Abstract
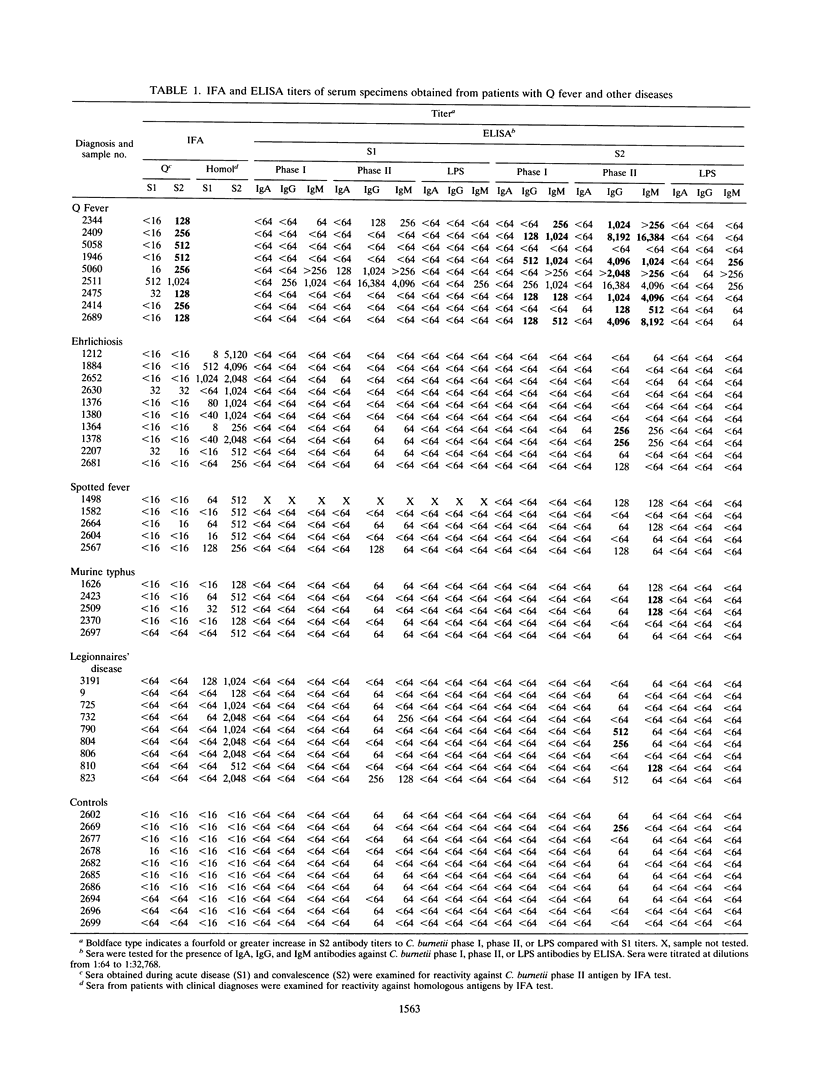
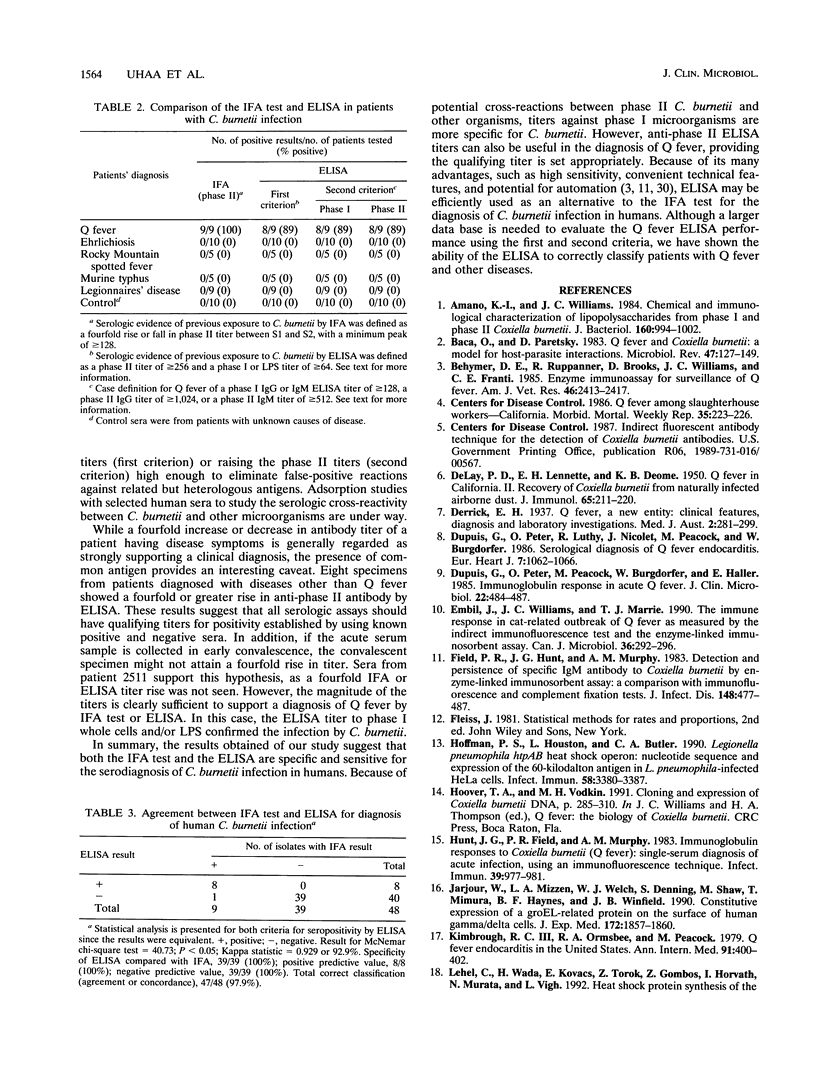
Ninety-five acute- and convalescent-phase serum specimens from 48 patients suspected of having rickettsial or Legionella infections were assayed for antibodies to Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of Q fever. To evaluate the specificity of the indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for human Q fever, we compared the ELISA results with those of the indirect immunofluorescence antibody (IFA) test. The ELISA data were analyzed by two different criteria for a positive test. The first criterion for positive results by ELISA was based upon diagnostic titers established in a study of 150 subjects who had no demonstrable cellular or humoral immune responses to C. burnetii phase I or phase II whole cells or phase I lipopolysaccharide. The second criterion was based upon diagnostic antibody titers in a study of 51 subjects who had been diagnosed as having clinical Q fever and had fourfold or greater rises in humoral immune responses to C. burnetii phase I and phase II whole-cell antigens. A comparison of the ELISA and IFA test results of the 95 serum specimens indicated excellent agreement between the tests (Kappa = 92.9%; P < 0.05). None of the 38 patients whose etiologies were confirmed serologically as Legionnaires' disease or rickettsial diseases other than Q fever were classified as positive for C. burnetii by the ELISA. Only one patient identified by the IFA test as having Q fever was not scored positive by the ELISA. These results suggest that the ELISA is useful for epidemiologic screening and as a diagnostic test for human Q fever.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Williams J. C. Chemical and immunological characterization of lipopolysaccharides from phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.994-1002.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Q fever and Coxiella burnetii: a model for host-parasite interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):127–149. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.127-149.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behymer D. E., Ruppanner R., Brooks D., Williams J. C., Franti C. E. Enzyme immunoassay for surveillance of Q fever. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Nov;46(11):2413–2417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLAY P. D., LENNETTE E. H., DEOME K. B. Q fever in California; recovery of Coxiella burnetii from naturally-infected air-borne dust. J Immunol. 1950 Aug;65(2):211–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis G., Péter O., Lüthy R., Nicolet J., Peacock M., Burgdorfer W. Serological diagnosis of Q fever endocarditis. Eur Heart J. 1986 Dec;7(12):1062–1066. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis G., Péter O., Peacock M., Burgdorfer W., Haller E. Immunoglobulin responses in acute Q fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):484–487. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.484-487.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embil J., Williams J. C., Marrie T. J. The immune response in a cat-related outbreak of Q fever as measured by the indirect immunofluorescence test and the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Apr;36(4):292–296. doi: 10.1139/m90-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field P. R., Hunt J. G., Murphy A. M. Detection and persistence of specific IgM antibody to Coxiella burnetii by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: a comparison with immunofluorescence and complement fixation tests. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):477–487. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Houston L., Butler C. A. Legionella pneumophila htpAB heat shock operon: nucleotide sequence and expression of the 60-kilodalton antigen in L. pneumophila-infected HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3380–3387. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3380-3387.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. G., Field P. R., Murphy A. M. Immunoglobulin responses to Coxiella burnetii (Q fever): single-serum diagnosis of acute infection, using an immunofluorescence technique. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):977–981. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.977-981.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarjour W., Mizzen L. A., Welch W. J., Denning S., Shaw M., Mimura T., Haynes B. F., Winfield J. B. Constitutive expression of a groEL-related protein on the surface of human gamma/delta cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1857–1860. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrough R. C., 3rd, Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M., Rogers W. R., Bennetts R. W., Raaf J., Krause A., Gardner C. Q fever endocarditis in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):400–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNETTE E. H., WELSH H. H. Q fever in California. X. Recovery of Coxiella burneti from the air of premises harboring infected goats. Am J Hyg. 1951 Jul;54(1):44–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehel C., Wada H., Kovács E., Török Z., Gombos Z., Horváth I., Murata N., Vigh L. Heat shock protein synthesis of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803: purification of the GroEL-related chaperonin. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(2):327–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00034959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McINTIRE M. S., WIEBELHAUS H. A., YOUNGSTROM J. A. Serological survey of packing house workers in Omaha for Q fever. Nebr State Med J. 1958 May;43(5):206–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhouse V. F., Shepard C. C., Redus M. D., Tzianabos T., McDade J. E. A comparison of the complement fixation, indirect fluorescent antibody, and microagglutination tests for the serological diagnosis of rickettsial diseases. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 Mar;28(2):387–395. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAVILANIS V., DUVAL L., FOLEY A. R., L'HEUREUX M. An epidemic of Q fever at Princeville, Quebec. Can J Public Health. 1958 Dec;49(12):520–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock M. G., Philip R. N., Williams J. C., Faulkner R. S. Serological evaluation of O fever in humans: enhanced phase I titers of immunoglobulins G and A are diagnostic for Q fever endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1089–1098. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1089-1098.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky R. L., Fishbein D. B., Greene C. R., Gensheimer K. F. An outbreak of cat-associated Q fever in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):202–204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péter O., Dupuis G., Burgdorfer W., Peacock M. Evaluation of the complement fixation and indirect immunofluorescence tests in the early diagnosis of primary Q fever. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;4(4):394–396. doi: 10.1007/BF02148690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péter O., Dupuis G., Peacock M. G., Burgdorfer W. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and complement fixation and indirect fluorescent-antibody tests for detection of Coxiella burnetii antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1063–1067. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1063-1067.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch A. M., Tanner M., Pacer R. E., Barrett M. J., Brokopp C. D., Schonberger L. B. Sheep-associated outbreak of Q fever, Idaho. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Feb;147(2):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner D. S., Shinnick T. M., Ardeshir F., Gillin F. D. Encystation of Giardia lamblia leads to expression of antigens recognized by antibodies against conserved heat shock proteins. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5312–5315. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5312-5315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke de Wit T. F., Bekelie S., Osland A., Miko T. L., Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Drijfhout J. W., Schöningh R., Janson A. A., Thole J. E. Mycobacteria contain two groEL genes: the second Mycobacterium leprae groEL gene is arranged in an operon with groES. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):1995–2007. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roges G., Edlinger E. Immunoenzymatic test for Q-fever. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;4(2):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychowdhury H. S., Kapoor M. Heat shock response in Neurospora crassa: purification and some properties of HSP 80. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;68(10):1218–1221. doi: 10.1139/o90-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L. A., Fishbein D. B., McDade J. E. Q fever: current concepts. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9(5):935–946. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.5.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman MYu, Goldberg A. L. Heat shock in Escherichia coli alters the protein-binding properties of the chaperonin groEL by inducing its phosphorylation. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):167–169. doi: 10.1038/357167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. Y., Goldberg A. L. Formation in vitro of complexes between an abnormal fusion protein and the heat shock proteins from Escherichia coli and yeast mitochondria. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7249–7256. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7249-7256.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover C. K., Marana D. P., Dasch G. A., Oaks E. V. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the Sta58 major antigen gene of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi: sequence homology and antigenic comparison of Sta58 to the 60-kilodalton family of stress proteins. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1360–1368. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1360-1368.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchio T. J. Predictive value of a single diagnostic test in unselected populations. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 26;274(21):1171–1173. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605262742104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. A heat shock operon in Coxiella burnetti produces a major antigen homologous to a protein in both mycobacteria and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1227–1234. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1227-1234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELSH H. H., LENNETTE E. H., ABINANTI F. R., WINN J. F. Air-borne transmission of Q fever: the role of parturition in the generation of infective aerosols. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jun 3;70(3):528–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb35409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waag D. M., Galloway A., Sandstrom G., Bolt C. R., England M. J., Nelson G. O., Williams J. C. Cell-mediated and humoral immune responses induced by scarification vaccination of human volunteers with a new lot of the live vaccine strain of Francisella tularensis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Sep;30(9):2256–2264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.9.2256-2264.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagar E. A., Schachter J., Bavoil P., Stephens R. S. Differential human serologic response to two 60,000 molecular weight Chlamydia trachomatis antigens. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):922–927. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Hoover T. A., Waag D. M., Banerjee-Bhatnagar N., Bolt C. R., Scott G. H. Antigenic structure of Coxiella burnetii. A comparison of lipopolysaccharide and protein antigens as vaccines against Q fever. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:370–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Peacock M. G., McCaul T. F. Immunological and biological characterization of Coxiella burnetii, phases I and II, separated from host components. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):840–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.840-851.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Walker D. H., Peacock M. G., Stewart S. T. Humoral immune response to Rocky Mountain spotted fever in experimentally infected guinea pigs: immunoprecipitation of lactoperoxidase 125I-labeled proteins and detection of soluble antigens of Rickettsia rickettsii. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.120-127.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Garbe T. R. Heat shock proteins and antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3086–3093. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3086-3093.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


