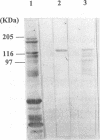
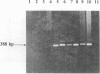
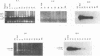
Abstract
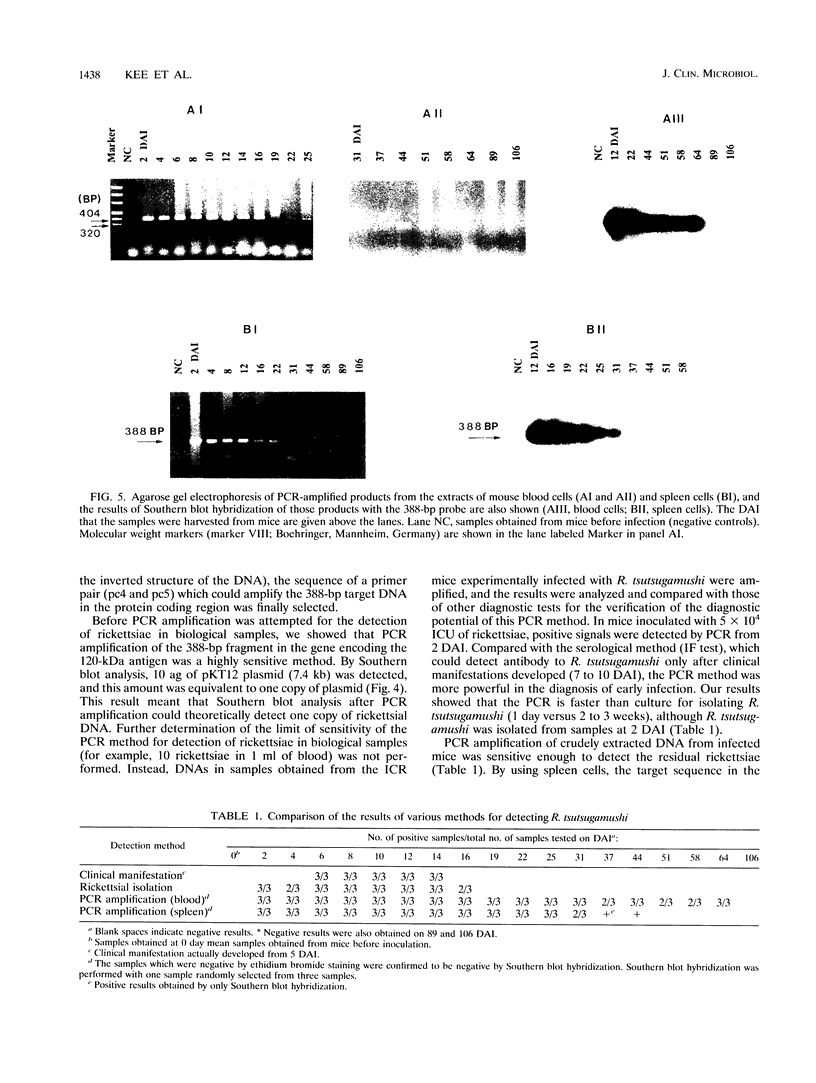
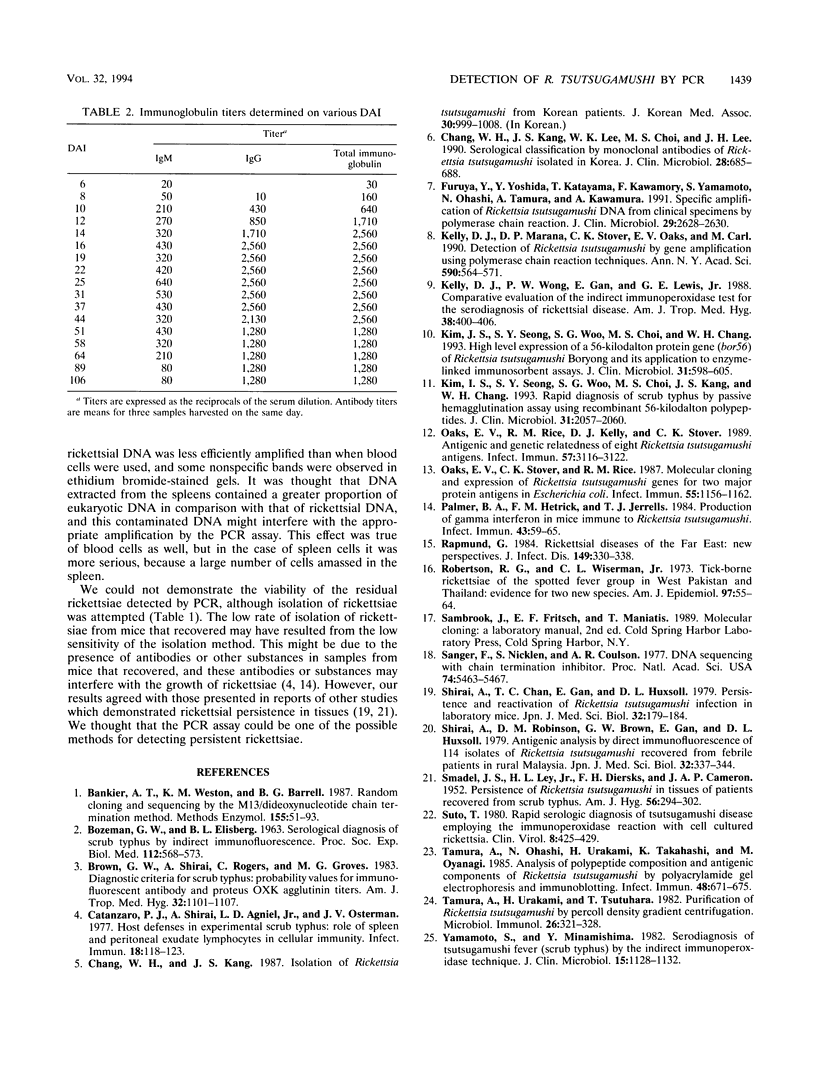
We developed a rapid procedure for the detection of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi DNA by the PCR technique. The primer pair used for the PCR was designed from the DNA sequence of the gene encoding a 120-kDa antigen, which was proven to be group specific by immunoblot analysis with mouse hyperimmune sera against various rickettsial strains. This PCR method was able to detect up to 10 ag of plasmid DNA (pKT12). Specific PCR products were obtained with DNAs from R. tsutsugamushi Kato, Karp, Gilliam, TA716, TA1817, and Boryong, but not with DNAs from other rickettsiae, such as R. prowazekii, R. typhi, R. akari, and strain TT118. In a study with experimentally infected mice, the PCR method could detect rickettsial DNA from 2 days after inoculation (DAI), whereas serum antibody against R. tsutsugamushi could be detected from 6 to 8 DAI by an immunofluorescence test. Although clinical manifestations subsided after 14 DAI, rickettsial DNA in blood samples could be detected by PCR for up to 64 DAI. These results suggest that this PCR method can be applied to the early diagnosis of scrub typhus and can also be used to detect the residual rickettsiae after clinical symptoms subside.
Full text
PDF

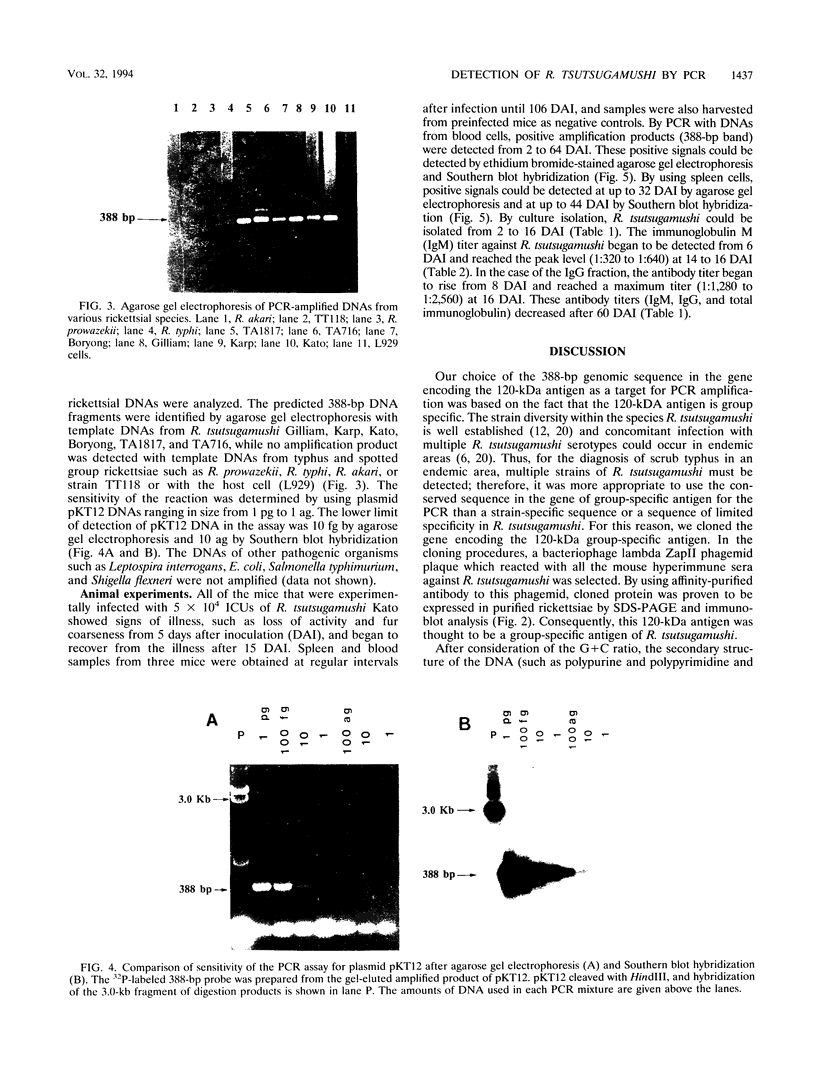
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOZEMAN F. M., ELISBERG B. L. Serological diagnosis of scrub typhus by indirect immunofluorescence. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Mar;112:568–573. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankier A. T., Weston K. M., Barrell B. G. Random cloning and sequencing by the M13/dideoxynucleotide chain termination method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:51–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. W., Shirai A., Rogers C., Groves M. G. Diagnostic criteria for scrub typhus: probability values for immunofluorescent antibody and Proteus OXK agglutinin titers. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Sep;32(5):1101–1107. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro P. J., Shiral A., Agniel L. D., Jr, Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: role of spleen and peritoneal exudate lymphocytes in cellular immunity. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):118–123. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.118-123.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. H., Kang J. S., Lee W. K., Choi M. S., Lee J. H. Serological classification by monoclonal antibodies of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi isolated in Korea. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):685–688. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.685-688.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya Y., Yoshida Y., Katayama T., Kawamori F., Yamamoto S., Ohashi N., Tamura A., Kawamura A., Jr Specific amplification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi DNA from clinical specimens by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2628–2630. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2628-2630.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. J., Marana D. P., Stover C. K., Oaks E. V., Carl M. Detection of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by gene amplification using polymerase chain reaction techniques. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:564–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. J., Wong P. W., Gan E., Lewis G. E., Jr Comparative evaluation of the indirect immunoperoxidase test for the serodiagnosis of rickettsial disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Mar;38(2):400–406. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim I. S., Seong S. Y., Woo S. G., Choi M. S., Chang W. H. High-level expression of a 56-kilodalton protein gene (bor56) of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi Boryong and its application to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):598–605. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.598-605.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim I. S., Seong S. Y., Woo S. G., Choi M. S., Kang J. S., Chang W. H. Rapid diagnosis of scrub typhus by a passive hemagglutination assay using recombinant 56-kilodalton polypeptides. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2057–2060. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2057-2060.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Rice R. M., Kelly D. J., Stover C. K. Antigenic and genetic relatedness of eight Rickettsia tsutsugamushi antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3116–3122. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3116-3122.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Stover C. K., Rice R. M. Molecular cloning and expression of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi genes for two major protein antigens in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1156–1162. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1156-1162.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer B. A., Hetrick F. M., Jerrells T. J. Production of gamma interferon in mice immune to Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):59–65. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.59-65.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapmund G. Rickettsial diseases of the Far East: new perspectives. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):330–338. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. G., Wisseman C. L., Jr Tick-borne rickettsiae of the spotted fever group in West Pakistan. II. Serological classification of isolates from West Pakistan and Thailand: evidence for two new species. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Jan;97(1):55–64. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMADEL J. E., LEY H. L., Jr, DIERCKS R. H., CAMERON J. A. P. Persistence of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in tissues of patients recovered from scrub typhus. Am J Hyg. 1952 Nov;56(3):294–302. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Chan T. C., Gan E., Huxsoll D. L. Persistence and reactivation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi infections in laboratory mice. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1979 Jun;32(3):179–184. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.32.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Robinson D. M., Brown G. W., Gan E., Huxsoll D. L. Antigenic analysis by direct immunofluorescence of 114 isolates of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi recovered from febrile patients in rural Malaysia. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1979 Dec;32(6):337–344. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.32.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Ohashi N., Urakami H., Takahashi K., Oyanagi M. Analysis of polypeptide composition and antigenic components of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):671–675. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.671-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Urakami H., Tsuruhara T. Purification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(4):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Minamishima Y. Serodiagnosis of tsutsugamushi fever (scrub typhus) by the indirect immunoperoxidase technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1128–1132. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1128-1132.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]