Abstract
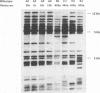
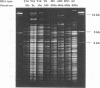
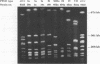
A combined clinical and molecular epidemiologic analysis of 46 strains of Clostridium difficile, including 16 nosocomial isolates from one ward (outbreak ward) plus 17 other nosocomial isolates and 13 community-acquired isolates, was performed. HindIII digests of total cellular DNA were analyzed by restriction enzyme analysis (REA) and ribotyping; SmaI digests were analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Isolates were assigned to typing groups on the basis of the profiles detected; isolates with closely related profiles were assigned to subgroups. The 16 isolates from the outbreak ward were resolved by both REA and PFGE into five distinct groups; 13 isolates represented two REA groups and three PFGE groups and two isolates were resolved as distinct groups by both techniques. DNA obtained from one isolate was persistently partially degraded, precluding analysis by PFGE. Seventeen sporadic nosocomial isolates were resolved by REA and PFGE into comparable numbers of groups (i.e., nine groups) and subgroups (i.e., 15 and 14 subgroups, respectively), with two isolates not evaluable by PFGE. The 13 epidemiologically unrelated community-acquired isolates were assigned to 11 groups by REA and to 12 groups by PFGE. Overall, ribotyping identified only nine groups among the 46 isolates. We conclude that REA and PFGE have comparable discriminatory powers for epidemiologic typing of C. difficile isolates and that ribotyping is appreciably less discriminatory. For a few isolates, partial DNA degradation prevented analysis by PFGE but not by REA or ribotyping; the cause of the degradation is unknown.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbeit R. D., Arthur M., Dunn R., Kim C., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Resolution of recent evolutionary divergence among Escherichia coli from related lineages: the application of pulsed field electrophoresis to molecular epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):230–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Arbeit R. D., Kim C., Beltran P., Crowe H., Steinbach S., Campanelli C., Wilson R. A., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms among uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates: pap-related sequences compared with rrn operons. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):471–479. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.471-479.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G. Clostridium difficile: clinical considerations. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12 (Suppl 2):S243–S251. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_2.s243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K. L., Squires C. L., Squires C. In vivo translation of a region within the rrnB 16S rRNA gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1691–1701. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1691-1701.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H., Jaskot D., Hammerberg O. Evaluation of restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of chromosomal DNA and plasmid profile analysis for characterization of multiresistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in bacteremic neonates. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):269–275. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.269-275.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chachaty E., Depitre C., Mario N., Bourneix C., Saulnier P., Corthier G., Andremont A. Presence of Clostridium difficile and antibiotic and beta-lactamase activities in feces of volunteers treated with oral cefixime, oral cefpodoxime proxetil, or placebo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Sep;36(9):2009–2013. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.9.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clabots C. R., Johnson S., Bettin K. M., Mathie P. A., Mulligan M. E., Schaberg D. R., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Development of a rapid and efficient restriction endonuclease analysis typing system for Clostridium difficile and correlation with other typing systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1870–1875. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1870-1875.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clabots C. R., Johnson S., Olson M. M., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Acquisition of Clostridium difficile by hospitalized patients: evidence for colonized new admissions as a source of infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):561–567. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clabots C. R., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Characterization of a nosocomial Clostridium difficile outbreak by using plasmid profile typing and clindamycin susceptibility testing. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):731–736. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. P., Kaplan E. L., Livdahl C., Skjold S. DNA fingerprints of Streptococcus pyogenes are M type specific. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1317–1323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Girolami P. C., Hanff P. A., Eichelberger K., Longhi L., Teresa H., Pratt J., Cheng A., Letourneau J. M., Thorne G. M. Multicenter evaluation of a new enzyme immunoassay for detection of Clostridium difficile enterotoxin A. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1085–1088. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1085-1088.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmée M., Laroche Y., Avesani V., Cornelis G. Comparison of serogrouping and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for typing Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):991–994. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.991-994.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin H. R., Au W., Foux L., Bradbury W. C. Restriction endonuclease analysis of nosocomial isolates of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2168–2172. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2168-2172.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard S. R., O'Farrell S., Holland D., Crook S., Barnett M. J., Tabaqchali S. The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile with use of a typing scheme: nosocomial acquisition and cross-infection among immunocompromised patients. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):159–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S., Adelmann A., Clabots C. R., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Recurrences of Clostridium difficile diarrhea not caused by the original infecting organism. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):340–343. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S., Clabots C. R., Linn F. V., Olson M. M., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Nosocomial Clostridium difficile colonisation and disease. Lancet. 1990 Jul 14;336(8707):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91605-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Oudbier J. H., Stuifbergen W. N., Jansz A., Zanen H. C. Application of whole-cell DNA restriction endonuclease profiles to the epidemiology of Clostridium difficile-induced diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):751–753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.751-753.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony D. E., Clow J., Atkinson L., Vakharia N., Schlech W. F. Development and application of a multiple typing system for Clostridium difficile. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jul;57(7):1873–1879. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.7.1873-1879.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslow J. N., Brecher S. M., Adams K. S., Durbin A., Loring S., Arbeit R. D. Relationship between indole production and differentiation of Klebsiella species: indole-positive and -negative isolates of Klebsiella determined to be clonal. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2000–2003. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2000-2003.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslow J. N., Mulligan M. E., Arbeit R. D. Molecular epidemiology: application of contemporary techniques to the typing of microorganisms. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;17(2):153–164. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland L. V., Mulligan M. E., Kwok R. Y., Stamm W. E. Nosocomial acquisition of Clostridium difficile infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 26;320(4):204–210. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901263200402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Peterson L. R., Kwok R. Y., Clabots C. R., Gerding D. N. Immunoblots and plasmid fingerprints compared with serotyping and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for typing Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):41–46. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.41-46.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevost G., Jaulhac B., Piemont Y. DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis is more effective than ribotyping in distinguishing among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):967–973. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.967-973.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvi R. J., Ahroon W., Saunders S. S., Arnold S. A. Evoked potentials: computer-automated threshold-tracking procedure using an objective detection criterion. Ear Hear. 1987 Jun;8(3):151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samore M. H., DeGirolami P. C., Tlucko A., Lichtenberg D. A., Melvin Z. A., Karchmer A. W. Clostridium difficile colonization and diarrhea at a tertiary care hospital. Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Feb;18(2):181–187. doi: 10.1093/clinids/18.2.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonmaker D., Heimberger T., Birkhead G. Comparison of ribotyping and restriction enzyme analysis using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for distinguishing Legionella pneumophila isolates obtained during a nosocomial outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1491–1498. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1491-1498.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell T. L., Schaberg D. R., Fekety F. R. Bacteriophage and bacteriocin typing scheme for Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1148–1152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1148-1152.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S. Epidemiologic markers of Clostridium difficile. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12 (Suppl 2):S192–S199. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_2.s192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler H., Mulligan M. E., Finegold S. M. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis patterns produced by Clostridium difficile. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S229–S234. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüst J., Sullivan N. M., Hardegger U., Wilkins T. D. Investigation of an outbreak of antibiotic-associated colitis by various typing methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1096–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1096-1101.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]