Abstract
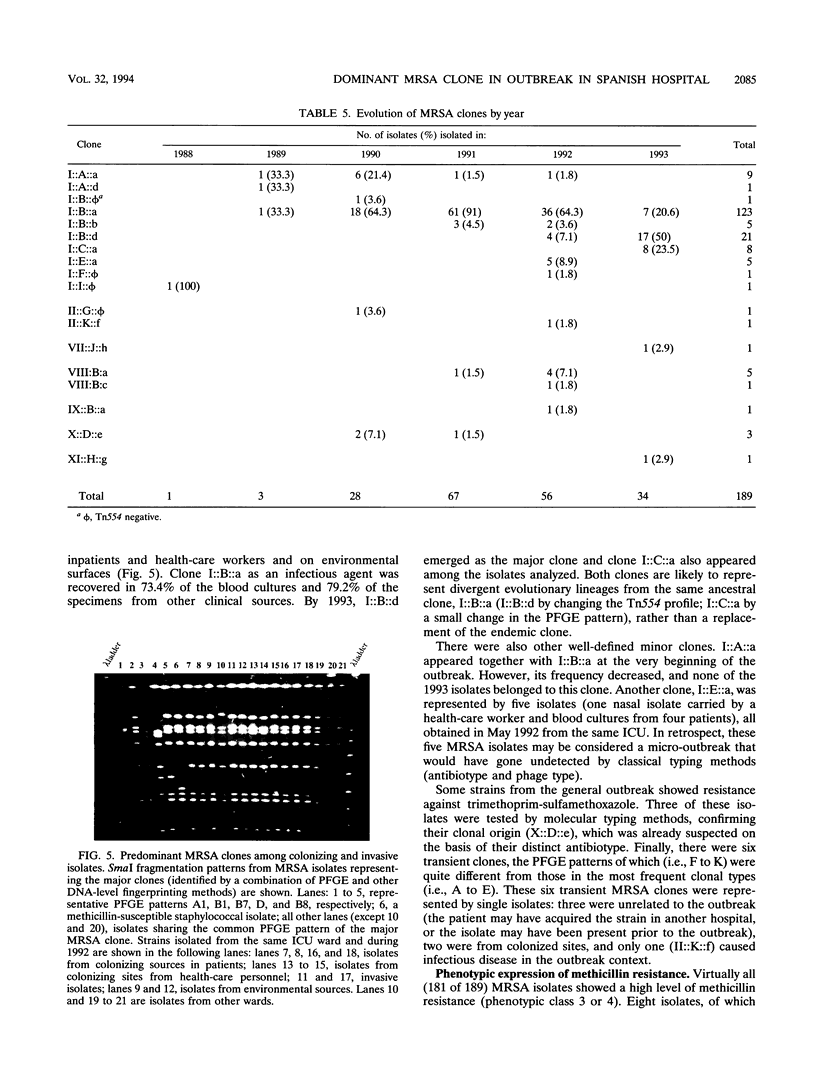
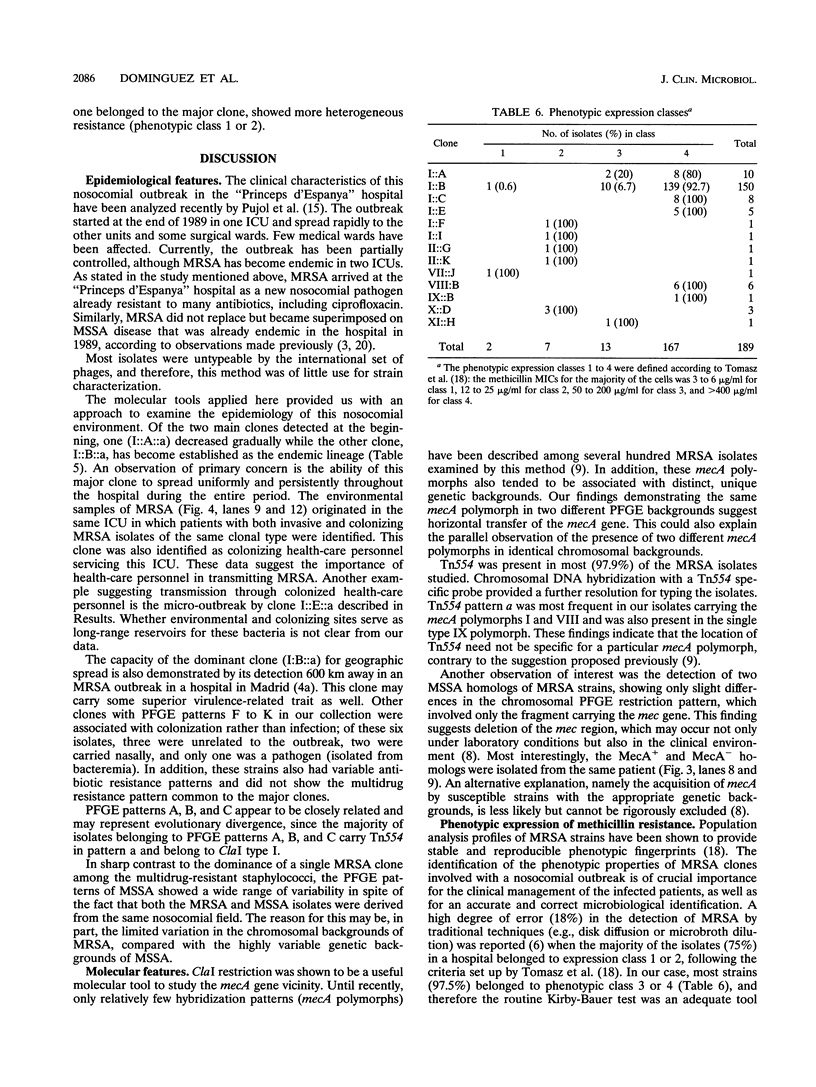
It was not until November 1989 that the 1,000-bed University-affiliated Hospital de Bellvitge "Princeps d'Espanya" in Barcelona first acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Since that time, the outbreak of MRSA disease has continued. We have analyzed by genomic DNA fingerprinting 189 MRSA isolates collected between late 1989 and the end of 1993. The isolates include both invasive and colonizing strains as well as isolates from health-care workers and environmental sources. In addition, 52 clinical isolates of methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) collected in the same hospital were also analyzed. Isolates were classified into clonal types on the basis of molecular typing techniques. A single MRSA clone (I::B::a) belonging to ClaI type I, pulsed-field gel electrophoretic pattern B, and Tn554 pattern a was responsible for the great majority of infections (73% of blood cultures and 79% of specimens from other clinical sources). This clone appeared at the very beginning of the outbreak, spread throughout the hospital wards, and was also carried by inpatients and health-care workers and on environmental surfaces. In contrast, no dominant lineage was apparent among MSSA isolates (33 distinct pulsed-field gel electrophoretic patterns among 52 isolates). Two MSSA isolates seem to have originated from the dominant clone by deletion of the mecA gene and some additional DNA. In several isolates, different mecA polymorphs were present in identical chromosomal backgrounds or cells with distinct chromosomal backgrounds carried the same mecA polymorph, suggesting horizontal transfer of the mecA gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyce J. M., Opal S. M., Potter-Bynoe G., Medeiros A. A. Spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a hospital after exposure to a health care worker with chronic sinusitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Sep;17(3):496–504. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.3.496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce J. M., White R. L., Spruill E. Y. Impact of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on the incidence of nosocomial staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):763–763. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Expression of methicillin resistance in heterogeneous strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):85–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis B., el-Adhami W., Stewart P. R. Methicillin-sensitive and -resistant homologues of Staphylococcus aureus occur together among clinical isolates. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):323–328. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B., Kornblum J., Arbeit R. D., Eisner W., Maslow J. N., McGeer A., Low D. E., Novick R. P. Evidence for a clonal origin of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):227–230. doi: 10.1126/science.8093647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Tomasz A. Involvement of multiple genetic determinants in high-level methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):874–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.874-879.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Kapur V. Clonal analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from intercontinental sources: association of the mec gene with divergent phylogenetic lineages implies dissemination by horizontal transfer and recombination. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2058–2063. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2058-2063.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevost G., Jaulhac B., Piemont Y. DNA fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis is more effective than ribotyping in distinguishing among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):967–973. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.967-973.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prévost G., Pottecher B., Dahlet M., Bientz M., Mantz J. M., Piémont Y. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis as a new epidemiological tool for monitoring methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an intensive care unit. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Apr;17(4):255–269. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90270-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pujol M., Peña C., Pallares R., Ayats J., Ariza J., Gudiol F. Risk factors for nosocomial bacteremia due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994 Jan;13(1):96–102. doi: 10.1007/BF02026134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struelens M. J., Deplano A., Godard C., Maes N., Serruys E. Epidemiologic typing and delineation of genetic relatedness of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by macrorestriction analysis of genomic DNA by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2599–2605. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2599-2605.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Nachman S., Leaf H. Stable classes of phenotypic expression in methicillin-resistant clinical isolates of staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vindel A., Sáez-Nieto J. A. Caracterización de cepas de Staphylococcus aureus resistentes a meticilina causantes de brotes mediante fagotipificación. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 1992 Nov;10 (Suppl 3):36–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge B. L., de Lencastre H., Tomasz A. Suppression of autolysis and cell wall turnover in heterogeneous Tn551 mutants of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1105–1110. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1105-1110.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lencastre H., Couto I., Santos I., Melo-Cristino J., Torres-Pereira A., Tomasz A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus disease in a Portuguese hospital: characterization of clonal types by a combination of DNA typing methods. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994 Jan;13(1):64–73. doi: 10.1007/BF02026129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lencastre H., Sá Figueiredo A. M., Urban C., Rahal J., Tomasz A. Multiple mechanisms of methicillin resistance and improved methods for detection in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):632–639. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]