Abstract
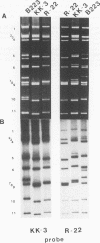
Serotype G3 equine rotaviruses isolated in Japan made up a common genogroup and were classified into two different genotypes. The genomes of serotype G3 equine rotaviruses with an identical electropherotype (isolated from 1982 to 1989) were very closely related to each other regardless of the year in which they were isolated. Serotype G3 equine rotavirus BI originating from England belonged to the same genogroup of serotype G3 equine rotaviruses isolated in Japan, although BI was classified as having a different genotype. The genomes of both serotype G10 equine rotavirus R-22 and serotype G10 calf rotavirus were closely related to each other.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Browning G. F., Chalmers R. M., Fitzgerald T. A., Corley K. T., Campbell I., Snodgrass D. R. Rotavirus serotype G3 predominates in horses. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):59–62. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.59-62.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning G. F., Chalmers R. M., Fitzgerald T. A., Snodgrass D. R. Evidence for two serotype G3 subtypes among equine rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):485–491. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.485-491.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning G. F., Chalmers R. M., Fitzgerald T. A., Snodgrass D. R. Serological and genomic characterization of L338, a novel equine group A rotavirus G serotype. J Gen Virol. 1991 May;72(Pt 5):1059–1064. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-5-1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning G. F., Chalmers R. M., Snodgrass D. R., Batt R. M., Hart C. A., Ormarod S. E., Leadon D., Stoneham S. J., Rossdale P. D. The prevalence of enteric pathogens in diarrhoeic thoroughbred foals in Britain and Ireland. Equine Vet J. 1991 Nov;23(6):405–409. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1991.tb03751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning G. F., Fitzgerald T. A., Chalmers R. M., Snodgrass D. R. A novel group A rotavirus G serotype: serological and genomic characterization of equine isolate FI23. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2043–2046. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2043-2046.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüssow H., Nakagomi O., Gerna G., Eichhorn W. Isolation of an avianlike group A rotavirus from a calf with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):67–73. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.67-73.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Hoshino Y., Boeggeman E., Purcell R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic relatedness among animal rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1986;87(3-4):273–285. doi: 10.1007/BF01315305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. E., Woode G. N., Xu Z. C., Williams J. D., Conner M. E., Dwyer R. M., Powell D. G. Analysis of serotypes and electropherotypes of equine rotaviruses isolated in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):889–893. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.889-893.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Isolation and characterization of an equine rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):585–591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.585-591.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Isolation, propagation, and characterization of a second equine rotavirus serotype. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1031–1037. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1031-1037.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa H., Sekiguchi K., Anzai T., Fukunaga Y., Kanemaru T., Ohishi H., Higuchi T., Kamada M. Epidemiology of equine rotavirus infection among foals in the breeding region. J Vet Med Sci. 1991 Dec;53(6):1079–1080. doi: 10.1292/jvms.53.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa H., Tanaka T., Sekiguchi K., Fukunaga Y., Anzai T., Minamoto N., Kamada M. Electropherotypes, serotypes, and subgroups of equine rotaviruses isolated in Japan. Arch Virol. 1993;131(1-2):169–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01379088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa H., Wada R., Hirasawa K., Akiyama Y., Oda T. Isolation of equine rotavirus in cell cultures from foals with diarrhea. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1984 Feb;46(1):1–9. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.46.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki M., Nakagomi O., Shibata S. Hemagglutinin activity of two distinct genogroups of feline and canine rotavirus strains. Arch Virol. 1992;122(3-4):373–381. doi: 10.1007/BF01317199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Nishioka N., Hashiguchi Y., Kuniyasu C. Serotypes of bovine rotaviruses distinguished by serum neutralization. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):851–855. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.851-855.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Akatani K., Ikegami N. Identification of rotavirus genogroups by RNA-RNA hybridization. Mol Cell Probes. 1989 Sep;3(3):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(89)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T. Genetic diversity and similarity among mammalian rotaviruses in relation to interspecies transmission of rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1991;120(1-2):43–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01310948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Hoshino Y., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic analysis of a human rotavirus that belongs to subgroup I but has an RNA pattern typical of subgroup II human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1159–1164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1159-1164.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Ohshima A., Aboudy Y., Shif I., Mochizuki M., Nakagomi T., Gotlieb-Stematsky T. Molecular identification by RNA-RNA hybridization of a human rotavirus that is closely related to rotaviruses of feline and canine origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1198-1203.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Matsuda Y., Ohshima A., Mochizuki M., Nakagomi O. Characterization of a canine rotavirus strain by neutralization and molecular hybridization assays. Arch Virol. 1989;106(1-2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF01311046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi T., Nakagomi O. RNA-RNA hybridization identifies a human rotavirus that is genetically related to feline rotavirus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1431–1434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1431-1434.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta C., Hoshi A., Goto H., Tsunoda N., Tagami M., Akita H. Epizootiological and virological studies of foal diarrhea associated with serotype 3 rotavirus. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1990 Oct;52(5):1049–1056. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.52.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Fitzgerald T., Campbell I., Scott F. M., Browning G. F., Miller D. L., Herring A. J., Greenberg H. B. Rotavirus serotypes 6 and 10 predominate in cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):504–507. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.504-507.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Hoshi A., Ohta C., Shirahata T., Goto H., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S. A minor prevalent strain in a severe outbreak of foal diarrhea associated with serotype 3 rotavirus. J Vet Med Sci. 1993 Aug;55(4):661–663. doi: 10.1292/jvms.55.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]