of the search for treatment strategies, including environmental enrichment and new pharmacological interventions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell lines
SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells (American Type Culture Collection) were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium supplemented with 15% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), MEM NEAA (Gibco), 10 mm Hepes pH 7.3 (Gibco) and 2-mercaptoethanol (Gibco). Cells for ChIP were grown to ∼70–80% confluency in T175 cm2 flasks and cells for RNA interference (RNAi) were grown in two-chamber slides coated with poly-d-lysine (Sigma) or six-well plates.
RNA interference
siRNAs specifically targeting MECP2 and EGR2 were purchased from Dharmacon® (Supplementary Material, Table S2). Transfection of a pool of these siRNAs was conducted in six-well plates and two-chamber slides using DharmaFECT1® transfection reagent. SH-SY5Y cells were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2. The media formulation contained Gibco MEM with Earle’s salts supplemented by non-essential amino acids (1% final concentration), Hepes buffer (1% final concentration) and beta-mercaptoethanol (0.5% final concentration). Cells were cultured with no antibiotics present in the media. When cells reached 70–80% confluence, they were trypsinized and seeded in the six-well plates and chamber slides at ∼2.5 × 104 cells per well or chamber and incubated overnight at 37°C. The next day, treated cells were transfected using DharmaFECT1® siRNA transfection reagent and either no siRNA, EGR2 siRNA, MECP2 siRNA, a non-targeting Control siRNA or DharmaFECT1® only. Transfections were conducted according to the manufacturer’s general transfection protocol. Four hours after the transfection, the cells were stimulated to differentiate by the addition of PMA to a final concentration of 160 nm per well or chamber. Twenty-four hours after the first siRNA transfection, a second transfection was performed. Separate aliquots of untreated cells and aliquots of cells which were transfected with siRNA but not stimulated with PMA were cultured in parallel as additional Controls.
cDNA synthesis and qPCR
qPCR was performed with a LightCycler (Roche, Indianapolis, IN, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Primers for EGR2, MECP2 and GAPDH were designed using primer3 software with one of the primers of each primer pair spanning an intron–exon junction so as not to amplify genomic DNA (Supplementary Material, Table S3). Primer pairs were analyzed with BLAST to verify that the sequences were unique to the appropriate amplicon. PCR reactions include 1X DNA master SYBR Green I reaction buffer (Roche), 1.5–2 mm MgCl2, 0.5 micromolar of primers and 10–20 ng of cDNA or ChIP DNA. In the case of RNAi experiments, total RNA was extracted from SH-SY5Y cells in culture using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) and cDNA was synthesized using a QuantiTect Reverse Transcription kit (Qiagen). Melting curve analysis was conducted to confirm specificity of the amplicon. Quantitation was conducted using the comparative CT method (Applied Biosystems) and is reported as n-fold difference, relative to a calibrator, following normalization to GAPDH or input DNA in the case of ChIP PCR.
Sequence analysis
A search for possible MeCP2-binding sites in the EGR2 intron and EGR2-binding sites in MECP2 regulatory regions was performed using MAR-Wiz (Futuresoft at http://www.futuresoft.org/MAR-Wiz/) and TESS (43, http://www.mrw.interscience.wiley.com/emrw/9780471250951/cp/cpbi/article/bi0206/current/pdf). The MeCP2 homolog in chicken, ARBP, recognizes MARS. MARs, DNA sequences which bind to the nuclear matrix, may function as anchoring sites for higher order chromatin structures including loops (41,82). Because other members of the MBD family bind a region in the EGR2 intron (39), this same region was examined for MeCP2-binding potential. MAR-Wiz analysis of the EGR2 intron revealed a high-scoring putative MAR with an average MAR potential or strength of 0.83 (Supplementary Material, Fig. S1). This same region also contained CpGs in the vicinity of A/T runs which are a prerequisite for MeCP2 binding (Supplementary Material, Fig. S1) (83). The sequences of predicted EGR2 sites were confirmed by comparison with potential EGR2-binding sites defined in (84) or (85). TESS predicted EGR2-binding sites in the MECP2 promoter region and in an enhancer sequence, identified by Liu and Francke (44), within the MECP2 3′-UTR (Supplementary Material, Fig. S2). The predicted EGR2-binding site located in the MECP2 promoter region is highly conserved (Supplementary Material, Fig. S3A) whereas the predicted site in the MECP2 3′-UTR is not (Supplementary Material, Fig. S3B).
ChIP and qPCR for ChIP
Chromatin from PMA-stimulated SH-SY5Y cells was isolated as described previously with some modifications (45,72). For each experiment, 150–200 μg of chromatin were digested into ∼300–500 bp fragments with HindIII, SpeI and SphI (New England Biolabs) and precleared by incubation with agarose beads (PrecipHen agarose, Aves labs or protein A/G agarose, Pierce) followed by incubation with the appropriate preimmune serum (chicken IgY or rabbit IgG) and a second incubation with agarose beads. Precleared chromatin was divided (∼40 μg per tube) and incubated overnight with an excess of C-terminal anti-MeCP2 (raised in chicken to the C-terminal peptide N-RPNREEPVDSRTPVTERVS-C, Aves labs); preabsorbed IgY as a Control for non-specific binding; anti-EGR2 (Santa Cruz) or rabbit IgG Control. Antibody incubations were followed by additional incubation for 4–6 h with the appropriate agarose beads as described earlier. An aliquot of precleared chromatin was set aside as total input Control. Immunoprecipitates were collected by centrifugation, washed and digested with 50 µ/ml DNase free RNase A for 30 min at 37°C, followed by SDS/proteinase K digestion and subjected to phenol/chloroform extraction prior to ethanol precipitation with glycogen.
qPCR was performed using a Lightcycler (Roche, Indianapolis, IN, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Primer sequences specific to the MECP2 core promoter, the MECP2 enhancer region, the EGR2 intron, a known EGR2-binding site and an MeCP2-binding site near the SNRPN gene are listed in Supplementary Material, Table S3. Primer sequences were designed to be compatible with the restriction enzyme cocktail used to digest the chromatin. The data were analyzed by LightCycler software version 2.0. Final quantification was performed using the comparative CT method (Applied Biosystems) and is reported as the n-fold difference in input-normalized, antibody-precipitated chromatin relative to input-normalized serum-incubated chromatin.
Tissue microarrays
A mouse developmental tissue array, including triplicate 600 μm cores of brain cortical tissue from wild-type C57BL/6J and Mecp2tm1Bird/y for a number of age-matched timepoints including P7, P28, P35, P49, P56 and P70, was fixed and embedded in paraffin as previously described (72).
A second mouse tissue microarray, created in a similar manner, contained wild-type male and female as well as Mecp2tm1Bird/y and Mecp2tm1Bird/+ cortical cores for age-matched timepoints including E15, E19, P7, P21, P35 and P70 was also fixed and embedded in paraffin.
Human brain tissue array
The human brain tissue array including triplicate 600 µm diameter tissue cores were extracted and processed as described previously from cerebral cortical samples (layers III–IV of Brodmann Area 9) and fusiform gyrus samples (Nagarajan et al., 2006). Immunofluorescence was performed on tissue microarray slides with anti-MeCP2 and anti-EGR2 antibodies and the slides were scanned by LSC. Fluorescence was normalized to histone H1 as previously described (12). Triplicate cores for each disorder and TD Controls were analyzed for each experimental replicate and mean normalized MeCP2 and EGR2 fluorescence was calculated for each tissue core in three replicate arrays (N = 9). Normalized immunofluorescence for each disorder sample was compared with that of the three closest, age-matched Controls (n = 27) and statistical significance was determined by t-test. Group comparisons were also conducted and statistical significance for these comparisons was determined by t-test.
Immunofluorescence and LSC
LSC shares some similarities with flow cytometry in its ability to quantitate fluorescence of individual cells. However, with LSC solid-phase samples such as adherent cultured cells, tissue sections and cytology smears can be examined for genetic, biochemical or morphological properties (http://www.compucyte.com/laserscanning.htm). Here, paraffin-embedded tissue microarrays (human or mouse) or sagittal brain hemispheres (mouse) were cut into 5 μm sections, placed on glass slides and stained as previously described (72). Primary antibodies used were: anti-EGR2 (Santa Cruz, rabbit polyclonal), 1:100, anti-MeCP2 (Aves, C-terminal, chicken polyclonal) 1:1000 and anti-Histone H1 (Upstate, mouse polyclonal) 1:100. The anti-Mecp2 Aves, C-terminal chicken polyclonal detects both the E1 and E2 isoforms of MeCP2. Secondary antibodies used were: goat anti-rabbit IgG-Oregon Green (Molecular Probes) 1:100, donkey anti-chicken IgG-Cy5 and goat anti-mouse IgG-Cascade Blue (Molecular Probes) 1:100. Rabbit IgG (Upstate), Chicken IgY (Aves) and Mouse IgG (Upstate) were used on Control slides with the same secondary as the experimental slides to test for background levels of staining or immunofluorescence. Replicate slides were stained and scanned by LSC to increase the power of our statistical analyses.
The procedure used for staining cultured neuroblastoma cells on chamber slides was similar to the procedure for staining tissue with a few exceptions. Chamber slides were washed in 1X PBS, placed in HistoChoice (Amresco) for 10–15 min followed by 1X PBS/Tween 0.02% for 4 min then placed in 70% ethanol for 10 min or for storage at −20°C. Slides to be stained were first rinsed in 1X PBS then stained as with the tissue arrays or sagittal brain sections above.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
FUNDING
This work was supported by NIH 5T32MH073124-U.C. Davis M.I.N.D. Institute Autism Research Training Program and NIH 1F32HD055143 NRSA Postdoctoral Fellowship (S.S.); RO1HD041462 and R01HD048799 and Autism Speaks (J.M.L.), and a NAAR/Autism Speaks predoctoral fellowship (S.P.). NICHD Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders and the Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center is supported in part by R24MH068855. Funding to pay the Open Access charge was provided by Autism Speaks.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful for access to human brain samples through the NICHD Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders and the Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center.
Conflict of Interest statement. None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.American Psychiatric Association and Task Force on DSM-IV. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-IV. 4th edn. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nomura Y. Early behavior characteristics and sleep disturbance in Rett syndrome. Brain. Dev. 2005;27(Suppl. 1):S35–S42. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2005.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nomura Y., Segawa M. Natural history of Rett syndrome. J. Child. Neurol. 2005;20:764–778. doi: 10.1177/08830738050200091201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hagberg B. Rett syndrome: long-term clinical follow-up experiences over four decades. J. Child Neurol. 2005;20:722–727. doi: 10.1177/08830738050200090401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kerr A.M., Julu P.O. Recent insights into hyperventilation from the study of Rett syndrome. Arch. Dis. Child. 1999;80:384–387. doi: 10.1136/adc.80.4.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Motil K.J., Schultz R.J., Browning K., Trautwein L., Glaze D.G. Oropharyngeal dysfunction and gastroesophageal dysmotility are present in girls and women with Rett syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999;29:31–37. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199907000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Amir R.E., Van den Veyver I.B., Wan M., Tran C.Q., Francke U., Zoghbi H.Y. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat. Genet. 1999;23:185–188. doi: 10.1038/13810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kumar A., Kamboj S., Malone B.M., Kudo S., Twiss J.L., Czymmek K.J., LaSalle J.M., Schanen N.C. Analysis of protein domains and Rett syndrome mutations indicate that multiple regions influence chromatin-binding dynamics of the chromatin-associated protein MECP2 in vivo. J. Cell. Sci. 2008;121:1128–1137. doi: 10.1242/jcs.016865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yasui D.H., Peddada S., Bieda M.C., Vallero R.O., Hogart A., Nagarajan R.P., Thatcher K.N., Farnham P.J., Lasalle J.M. Integrated epigenomic analyses of neuronal MeCP2 reveal a role for long-range interaction with active genes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:19416–19421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707442104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chahrour M., Jung S.Y., Shaw C., Zhou X., Wong S.T., Qin J., Zoghbi H.Y. MeCP2, a key contributor to neurological disease, activates and represses transcription. Science. 2008;320:1224–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.1153252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shahbazian M.D., Zoghbi H.Y. Molecular genetics of Rett syndrome and clinical spectrum of MECP2 mutations. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2001;14:171–176. doi: 10.1097/00019052-200104000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Balmer D., Goldstine J., Rao Y.M., LaSalle J.M. Elevated methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 expression is acquired during postnatal human brain development and is correlated with alternative polyadenylation. J. Mol. Med. 2003;81:61–68. doi: 10.1007/s00109-002-0396-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Braunschweig D., Simcox T., Samaco R.C., LaSalle J.M. X-Chromosome inactivation ratios affect wild-type MeCP2 expression within mosaic Rett syndrome and Mecp2−/+ mouse brain. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004;13:1275–1286. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Villard L. MECP2 mutations in males. J. Med. Genet. 2007;44:417–423. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2007.049452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smyk M., Obersztyn E., Nowakowska B., Nawara M., Cheung S.W., Mazurczak T., Stankiewicz P., Bocian E. Different-sized duplications of Xq28, including MECP2, in three males with mental retardation, absent or delayed speech, and recurrent infections. Am. J. Med. Genet. B. Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2007;6:799–806. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nagarajan R.P., Hogart A.R., Gwye Y., Martin M.R., LaSalle J.M. Reduced MeCP2 expression is frequent in autism frontal cortex and correlates with aberrant MECP2 promoter methylation. Epigenetics. 2006;1:1–11. doi: 10.4161/epi.1.4.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Loat C., Curran S., Lewis C., Abrahams B., Duvall J., Geschwind D., Bolton P., Craig I. Methyl-CpG-binding protein (MECP2) polymorphisms and vulnerability to autism. Genes Brain Behav. 2008;7:754–760. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2008.00414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Samaco R.C., Fryer J.D., Ren J., Fyffe S., Chao H.T., Sun Y., Greer J.J., Zoghbi H.Y., Neul J.L. A partial loss of function allele of methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 predicts a human neurodevelopmental syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008;17:1718–1727. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kerr B., Alvarez-Saavedra M., Saez M.A., Saona A., Young J.I. Defective body-weight regulation, motor control and abnormal social interactions in Mecp2 hypomorphic mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008;17:1707–1717. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Katz L.C., Shatz C.J. Synaptic activity and the construction of cortical circuits. Science. 1996;274:1133–1138. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5290.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen W.G., Chang Q., Lin Y., Meissner A., West A.E., Griffith E.C., Jaenisch R., Greenberg M.E. Derepression of BDNF transcription involves calcium-dependent phosphorylation of MeCP2. Science. 2003;302:885–889. doi: 10.1126/science.1086446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhou Z., Hong E.J., Cohen S., Zhao W.N., Ho H.Y., Schmidt L., Chen W.G., Lin Y., Savner E., Griffith E.C., et al. Brain-specific phosphorylation of MeCP2 regulates activity-dependent Bdnf transcription, dendritic growth, and spine maturation. Neuron. 2006;52:255–269. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.09.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Herdegen T., Leah J.D. Inducible and constitutive transcription factors in the mammalian nervous system: control of gene expression by Jun, Fos and Krox, and CREB/ATF proteins. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1998;28:370–490. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(98)00018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dragunow M. A role for immediate-early transcription factors in learning and memory. Behav. Genet. 1996;26:293–299. doi: 10.1007/BF02359385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sng J.C., Taniura H., Yoneda Y. A tale of early response genes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004;27:606–612. doi: 10.1248/bpb.27.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shaulian E., Karin M. AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:E131–E136. doi: 10.1038/ncb0502-e131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Davis S., Bozon B., Laroche S. How necessary is the activation of the immediate early gene zif268 in synaptic plasticity and learning? Behav. Brain Res. 2003;142:17–30. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(02)00421-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Colantuoni C., Jeon O.H., Hyder K., Chenchik A., Khimani A.H., Narayanan V., Hoffman E.P., Kaufmann W.E., Naidu S., Pevsner J. Gene expression profiling in postmortem Rett Syndrome brain: differential gene expression and patient classification. Neurobiol. Dis. 2001;8:847–865. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2001.0428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Martinowich K., Hattori D., Wu H., Fouse S., He F., Hu Y., Fan G., Sun Y.E. DNA methylation-related chromatin remodeling in activity-dependent BDNF gene regulation. Science. 2003;302:890–893. doi: 10.1126/science.1090842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chang Q., Khare G., Dani V., Nelson S., Jaenisch R. The disease progression of Mecp2 mutant mice is affected by the level of BDNF expression. Neuron. 2006;49:341–348. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.12.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Glorioso C., Sabatini M., Unger T., Hashimoto T., Monteggia L.M., Lewis D.A., Mirnics K. Specificity and timing of neocortical transcriptome changes in response to BDNF gene ablation during embryogenesis or adulthood. Mol. Psychiatry. 2006;11:633–648. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.De S., Shuler C.F., Turman J.E., Jr The ontogeny of Krox-20 expression in brainstem and cerebellar neurons. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2003;25:213–226. doi: 10.1016/s0891-0618(03)00011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Williams J., Dragunow M., Lawlor P., Mason S., Abraham W.C., Leah J., Bravo R., Demmer J., Tate W. Krox20 may play a key role in the stabilization of long-term potentiation. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1995;28:87–93. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)00187-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Inokuchi K., Murayama A., Ozawa F. mRNA differential display reveals Krox-20 as a neural plasticity-regulated gene in the rat hippocampus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996;221:430–436. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lumsden A., Krumlauf R. Patterning the vertebrate neuraxis. Science. 1996;274:1109–1115. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5290.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Borday C., Chatonnet F., Thoby-Brisson M., Champagnat J., Fortin G. Neural tube patterning by Krox20 and emergence of a respiratory control. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2005;149:63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2005.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.DeSteno D.A., Schmauss C. Induction of early growth response gene 2 expression in the forebrain of mice performing an attention-set-shifting task. Neuroscience. 2008;152:417–428. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hu V.W., Frank B.C., Heine S., Lee N.H., Quackenbush J. Gene expression profiling of lymphoblastoid cell lines from monozygotic twins discordant in severity of autism reveals differential regulation of neurologically relevant genes. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:118. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Unoki M., Nakamura Y. Methylation at CpG islands in intron 1 of EGR2 confers enhancer-like activity. FEBS Lett. 2003;554:67–72. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)01092-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Horike S., Cai S., Miyano M., Cheng J.F., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Loss of silent-chromatin looping and impaired imprinting of DLX5 in Rett syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:31–40. doi: 10.1038/ng1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Namciu S.J., Friedman R.D., Marsden M.D., Sarausad L.M., Jasoni C.L., Fournier R.E. Sequence organization and matrix attachment regions of the human serine protease inhibitor gene cluster at 14q32.1. Mamm. Genome. 2004;15:162–178. doi: 10.1007/s00335-003-2311-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jung B.P., Jugloff D.G., Zhang G., Logan R., Brown S., Eubanks J.H. The expression of methyl CpG binding factor MeCP2 correlates with cellular differentiation in the developing rat brain and in cultured cells. J. Neurobiol. 2003;55:86–96. doi: 10.1002/neu.10201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schug J. Using TESS to predict transcription factor binding sites in DNA sequence. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics. 2008 doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0206s21. Chapter 2, Supplement 21, Unit 2.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Liu J., Francke U. Identification of cis-regulatory elements for MECP2 expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006;15:1769–1782. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Thatcher K.N., Peddada S., Yasui D.H., Lasalle J.M. Homologous pairing of 15q11–13 imprinted domains in brain is developmentally regulated but deficient in Rett and autism samples. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005;14:785–797. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Jang S.W., LeBlanc S.E., Roopra A., Wrabetz L., Svaren J. In vivo detection of Egr2 binding to target genes during peripheral nerve myelination. J. Neurochem. 2006;98:1678–1687. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Samaco R.C., Nagarajan R.P., Braunschweig D., LaSalle J.M. Multiple pathways regulate MeCP2 expression in normal brain development and exhibit defects in autism-spectrum disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004;13:629–639. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yamada K., Gerber D.J., Iwayama Y., Ohnishi T., Ohba H., Toyota T., Aruga J., Minabe Y., Tonegawa S., Yoshikawa T. Genetic analysis of the calcineurin pathway identifies members of the EGR gene family, specifically EGR3, as potential susceptibility candidates in schizophrenia. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:2815–2820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610765104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gallitano-Mendel A., Wozniak D.F., Pehek E.A., Milbrandt J. Mice lacking the immediate early gene Egr3 respond to the anti-aggressive effects of clozapine yet are relatively resistant to its sedating effects. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:1266–1275. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Orsetti M., Di Brisco F., Canonico P.L., Genazzani A.A., Ghi P. Gene regulation in the frontal cortex of rats exposed to the chronic mild stress paradigm, an animal model of human depression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008;27:2156–2164. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gallitano-Mendel A., Izumi Y., Tokuda K., Zorumski C.F., Howell M.P., Muglia L.J., Wozniak D.F., Milbrandt J. The immediate early gene early growth response gene 3 mediates adaptation to stress and novelty. Neuroscience. 2007;148:633–643. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.05.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rinehart N.J., Bradshaw J.L., Moss S.A., Brereton A.V., Tonge B.J. A deficit in shifting attention present in high-functioning autism but not Asperger’s disorder. Autism. 2001;5:67–80. doi: 10.1177/1362361301005001007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Shafritz K.M., Dichter G.S., Baranek G.T., Belger A. The neural circuitry mediating shifts in behavioral response and cognitive set in autism. Biol. Psychiatry. 2008;63:974–980. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.06.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Massa V., Gaudenzi G., Sangiorgio L., Cotelli F., Giavini E. Krox20 is down-regulated following triazole in vitro embryonic exposure: a polycompetitor-based assay. Toxicol. Lett. 2007;169:196–204. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Guennoun R., Benmessahel Y., Delespierre B., Gouezou M., Rajkowski K.M., Baulieu E.E., Schumacher M. Progesterone stimulates Krox-20 gene expression in Schwann cells. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2001;90:75–82. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(01)00094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Honkaniemi J., Zhang J.S., Longo F.M., Sharp F.R. Stress induces zinc finger immediate early genes in the rat adrenal gland. Brain Res. 2000;877:203–208. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02673-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Honkaniemi J., Sharp F.R. Prolonged expression of zinc finger immediate-early gene mRNAs and decreased protein synthesis following kainic acid induced seizures. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999;11:10–17. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Okada A., Kushima K., Aoki Y., Bialer M., Fujiwara M. Identification of early-responsive genes correlated to valproic acid-induced neural tube defects in mice. Birth Defects Res. A. Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2005;73:229–238. doi: 10.1002/bdra.20131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wagner G.C., Reuhl K.R., Cheh M., McRae P., Halladay A.K. A new neurobehavioral model of autism in mice: pre- and postnatal exposure to sodium valproate. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2006;36:779–793. doi: 10.1007/s10803-006-0117-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Alsdorf R., Wyszynski D.F. Teratogenicity of sodium valproate. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2005;4:345–353. doi: 10.1517/14740338.4.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Arndt T.L., Stodgell C.J., Rodier P.M. The teratology of autism. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2005;23:189–199. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2004.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Williams G., King J., Cunningham M., Stephan M., Kerr B., Hersh J.H. Fetal valproate syndrome and autism: additional evidence of an association. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2001;43:202–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Helmbacher F., Pujades C., Desmarquet C., Frain M., Rijli F.M., Chambon P., Charnay P. Hoxa1 and Krox-20 synergize to control the development of rhombomere 3. Development. 1998;125:4739–4748. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.23.4739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chatonnet F., Thoby-Brisson M., Abadie V., Dominguez del Toro E., Champagnat J., Fortin G. Early development of respiratory rhythm generation in mouse and chick. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2002;131:5–13. doi: 10.1016/s1569-9048(02)00033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kubik S., Miyashita T., Guzowski J.F. Using immediate-early genes to map hippocampal subregional functions. Learn Mem. 2007;14:758–770. doi: 10.1101/lm.698107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kamholz J., Awatramani R., Menichella D., Jiang H., Xu W., Shy M. Regulation of myelin-specific gene expression. Relevance to CMT1. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1999;883:91–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.LeBlanc S.E., Jang S.W., Ward R.M., Wrabetz L., Svaren J. Direct regulation of myelin protein zero expression by the Egr2 transactivator. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:5453–5460. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512159200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Mechta-Grigoriou F., Garel S., Charnay P. Nab proteins mediate a negative feedback loop controlling Krox-20 activity in the developing hindbrain. Development. 2000;127:119–128. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Maconochie M.K., Nonchev S., Manzanares M., Marshall H., Krumlauf R. Differences in Krox20-dependent regulation of Hoxa2 and Hoxb2 during hindbrain development. Dev. Biol. 2001;233:468–481. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ghislain J., Desmarquet-Trin-Dinh C., Gilardi-Hebenstreit P., Charnay P., Frain M. Neural crest patterning: autoregulatory and crest-specific elements co-operate for Krox20 transcriptional control. Development. 2003;130:941–953. doi: 10.1242/dev.00318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mager G.M., Ward R.M., Srinivasan R., Jang S.W., Wrabetz L., Svaren J. Active gene repression by the Egr2.NAB Complex during peripheral nerve myelination. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:18187–18197. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803330200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Peddada S., Yasui D.H., LaSalle J.M. Inhibitors of differentiation (ID1, ID2, ID3 and ID4) genes are neuronal targets of MeCP2 that are elevated in Rett syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006;15:2003–2014. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Tischfield M.A., Bosley T.M., Salih M.A., Alorainy I.A., Sener E.C., Nester M.J., Oystreck D.T., Chan W.M., Andrews C., Erickson R.P., et al. Homozygous HOXA1 mutations disrupt human brainstem, inner ear, cardiovascular and cognitive development. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:1035–1047. doi: 10.1038/ng1636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Morrow E.M., Yoo S.Y., Flavell S.W., Kim T.K., Lin Y., Hill R.S., Mukaddes N.M., Balkhy S., Gascon G., Hashmi A., et al. Identifying autism loci and genes by tracing recent shared ancestry. Science. 2008;321:218–223. doi: 10.1126/science.1157657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hogart A., Nagarajan R.P., Patzel K.A., Yasui D.H., Lasalle J.M. 15q11–13 GABAA receptor genes are normally biallelically expressed in brain yet are subject to epigenetic dysregulation in autism-spectrum disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007;16:691–703. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Courchesne E. Brain development in autism: early overgrowth followed by premature arrest of growth. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2004;10:106–111. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Zoghbi H.Y. Postnatal neurodevelopmental disorders: meeting at the synapse? Science. 2003;302:826–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1089071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kondo M., Gray L.J., Pelka G., Christodoulou J., Tam P.P.L., Hannan A.J. Environmental enrichment ameliorates a motor coordination deficit in a mouse model of Rett syndrome–Mecp2 gene dosage effects and BDNF expression. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008;12:3342–3350. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Nag N., Moriuchi J.M., Peitzman C.G., Ward B.C., Klodny N.H., Berger-Sweeney J.E. Environmental enrichment alters locomotor behaviour and ventricular volume in Mecp2(1lox) mice. Behav. Brain. Res. 2008 doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.07.008. epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Rogers S.J., Vismara L.A. Evidence-based comprehensive treatments for early autism. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2008;37:8–38. doi: 10.1080/15374410701817808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Cheng M.C., Liao D.L., Hsiung C.A., Chen C.Y., Liao Y.C., Chen C.H. Chronic treatment with aripiprazole induces differential gene expression in the rat frontal cortex. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;11:207–216. doi: 10.1017/S1461145707008048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Koch C., Stratling W.H. DNA binding of methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 in human MCF7 cells. Biochemistry. 2004;43:5011–5021. doi: 10.1021/bi0359271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Klose R.J., Sarraf S.A., Schmiedeberg L., McDermott S.M., Stancheva I., Bird A.P. DNA binding selectivity of MeCP2 due to a requirement for A/T sequences adjacent to methyl-CpG. Mol. Cell. 2005;19:667–678. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.07.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Nardelli J., Gibson T., Charnay P. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: analysis of base specificity by site-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992;20:4137–4144. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Swirnoff A.H., Milbrandt J. DNA-binding specificity of NGFI-A and related zinc finger transcription factors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995;15:2275–2287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.4.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.