Abstract
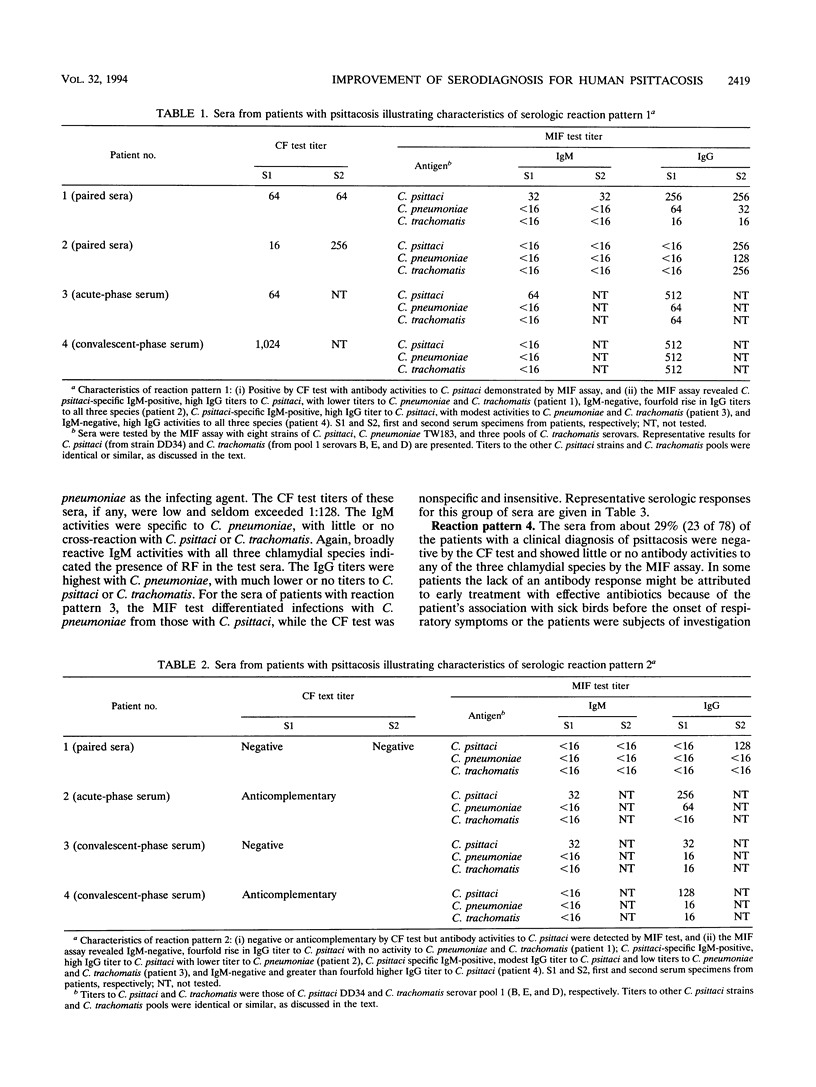
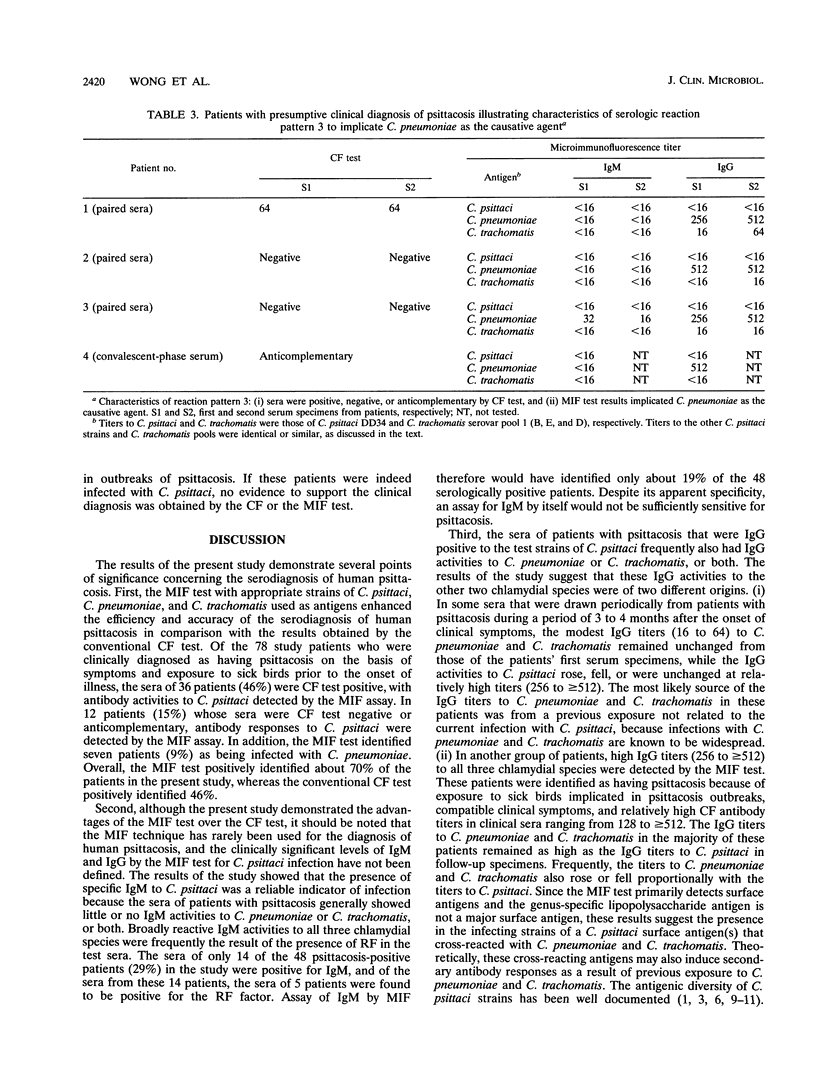
The serodiagnosis of human psittacosis was considerably improved by a microimmunofluorescence (MIF) assay that uses selected strains of Chlamydia psittaci, C. pneumoniae, and C. trachomatis as antigens. The 78 patients examined in the study were clinically diagnosed as having psittacosis on the basis of compatible clinical symptoms following exposure to sick birds. The conventional complement fixation (CF) test identified 36 patients, or 46% (36 of 78) of the total, as positive. Antibody responses to C. psittaci were demonstrated by the MIF test in all 36 CF-positive patients. The MIF test also detected antibody responses to C. psittaci in 12 patients (15% of the total) whose sera were negative or anticomplementary in the CF test. Seven patients, or 9% (7 of 78) of the total, were identified by the MIF test as having C. pneumoniae infections. About 30% of the study patients (23 of 78) showed no serologic evidence of either C. psittaci or C. pneumoniae infection by both the CF and the MIF tests. Four distinctive serologic reaction patterns were observed in the study patients. Recognition of these reaction patterns and judicious corroboration of serologic responses to the chlamydial species by the MIF test with epidemiologic and clinical information will increase the efficiency and accuracy of serodiagnosis for human psittacosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen A. A. Serotyping of Chlamydia psittaci isolates using serovar-specific monoclonal antibodies with the microimmunofluorescence test. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):707–711. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.707-711.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydén A., Kihlström E., Maller R., Persson K., Romanus V., Anséhn S. A clinical and epidemiological study of "ornithosis" caused by Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia pneumoniae (strain TWAR). Scand J Infect Dis. 1989;21(6):681–691. doi: 10.3109/00365548909021698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushi H., Hirai K. Immunochemical diversity of the major outer membrane protein of avian and mammalian Chlamydia psittaci. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.675-680.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuritsky J. N., Schmid G. P., Potter M. E., Anderson D. C., Kaufmann A. F. Psittacosis. A diagnostic challenge. J Occup Med. 1984 Oct;26(10):731–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Martinez J. A., Storz J. Antigenic diversity of Chlamydia psittaci of mammalian origin determined by microimmunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):905–910. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.905-910.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson K., Treharne J. Diagnosis of infection caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae (strain TWAR) in patients with "ornithosis" in southern Sweden 1981-1987. Scand J Infect Dis. 1989;21(6):675–679. doi: 10.3109/00365548909021697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pether J. V., Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Chlamydia pneumoniae, strain TWAR, as the cause of an outbreak in a boys' school previously called psittacosis. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Oct;103(2):395–400. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Banks J., Sugg N., Sung M., Storz J., Meyer K. F. Serotyping of Chlamydia. I. Isolates of ovine origin. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):92–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.92-94.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Banks J., Sugg N., Sung M., Storz J., Meyer K. F. Serotyping of Chlamydia: isolates of bovine origin. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):904–907. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.904-907.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyofuku H., Takashima I., Arikawa J., Hashimoto N. Monoclonal antibodies against Chlamydia psittaci. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(10):945–955. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb03025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Immunologic relationship between genital TRIC, lymphogranuloma venereum, and related organisms in a new microtiter indirect immunofluorescence test. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;70(3):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. Formalinized Chlamydia trachomatis organisms as antigen in the micro-immunofluorescence test. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):259–261. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.259-261.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. H., Skelton S. K., Chan Y. K. Efficient culture of Chlamydia pneumoniae with cell lines derived from the human respiratory tract. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1625–1630. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1625-1630.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreghitt T. G., Barker C. E., Treharne J. D., Phipps J. M., Robinson V., Buttery R. B. A study of human respiratory tract chlamydial infections in Cambridgeshire 1986-88. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Jun;104(3):479–488. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



