Abstract
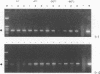
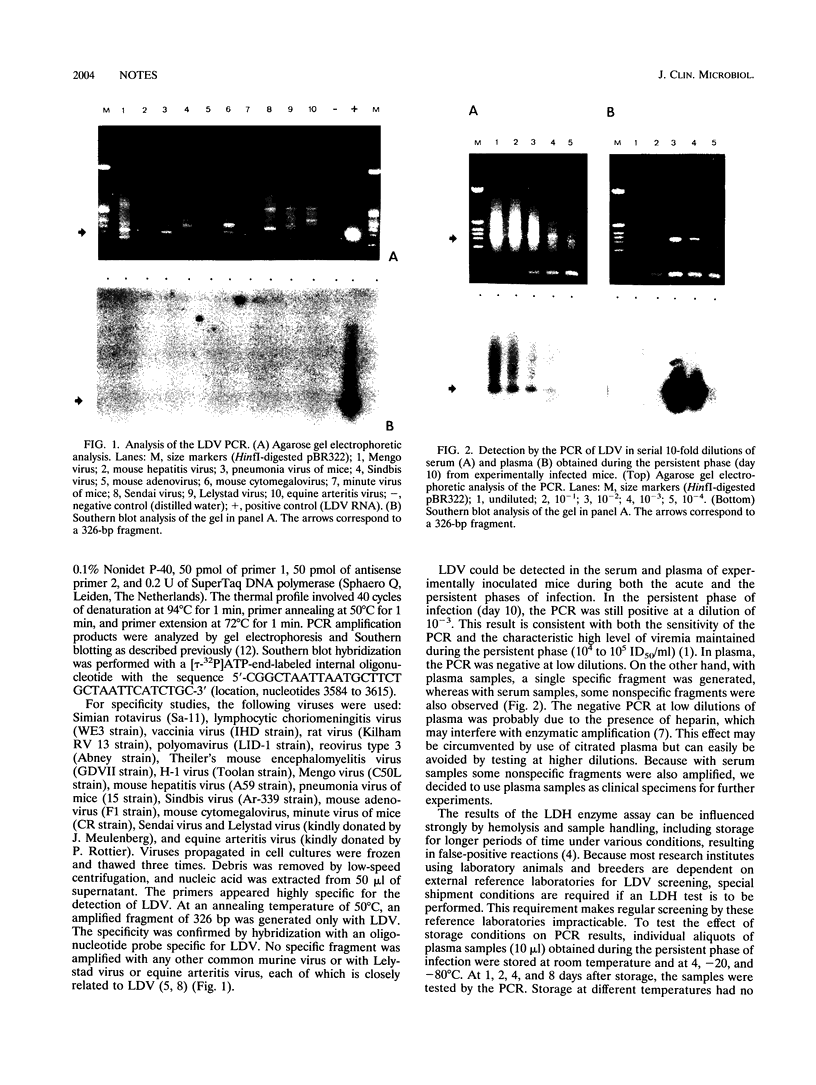
To improve the detection of lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus (LDV), we developed a PCR assay. Primers were selected from ORF7, encoding nucleocapsid protein VP1. No specific amplification was observed with any other common murine virus or with RNAs from the closely related Lelystad virus and equine arteritis virus. In experimentally infected mice, LDV could be detected in plasma in both the acute and the persistent phases. LDV was also detected by the PCR in contaminated pools of Plasmodium berghei parasites which were maintained in mice, both by a direct analysis of the samples and by testing of plasma from mice inoculated with these pools. There was a complete agreement between the results of the PCR assay and the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzyme assay of plasma from the inoculated mice. In contrast to the results of the LDH enzyme assay, no false-positive reactions were obtained in the PCR assay with negative control samples showing visible hemolysis. Storage of plasma samples at room temperature and at 4, -20, and -80 degrees C for up to 8 days did not influence the results of the PCR. These results show that the PCR is a valuable technique which may replace the LDH test as a diagnostic tool.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen Z., Kuo L., Rowland R. R., Even C., Faaberg K. S., Plagemann P. G. Sequences of 3' end of genome and of 5' end of open reading frame 1a of lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus and common junction motifs between 5' leader and bodies of seven subgenomic mRNAs. J Gen Virol. 1993 Apr;74(Pt 4):643–659. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-4-643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillberger J. E., Monroy P., Altman N. H. The effect of three bleeding techniques on lactic dehydrogenase levels in mice: implications for lactic dehydrogenase virus bioassay. Lab Anim Sci. 1987 Jun;37(3):356–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godeny E. K., Chen L., Kumar S. N., Methven S. L., Koonin E. V., Brinton M. A. Complete genomic sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus (LDV). Virology. 1993 Jun;194(2):585–596. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godeny E. K., Speicher D. W., Brinton M. A. Map location of lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus (LDV) capsid protein (Vp1) gene. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):768–771. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90546-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holodniy M., Kim S., Katzenstein D., Konrad M., Groves E., Merigan T. C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus gene amplification by heparin. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):676–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.676-679.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulenberg J. J., Hulst M. M., de Meijer E. J., Moonen P. L., den Besten A., de Kluyver E. P., Wensvoort G., Moormann R. J. Lelystad virus, the causative agent of porcine epidemic abortion and respiratory syndrome (PEARS), is related to LDV and EAV. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):62–72. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. IDENTIFICATION OF WM1 AS LDH VIRUS, AND ITS RECOVERY FROM WILD MICE IN MARYLAND. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:1015–1019. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley V., Spackman D. H., Santisteban G. A., Dalldorf G., Hellstrom I., Hellstrom K. E., Lance E. M., Rowson K. E., Mahy B. W., Alexander P. The LDH virus: an interfering biological contaminant. Science. 1978 Apr 14;200(4338):124–126. doi: 10.1126/science.263259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoll G. J., Melchers W. J., Kopecka H., Jambroes G., van der Poel H. J., Galama J. M. General primer-mediated polymerase chain reaction for detection of enteroviruses: application for diagnostic routine and persistent infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):160–165. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.160-165.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kuppeveld F. J., van der Logt J. T., Angulo A. F., van Zoest M. J., Quint W. G., Niesters H. G., Galama J. M., Melchers W. J. Genus- and species-specific identification of mycoplasmas by 16S rRNA amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2606–2615. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2606-2615.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]