Abstract
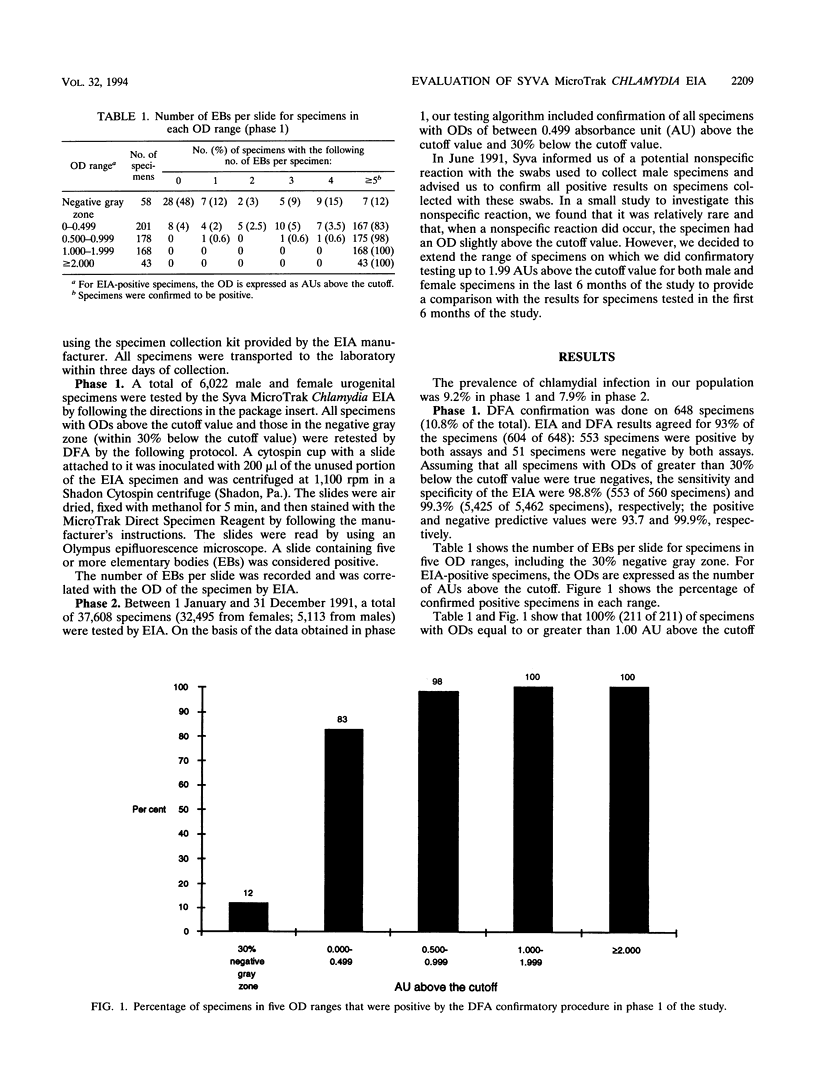
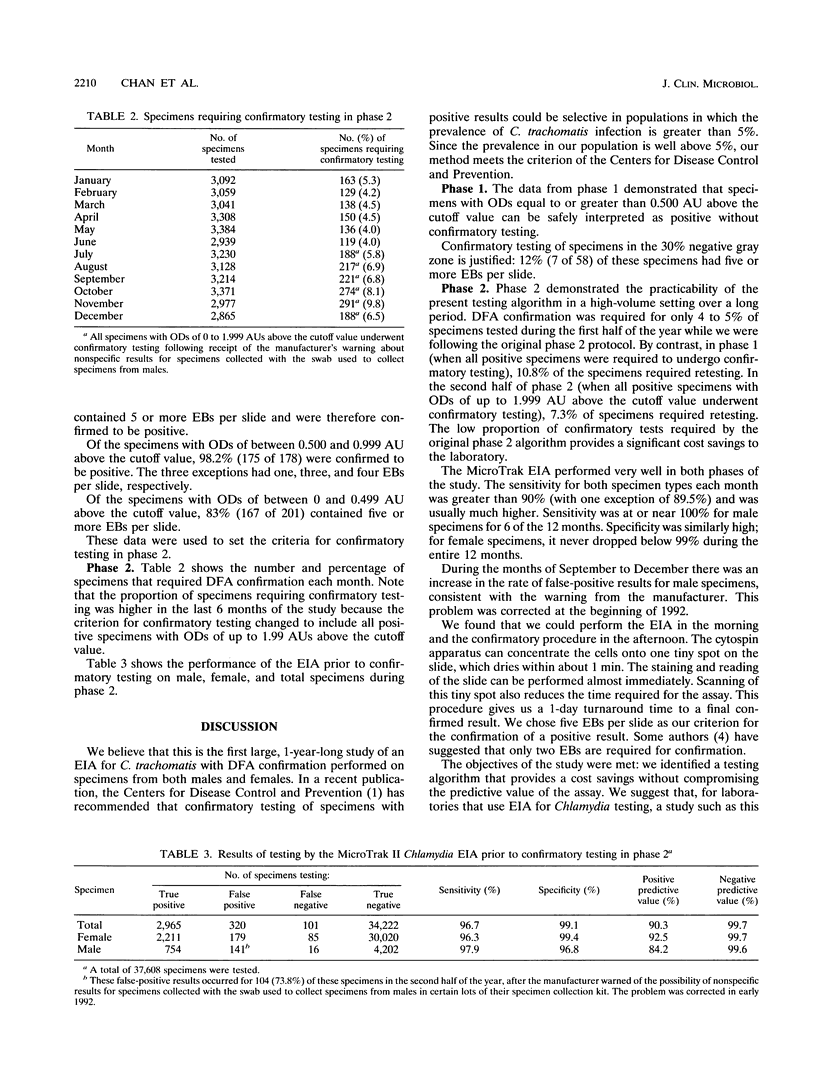
TThe Syva MicroTrak Chlamydia enzyme immunoassay (EIA; Syva Company, San Jose, Calif.) with cytospin and direct fluorescent-antibody assay (DFA) confirmation was evaluated on 43,630 urogenital specimens over a 1-year period in the Provincial Laboratory in Regina, Saskatchewan, Canada. This was a two-phase study intended to define a testing algorithm for Chlamydia trachomatis that would be both highly accurate and cost-effective in our high-volume (> 3,000 tests per month) laboratory. The prevalence of C. trachomatis infection in our population is moderate (8 to 9%). In phase 1, we tested 6,022 male and female urogenital specimens by EIA. All specimens with optical densities above the cutoff value and those within 30% below the cutoff value were retested by DFA. This was 648 specimens (10.8% of the total). A total of 100% (211 of 211) of the specimens with optical densities equal to or greater than 1.00 absorbance unit (AU) above the cutoff value, 98.2% (175 of 178) of the specimens with optical densities of between 0.500 and 0.999 AU above the cutoff value, and 83% (167 of 201) of the specimens with optical densities within 0.499 AU above the cutoff value were confirmed to be positive. A total of 12% (7 of 58) of the specimens with optical densities within 30% below the cutoff value were positive by DFA. In phase 2, we tested 37,608 specimens (32,495 from females; 5,113 from males) by EIA. Only those specimens with optical densities of between 0.499 AU above and 30% below the cutoff value required confirmation on the basis of data from phase 1 of the study. This was 4.5% of all specimens tested. This decrease in the proportion of specimens requiring confirmation provides a significant cost savings to the laboratory. The testing algorithm gives us a 1-day turnaround time to the final confirmed test results. The MicroTrak EIA performed very well in both phases of the study, with a sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of 96.1, 99.1, 90.3, and 99.7%, respectively, in phase 2. We suggest that for laboratories that use EIA for Chlamydia testing, a study such as this one will identify an appropriate optical density range for confirmatory testing for samples from that particular population.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kellogg J. A., Seiple J. W., Stroll E. S. Direct fluorescent-antibody confirmation of chlamydial antigen below the detection threshold of the chlamydiazyme enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jun;31(6):1646–1647. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.6.1646-1647.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada J., Schachter J., Bolan G., Nathan J., Shafer M. A., Clark A., Schwebke J., Stamm W., Mroczkowski T., Seliborska Z. Evaluation of Syva's enzyme immunoassay for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis in urogenital specimens. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Nov-Dec;15(8):663–668. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(92)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwebke J. R., Stamm W. E., Handsfield H. H. Use of sequential enzyme immunoassay and direct fluorescent antibody tests for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis infections in women. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2473–2476. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2473-2476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. E., Washington A. E. Epidemiology of sexually transmitted Chlamydia trachomatis infections. Epidemiol Rev. 1983;5:96–123. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


