Abstract
NF-κB transcription factors regulate the expression of tissue factor (TF), a principal initiator of the coagulation cascade. Dominant among them is the p50/p65 heterodimer. Here we report that Andrographolide (Andro; a p50 inhibitor) and genetic deletion of p50 attenuated TF activity in stimulated endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages. Results of the electrophoretic mobility “supershift” assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation demonstrated the direct interaction of the p50/p65 heterodimer with the NF-κB site of the human TF promoter. Andro-treated and p50 null mice both exhibited blunted TF expression and reduced venous thrombosis, which were recapitulated by an anti-murine TF antibody in vivo. Our findings thus indicate that regulation of TF by NF-κB transcription factor p50 is essential for the pathogenesis of deep vein thrombosis and suggest that specific inhibitors of p50, such as Andro, may be therapeutically valuable for preventing and perhaps treating venous thrombosis.
Tissue factor (TF)3 is a key trigger of blood coagulation (1–3) and an important determinant of the hypercoagulable state associated with venous thrombosis (4). TF is a 47-kDa membrane glycoprotein that forms a cell-surface complex with coagulation factor VII/VIIa that proteolytically activates factors IX to IXa and X to Xa. The consequent activation of prothrombinase complex generates thrombin, which in turn leads to fibrin formation and platelet activation (5–7). Very low or undetectable levels of TF are constitutively expressed by resting endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages, although levels may be dramatically increased in certain forms of thrombosis.
The expression of TF is regulated principally at the transcriptional level (5). The promoter of human TF contains five binding sites for specificity protein 1 (Sp1), three sites for epidermal growth response-1 (Egr-1), two sites for activator protein-1 (AP-1), and one site for NF-κB. Notably, there has been a non-conservative change of guanine to cytosine in the oligonucleotide sequence of the NF-κB site in the human TF promoter, namely the TF-κB site. It is currently believed that Sp1 sites are mainly responsible for constitutive expression of the basal level of TF, whereas Egr-1, AP-1, and NF-κB sites are chiefly accountable for inducible expression of TF. Several agonists, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β, CD40, bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS), vascular endothelial growth factor, oxidized and acetylated low density lipoprotein (LDL), hypoxia, shear stress, and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), are known to induce the expression of TF in vascular endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages.
The family of NF-κB transcription factors has five cellular members, called p105/p50 (NF-κB1), p100/p52 (NF-κB2), p65 (RelA), RelB and c-Rel (8–10). Dominant among the five cellular members of NF-κB transcription factors is the p50/p65 heterodimer. In all cell types except B lymphocytes and plasma cells, NF-κB complexes are typically localized in the cytoplasm, where they bind to IκB inhibitory proteins, including IκBα, IκBβ, and IκBε. Upon stimulation, IκB proteins are rapidly phosphorylated by IκB kinase α and β (IKKα and -β) and degraded via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Degradation of IκB proteins exposes the nuclear localization signal on the p50/p65 heterodimer. Once translocated into nucleus, NF-κB triggers transcription of various targeting genes critical to thrombosis and inflammation, including TF, various cytokines/chemokines, and such cell adhesion molecules as E-selectin (CD62E) and VCAM-1 (5, 8–10).
The different subunits of NF-κB transcriptional factors apparently have distinctive roles in development and pathogenesis (8–10). For instance, p65-/-/p50-/- and c-Rel-/-/p65-/- mice manifest embryonic death due to extensive liver apoptosis; p52-/-/p50-/- mice manifest osteopetrosis due to failure of osteoclast maturation; and relB-/-/p50-/- mice manifest premature death within 1 month after birth due to multiorgan inflammation. In contrast, p50-/-/rel-/- mice grow normally from birth without obvious phenotypic alterations. However, p50 null mice have a significantly reduced inflammatory response in various models of inflammation, such as asthma (11), arthritis (12), and autoimmune encephalomyelitis (13), attesting to the critical role of p50 in the pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders.
The NF-κB transcription factor p65/c-Rel reportedly regulates TF expression in human monocytes and monocytic THP-1 cells in vitro (14, 15). However, whether other NF-κB transcription factors, such as p50 and p65 (presumably as the p50/p65 heterodimer), modulate the activity and expression of TF in monocytes/macrophages and vascular endothelial cells remains undetermined. Furthermore, the importance of transcriptional regulation of TF by NF-κB transcription factors, including the p65/c-Rel and p50/p65 heterodimers, has not been investigated in vivo.
We have recently reported (16, 18) that Andrographolide (Andro) covalently modifies reduced cysteine 62 of p50, thus blocking the NF-κB oligonucleotide from binding to nuclear proteins and preventing NF-κB-activated inflammation and neointimal hyperplasia in vitro and in vivo. Using Andro and primary cells isolated from p50 null mice, we investigated whether the NF-κB transcription factor p50 critically regulates TF expression in stimulated vascular endothelial cells and activated monocytes/macrophages. We further assessed the functional significance of p50 in modulation of TF-mediated experimental deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in mice.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Isolation of Primary Cells—The ethical review boards of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the University of Minnesota approved these studies. Informed consent was provided according to the Declaration of Helsinki. Human adherent monocytes were isolated from fresh human blood according to a previously published protocol (19). C57BL/6J (C57), B6;129P2-Nfkb1tm1Bal/J (p50 null mice), and B6129PF2/J (B6, background control for p50 null mice) were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). Murine macrophages were obtained by peritoneal lavage, according to a previously published method (20). The purity of monocytes was routinely >95% and viability was greater than >96% measured by trypan blue exclusion. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and murine pulmonary vein endothelial cells (PVECs) were cultured as previously described (17, 21–23).
Measurement of TF Activity—HUVECs, human monocytes, PVECs, and murine macrophages were treated with plain buffer, DMSO, and 15 μm 4H-Andro or Andro for 12 h followed by stimulation with 0.5 μg/ml LPS (serotype 055:B5; Sigma), 1,000 units/ml TNF-α (Pierce), or 0.1 μm PMA (Calbiochem, San Diego, CA) for 4 h, prior to measurements of TF activity. Human TF activity was determined by one-stage clotting assay for measurement of prothrombin time (23). TF concentrations were determined from prothormbin time, according to the standard curve generated by clotting of human platelet poor plasma using a serial dilution of commercial TF (Innovin™, Sysmex Corporation, Kobe, Japan) at a known concentration and a 4-channel coagulation instrument (Start 4 analyzer; Diagnostica Stago, Asnières, France). Due to the lack of a murine TF standard, relative TF units were used for measurement of murine TF activity, using a mixture of 10% rat plasma and 90% human plasma (24). For antibody inhibition experiments, cell lysates were preincubated with 0.2 μg/ml of rabbit preimmune IgG or anti-mTF Ab at 24 °C for 30 min.
Generation of Anti-murine TF Ab—A cDNA fragment encoding the 46–249-amino acid sequence of murine TF (20) (mTF; the entire extracellular portion of mTF truncated just before the transmembrane domain) was inserted into a pET-30a(+) vector with a His tag (Novagen, EMD Biosciences, Darmstadt, Germany) and recombinant mTF was expressed in Escherichia coli. After purification, it was used as an immunogen to generate rabbit antisera to mTF, which were further purified by Protein A chromatography as described before (20).
Transfection and Luciferase Assay—Human monocytic THP-1 cells (TIB-202; American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA) were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum, 4 mm l-glutamine, 100 units/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin at 37 °C in the presence of 5% CO2. Following washing twice with phosphate-buffered saline, an aliquot of 1 × 106 cells was transfected with plasmids of 1.5 μg of pL2, p2584, p2586, p2587, p2442, and p2447 and 0.5 μg of the pCMVβ vector (Clontech), respectively, in 1 ml of STBE (25 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 5 mm KCl, 0.7 mm CaCl2, 137 mm NaCl, 0.6 mm Na2HPO4, 0.5 mm MgCl2) supplemented with 150 μg of DEAE-Dextran (Sigma) at 37 °C for 20 min (25). After washing once with RPMI 1640 medium (without fetal bovine serum), the transfected cells were resuspended in 5 ml of complete RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 50 μm β-mercaptoethanol and plated at 2 × 105 cells/ml for each well of the 6-well tissue culture plate at 37 °C in the presence of 5% CO2 for 48 h. The transfected cells were incubated with DMSO or Andro for 12 h prior to treatment with 1,000 units/ml TNF-α. The cells were lysed and assayed for measurement of luciferase activities using the Luciferase Assay System (Promega, Madison, WI). Transfection efficiency was normalized with the β-galactosidase activities determined using a Luminescent β-Gal Detection Kit II (Clontech) (16).
Short Hairpin RNA-mediated Gene Suppression—The sequences of shRNAs targeting human c-Rel cDNA and human p50 cDNA were purchased from Open Biosystems (Huntsville, AL). The empty vector (mock) is pLKO.1. The sequence of c-Rel shRNA was: 5′-CCGGCCACCTATATAGATGCAGCATCTCGAGATGCTGCATCTATATAGGTGGTTTTTG-3′ (TRCN0000039983) and the sequence of non-inhibitory, control shRNA was: 5′-CCGGCCAGGAAGTTAGTGAATCTATCTCGAGATAGATTCACTAACTTCCTGGTTTTTG-3′ (TRCN0000039986). The sequence of p50 shRNA was: 5′-CCGGCCAGAGTTTACATCTGATGATCTCGAGATCATCAGATGTAAACTCTGGTTTTT-3′ (TRCN00006518), the sequence of control shRNA was: 5′-CCGGCGAATGACAGAGGCGTGTATACTCGAGTATACACGCCTCTGTCATTCGTTTTT-3′ (TRCN000006521). An aliquot of THP-1 cells (1 × 106 cells) was transfected with 3 μg of shRNA, using electroporation with Nucleofector Kit V (Amaxa Inc., Gaithersburg, MD) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
cDNA Cloning—The full-length cDNA encoding mouse p50 (1–430 amino acids) was directly amplified by polymerase chain reaction from the mouse lung cDNAs, using forward primer 5′-CTGAGGATCCATGGCAGACGATGATCCCTAC-3′ and reverse primer 5′-CTGCCTCGAGCTAATGGGTGACCCCTGCGTT-3′. The PCR product was digested with BamHI and XhoI and ligated into pCMV-3Tag-1A (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) with a FLAG tag at its N terminus. Its entire sequence was verified by nucleotide sequencing.
Mouse Macrophage Transfection—An aliquot of murine macrophages (1× 106 cells) was transfected with 2 μg of the plain pCMV-3Tag-1A vector or the plasmid of mouse p50 cDNA by electroporation with the Mouse Macrophage Nucleofetor Kit (Amaxa Inc.) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay—HUVECs were stimulated with 1 μg/ml LPS for 1 h, and nuclear proteins were prepared with a Nuclear Extract Kit (AY2002, Panomics, Redwood City, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Five μg of the nuclear protein was incubated with radiolabeled DNA probes (50 fmol) for 30 min at room temperature in a total 20-μl binding reaction, containing 20 mm HEPES, pH 7.9, 50 mm KCl, 0.5 mm EDTA, 5% glycerol, 1 mm dithiothreitol, 0.5 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin, 0.1% Nonidet P-40, and 50 μg/ml of poly(dI-dC)·poly(dI-dC). Protein-DNA complexes were separated from free DNA probe through 5% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel in 0.5× TBE buffer. Gels were dried and analyzed by autoradiography. For competition experiments, binding reactions were preincubated with unlabeled double-stranded oligonucleotides for the TF-κB consensus site (5′-GTCCCGGAGTTTCCTACCGGG-3′) and mutant control (5′-GTCCCGGAGTTAGATACCGGG-3′; Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc., Coralville, CA) for 30 min on ice before the addition of radiolabeled probes. Oligonucleotides were end-labeled with [γ-32P]ATP and T4 polynucleotide kinase (both from GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Piscataway, NJ). Identical competition experiments were carried out on oligonucleotides for the NF-κB consensus site (5′-AGTTGAGGGGACTTTCCCAGGC-3′) and mutant control (5′-AGTTGAGGCGACTTTCCCAGGC-3′; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA). For antibody supershift experiments, binding reactions were preincubated with p65 (sc-372x) and p50 (sc-7178x) supershift antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) for 30 min on ice before the addition of radiolabeled probes (16, 26).
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)—Confluent HUVECs were stimulated with 1 ng/ml TNF-α for 30 min and fixed by 1% formaldehyde (37% stock; Calbiochem) at 37 °C for 10 min. Following washing twice with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline, they were scraped and pelleted. HUVECs (1 × 106) were resuspended in 200 μl of SDS lysis buffer (50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.1, 10 mm EDTA, 1% SDS, 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 mg/ml aprotinin, and 1 mg/ml pepstatin A) and incubated on ice for 10 min. Cell lysates were sonicated to shear DNA using a Microson xL 2000 sonicator (3 × 10 s at 30% of the maximum potency). Sonicated cell supernatant was diluted 10 times with 16.7 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.1, 167 mm NaCl, 0.01% SDS, 1.1% Triton X-100, and 1.2 mm EDTA. One percent of the supernatant was saved as the input material control. The remaining supernatant was incubated with 4 μg of p65 (sc-372) or p50 (sc-7178) Abs (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) at 4 °C overnight. Immune complexes were collected with salmon sperm-saturated protein A and sequentially washed once with a low-salt immune complex washing buffer (20 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.1, 150 mm NaCl, 0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-100, and 2 mm EDTA), a high-salt immune complex washing buffer (20 mm Tris, pH 8.1, 0.5 m NaCl, 0.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-100 and 2 mm EDTA), a LiCl immune complex washing buffer (10 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.1, 0.25 m LiCl, 1% IGEPAL-CA630, 1% deoxycholic acid, and 1 mm EDTA), and finally washed twice with 10 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 1 mm EDTA. Immune complexes were then extracted by a 500-μl elution buffer (1% SDS and 0.1 m NaHCO3), and the protein-DNA cross-linking was reverted by heating the samples at 65 °C for 4 h (27). After digestion with 20 μg of proteinase K at 45 °C for 1 h, DNA was extracted by phenol-chloroform followed by ethanol precipitation. An aliquot of ⅓ immunoprecipitated DNA was subjected to PCR using specific TF promoter primers: forward, 5′-GCCCTCCCTTTCCTGCCATAGA-3′ and reverse, 5′-CCTCCCGGTAGGAAACTCCG-3′.
Immunoblotting—HUVECs, human monocytes, PVECs, and murine macrophages were treated with plain buffer, DMSO, and 15 μm 4H-Andro or Andro for 12 h followed by stimulation with 0.5 μg/ml LPS, 1,000 units/ml TNF-α, and 0.1 μm PMA for 4 h. Cells were lysed by the sample loading buffer and boiled for 5 min. Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes and detected with 1 μg/ml anti-mTF polyclonal Ab or Abs to c-Rel and p50 (both from Millipore, Billerica, MA) as well as FLAG tag (M2) and α-tubulin Ab (both from Sigma) followed by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG for chemiluminescent detection as described (16, 20).
Histology—The inferior vena cava was fixed by immersion in Bouin fixation solution (75% picric acid, 24% formaldehyde, 1% acetic acid) at 22 °C for 24 h followed by paraffin embedding, tissue sectioning (5 μm thick), and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (20). Leukocytes on the endothelium and within the venous wall were counted double blindly under a CX31 microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) at ×1,000 magnification.
DVT Model—To induce DVT, C57, B6, or p50 null mice (age 6–8 weeks; weight 20 to 25 g) were anesthetized with intraperitoneal injection of a solution composed of xylazine (12.5 mg/kg), ketamine (125 mg/kg), and atropine (0.025 mg/kg) diluted in an equal volume of saline (0.9% sodium chloride solution). A midline laparotomy was made; the small bowel was exteriorized from the body cavity and moved slightly to the left of the animal, and the inferior vena cava was directly approached by careful blunt dissection (28–30). Inferior vena cava was ligated below renal veins along with ligation of side branches. The incision was then closed in a two-layer fashion using 5-0 non-reactive suture material. On day 6, the inferior vena cava was removed, weighed, and measured for length. The weight was then normalized to length. For drug treatment experiments, 4H-Andro and Andro (5 μg/g of body weight) were intraperitoneally given 2 h before the surgery.
Immunohistochemical and Immunofluorescence Staining—For immunohistochemical staining, tissue sections were subsequently dewaxed and endogenous peroxidase was quenched with 3% H2O2 in methanol. Prior to staining, nonspecific binding was blocked by incubation with 10% bovine serum albumin in 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 0.15 m NaCl, and 0.02% NaN3 (TBS) at 37 °C for 30 min. Tissue sections were incubated with rabbit preimmune IgG (10 μg/ml), rabbit anti-mTF Ab (10 μg/ml), anti-fibrin II β chain monoclonal Ab (clone T2G1; 10 μg/ml; Accurate Chemical, Westbury, NY), rabbit anti-E-selectin polyclonal Ab (6 μg/ml), and anti-VCAM-1 polyclonal Ab (8 μg/ml; BD Pharmingen, San Diego, CA) in TBS containing 1% bovine serum albumin at 4 °C overnight in a humidified chamber. The horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit or rat IgG Ab (Sigma) was applied at 37 °C for 1 h. After washing, color development was carried out by incubation with 0.05% 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (Sigma) in TBS supplemented with 0.1% H2O2 for 10 min. All incubations were followed by washing three times in TBS over 15 min. Tissue sections were counterstained with hematoxylin and slides were finally mounted with coverslip (16, 20).
For immunofluorescence co-localization of TF, tissue sections were treated with the same immunohistochemical steps as described above. They were then incubated simultaneously with 10 μg/ml rabbit anti-mTF Ab and mouse anti-smooth muscle α-actin monoclonal antibody (Sigma), 20 μg/ml rat anti-mouse CD41 monoclonal antibody (BD Biosciences), and rat anti-mouse CD68 monoclonal antibody (AbD Serotec, Oxford, UK), or 16 μg/ml biotinylated rabbit anti-human von Willebrand factor Ab (Sigma). For gray level analysis after immunostaining, four sites of each vessel and totally four vessels with no hematoxylin staining were analyzed for staining density using the NIH Image (version 1.6) software package.
Statistical Analyses—To determine statistical significance, Student's unpaired t test was used for comparison between groups. A p value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
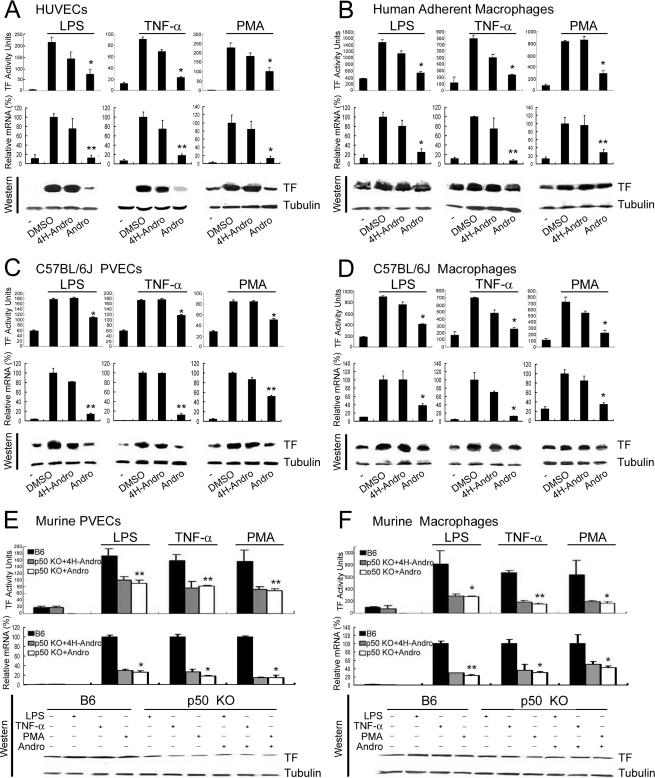
Andro Suppresses TF in Stimulated Endothelial Cells and Activated Monocytes/Macrophages—Using a rabbit anti-mTF polyclonal Ab, we found that treatment of HUVECs (Fig. 1A), human adherent monocytes (Fig. 1B), murine PVECs (Fig. 1C), and murine peritoneal macrophages (Fig. 1D) stimulated with LPS, TNF-α, and PMA dramatically increased the activity and expression of TF. Compared with DMSO (a solvent control) and 4H-Andro (4-hydro-andrographolide, an inactive structural analog), Andro attenuated the activity and expression of TF in activated human and murine endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages. Notably, in contrast to rabbit anti-mTF polyclonal Ab that neutralized TF activity, Andro did not affect the activity of TF when it was added directly to lysates of stimulated HUVECs (data not shown). As Andro binds to p50 and inhibits NF-κB activation (16), these results indicate that NF-κB transcription factor p50 is essential for transcriptional regulation of TF in stimulated human and murine endothelial cells and activated monocytes/macrophages.
FIGURE 1.
Andro treatment and p50 knock-out inhibit TF activity and expression in stimulated human and murine endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages. A–D, HUVECs (A), human adherent macrophages (B), C57BL/6J PVECs (C), and C57BL/6J macrophages (D) were stimulated with LPS, TNF-α, and PMA, in the presence of buffer (-), DMSO (a solvent control), 4H-Andro (an inactive structural analog), and Andro. Cell lysates were measured for TF activity (upper panels) and TF expression (lower panels). Results are presented as either the mean ± S.D. value of triplicate measurements of three independent experiments (upper panels,*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus DMSO group) or a representative of three independent experiments (lower panels). Although 4H-Andro appeared to partially inhibit TF activity and mRNA induced by TNF-α and PMA, these differences were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). E and F, TF activity and expression in stimulated endothelial cells and macrophages isolated from p50 null mice. PVECs (E) and macrophages (F) were isolated from B6 mice and p50 null mice. Following treatment with LPS, TNF-α, and PMA in the absence or presence of 4H-Andro and Andro, the activity (upper panels) and expression (lower panels) of TF were measured. Results are presented as either the mean ± S.D. value of triplicate measurements of three independent experiments (upper panels,*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus B6 group) or a representative of three independent experiments (lower panels).
Requirement of p50 for TF Up-regulation in Activated Endothelial Cells and Macrophages—Given that Andro targets p50 (16) and inhibits TF expression (16, 18 (Fig. 1, A–D), we reasoned that genetic deletion of p50 would blunt TF activity induced by various thrombogenic and inflammatory agonists. Indeed, compared with the cellular counterparts isolated from B6 mice, the TF activity and expression were reduced in cells isolated from p50 null mice to ∼50% in PVECs (Fig. 1E) and ∼70% in peritoneal macrophages (Fig. 1F) upon challenges with LPS, TNF-α, and PMA. Notably, the same dose of Andro that potently inhibited TF in activated wild-type endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages (Fig. 1, A–D) did not further suppress the TF activity and expression in stimulated PVECs and macrophages isolated from p50 null mice, indicating that Andro primarily targets p50 for down-regulation of TF expression.
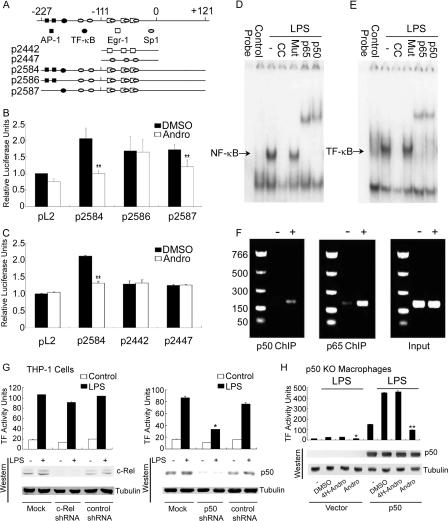
Andro Antagonizes the TF-κB Site in Human TF Promoter—To examine the effect of Andro on the activity of the human TF promoter (5, 14, 15), human monocytic THP-1 cells were transfected with various human TF promoter luciferase gene reporter plasmids that contained either five Sp1 sites, three Egr-1 sites, two AP-1 sites, or one TF-κB site (Fig. 2A). Luciferase activity was measured following incubation of transfectants with TNF-α in the presence of DMSO or Andro. As expected, TNF-α enhanced the activity of human TF promoter in THP-1 cells transfected with human TF promoter plasmids of wild-type (p2584), TF-κB site mutant (p2586), and AP-1 site mutant (p2587), but the plain vector (pL2) showed no change in activity (Fig. 2B). Compared with the activity of wild-type human TF promoter (p2584), TNF-α was apparently less potent at increasing of the promoter activities of THP-1 cells transfected with plasmids of the TF-κB site mutant (p2586) and AP-1 site mutant (p2587). Following treatment with Andro, but not with DMSO, the TNF-α-induced activity of the human TF promoter in THP-1 cells transfected with the plasmid of wild-type human TF promoter (p2584) was reduced to the basal level of luciferase activity seen in pL2 transfectants. Notably, compared with DMSO, Andro did not inhibit the activity of the human TF promoter in THP-1 cells transfected with the plasmid of the TF-κB site mutant with intact AP-1 sites (p2586), suggesting that Andro specifically acts on the TF-κB site, but not on the AP-1 sites. In addition, TNF-α failed to augment the activity of human TF promoter in THP-1 cells transfected with plasmids of plain vector (pL2), Sp1 site mutant (p2442), or Egr-1 site mutant (p2447), as compared with those transfected with the plasmid of wild-type (p2584) human TF promoter (Fig. 2C). Together, these data indicate that Andro specifically prevents the binding of p50 to the TF-κB site without affecting the AP-1, Sp1, and Egr-1 sites of the human TF promoter.
FIGURE 2.
Andro inhibits the promoter activity of the human TF gene and p50/p65 heterodimer binds to the TF-κB site. A, schematic description of the constructs of the human TF promoter. The plasmid of p2584 (-227 to +121) contains all the binding sites for AP-1, NF-κB, Sp1, and Egr-1 transcription factors. The plasmid of p2586 (-227 to +121) contains the AP-1, Sp1, and Egr-1 sites and a mutated NF-κB site. The plasmid of p2587 (-227 to +121) has the mutation of two AP-1 sites only. The plasmid of p2442 (-111 to +14) contains three Egr-1 sites, and the plasmid of p2447 (-111 to +14) contains the last three Sp1 sites. B, Andro targets the NF-κB site of the human TF promoter. THP-1 cells were transfected with plasmids of plain vector (pL2), p2584, p2586, and p2587 in the presence of DMSO and Andro. Transfectants were then incubated with TNF-α followed by measurements of luciferase activity using the Luciferase Assay System (Promega). C, Andro fails to antagonize the Egr-1 and Sp1 sites of the human TF promoter. THP-1 cells were transfected with the plasmids of pL2, p2584, p2442, and p2447 in the presence of DMSO and Andro. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. value of triplicate measurements from three separate experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus DMSO group). D–F, the binding of p50/p65 heterodimer to the TF-κB site in the promoter of human TF. Radiolabeled NF-κB(D) and TF-κB(E) oligonucleotides were bound to nuclear proteins isolated from resting, LPS-stimulated HUVECs in the absence or presence of their unlabeled consensus and mutant oligonucleotide or anti-p50 and p65 Abs. Alternatively, ChIP was employed using anti-p50 and p65 Abs followed by PCR for amplification of TF promoter (F). G, p50 shRNA, but not c-Rel shRNA, attenuates TF activity. THP-1 cells were transfected with the plain vector (mock) or the plasmid of c-Rel shRNA, p50 shRNA, or non-inhibitory, control shRNAs and incubated with LPS for measurements of TF activity and immunoblotting. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. value of triplicate measurements from three separate experiments. H, rescue of TF activity in p50-deficient macrophages and its inhibition by Andro. Macrophages isolated from p50 null mice were transfected with the plain vector or the plasmid of mouse p50 cDNA in the presence of DMSO, 4H-Andro, and Andro. They were then incubated with LPS for determination of TF activity and immunoblotting. Results are presented as the representative mean ± S.D. value of at least three separate experiments.
p50 Binds to the TF-κB Site in the Promoter of Human TF—To demonstrate whether p50 binds directly to the TF-κB site in the human TF promoter, we performed experiments using electrophoretic mobility shift assay and ChIP. Radiolabeled oligonucleotides of NF-κB (Fig. 2D) and TF-κB (Fig. 2E) were not retarded in the absence of incubation with nuclear proteins (designated as probe). However, both oligonucleotides bound avidly to nuclear proteins isolated from LPS-stimulated HUVECs, but not to those from unstimulated HUVECs. The specific protein/probe bindings were inhibited by excessive amounts of unlabeled consensus oligonucleotides, but not mutant oligonucleotides. Importantly, addition of p50 and p65 antibodies further retarded a majority of them (i.e. so-called “supershift”). In comparison with unstimulated HUVECs (still p65 and p50 antibodies added), both p50 and p65 antibodies immunoprecipitated the promoter of the human TF gene from chromatins of TNF-α-stimulated HUVECs (Fig. 2F). Thus, our findings obtained by two divergent approaches of electrophoretic mobility shift assay and ChIP provide convergent evidence for the direct interaction between the p50/p65 heterodimer and the TF-κB site in human TF promoter.
As the p65/c-Rel heterodimer has been previously reported to regulate TF expression (31), we used the small interfering RNA approach and examined the functional significance of c-Rel in modulation of TF activity. Compared with their non-inhibitory, control shRNAs, c-Rel and p50 shRNAs both abrogated the respective expression of c-Rel and p50 proteins in THP-1 cells (Fig. 2G). Interestingly, only p50 shRNA, but not c-Rel shRNA, suppressed LPS-induced TF activity. In addition, transfection of macrophages isolated from p50 null mice with the plasmid of mouse full-length, wild-type p50 cDNA resulted in overt p50 expression and drastically increased TF activity, especially following LPS challenge (Fig. 2H). Importantly, Andro, but not DMSO or 4H-Andro, almost completely neutralized TF activity. These results collectively argue for the biological importance of p50, but apparently not for c-Rel, in transcriptional regulation of TF in stimulated monocytes/macrophages.
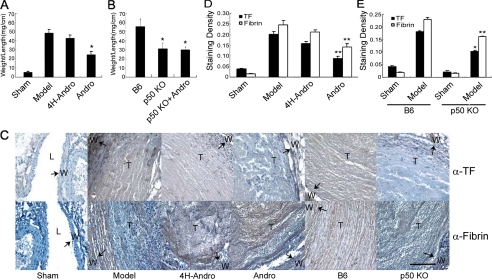
Inhibition or Deletion of p50 Suppresses Experimental DVT—Using murine models of experimental DVT, we investigated whether Andro treatment and p50 knock-out altered TF-mediated coagulation in venous thrombosis. Compared with the sham control, ligation of the inferior vena cava (the model group) caused venous thrombosis, as measured by an increased weight/length ratio of the thrombotic inferior vena cava (Fig. 3A). Andro decreased the weight/length ratio of venous thrombosis, as compared with 4H-Andro. Similarly, the initiation and propagation of DVT (Fig. 3B) were attenuated in p50 null mice when compared with pathologic lesions in B6 mice. The weight/length ratio of venous thrombosis was not further affected by Andro treatment (Fig. 3B) in p50 null mice, indicating that Andro specifically targets p50 and p50 critically regulates TF in vivo. Taken together, our results demonstrate the functional importance of p50 in murine models of experimental DVT.
FIGURE 3.
Inhibition of p50 attenuates DVT and down-regulates TF. A, Andro reduces venous thrombosis. C57 mice were either untreated (sham group, n = 5; model group, n = 9), treated with 4H-Andro (4H-Andro group, n = 9), or treated with Andro (Andro group, n = 8) intraperitoneally 2 h before surgery. Inferior vena cava was ligated below renal veins along with ligation of side branches. At day 6, inferior vena cava was removed, weighed, and measured for length. The weight was then normalized to length to assess venous thrombosis. B, p50 deficiency decreases venous thrombosis. B6 mice (n = 12) and p50 null mice untreated (n = 12) or treated with Andro (n = 8) were subjected to inferior vena cava ligation and the venous thrombosis measurement as described above. C–E, immunohistochemical staining of injured veins. The ligated inferior vena cava was fixed, paraffin-embedded, sectioned, and stained with the rabbit anti-mTF polyclonal Ab or a rat monoclonal Ab to fibrin followed by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit or rat IgG Ab and 3,3′-diaminobenzidine. Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Results are presented as either a representative of three independent experiments or the mean ± S.D. value of triplicate measurements of two independent experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus model group of C57 or B6). In panel C, arrows indicate positive staining. W, vessel wall; T, thrombus; L, lumen. Bar scale in all images is 50 μm.
Suppression or Knock-out of p50 Decreases TF Expression and Fibrin Deposition—We next examined TF expression and deposition of fibrin in our in vivo models of DVT. Compared with sham groups, TF expression was up-regulated in the model of DVT (Fig. 3, C and D). Treatment with Andro, but not 4H-Andro, significantly suppressed TF expression. Consistently, TF expression was also reduced in model groups of p50 null mice, as compared with those in model groups of B6 mice (Fig. 3, C and E). Compared with sham groups, we observed an increased deposition of fibrin in model groups (Fig. 3, C–E). Importantly, Andro treatment significantly lessened fibrin deposition as compared with 4H-Andro treatment (Fig. 3, C and D). Compared with B6 mice, p50 null mice also manifested a reduced deposition of fibrin (Fig. 3, C and E), suggesting that p50 is fundamentally important for TF-mediated deposition of fibrin in our experimental model of DVT.
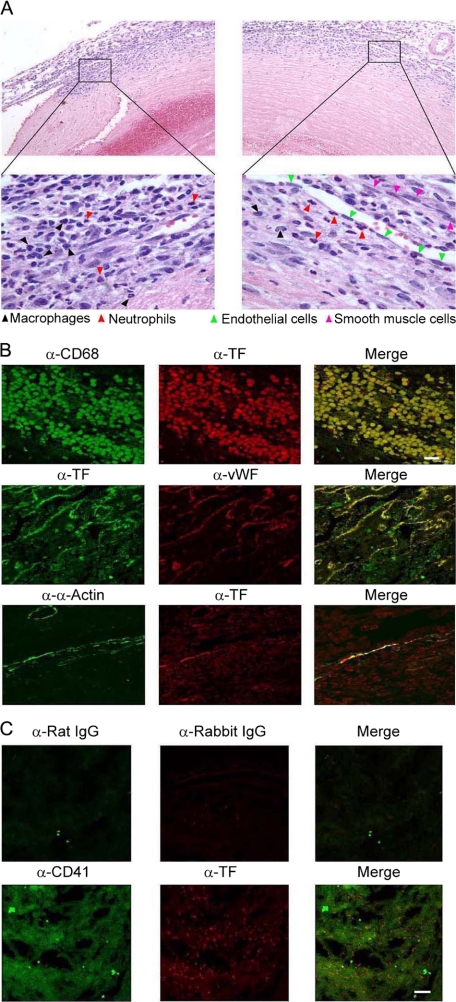
Infiltrated Macrophages, Aggregated Platelets, Stimulated Endothelial Cells, and Activated Smooth Muscle Cells Express TF—To determine the constituents of venous thrombi, we sectioned venous thrombi obtained from our murine model of experimental DVT and performed H&E staining. Clusters of macrophages and neutrophils were clearly visible within tissue sections of venous thrombi (Fig. 4A). In addition, vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells were scattered within the venous thrombi.
FIGURE 4.
Cellular origin of TF in experimental DVT. A, H&E staining of venous thrombus. Venous samples were sectioned (5 μm thick) continuously and stained with H&E. Results are representative of multiple venous thrombi obtained from separate experiments. Upper panels, ×200; lower panels, ×1,000. B and C, immunofluorescence co-localization of TF. Venous sections were stained for TF, which was completely co-localized with infiltrated macrophages (CD68 positive; B) and activated endothelial cells (von Willebrand factor, vWF positive; B) and partially co-localized with stimulated smooth muscle cells (α-actin positive; B) and aggregated platelets (CD41 positive; C). Results are representative of three independent experiments. Bar scale in all images is 10 μm.
In search of the cellular origin of TF, we carried out an immunofluorescence co-localization study using laser scanning confocal microscopy. TF expression was co-localized with CD68 (a marker for macrophages; Fig. 4B, upper panel), von Willebrand factor (a marker for endothelial cells; Fig. 4B, middle panel), α-actin (a marker for smooth muscle cells; Fig. 4B, lower panel), and CD41 (a marker for activated platelets; Fig. 4C) in DVT samples, attesting to the induction and/or localization of TF expression in macrophages, platelets, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells within the venous thrombotic lesion.
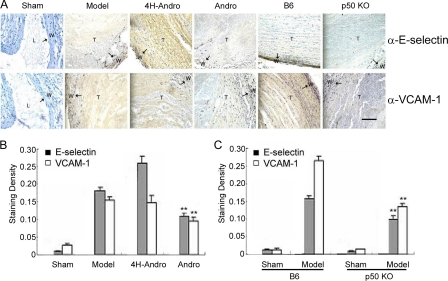
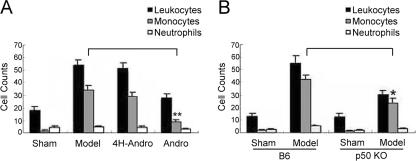
Elimination of p50 Reduces the Expression of NF-κB Targeting Genes in Vivo—The de novo synthesis of E-selectin and VCAM-1 on vascular endothelial cells is well known to be exclusively regulated by NF-κB transcription factors (16, 32–34). We thus determined whether the expression of E-selectin and VCAM-1 is regulated by p50-mediated NF-κB activation in our murine models of experimental DVT. As expected, the expression of E-selectin and VCAM-1 was undetectable in normal vein walls (Fig. 5, A and B). However, they were markedly up-regulated in the vein wall and thrombi of model groups. Compared with model groups and 4H-Andro treatment, Andro treatment significantly reduced the staining of E-selectin and VCAM-1 in the vein wall and thrombi (Fig. 5, A and B). Interestingly, vein wall thickness was significantly increased, and a strong staining of E-selectin and VCAM-1 was detected in vein walls and thrombi of the DVT model group, indicating that venous endothelial cells proliferate and migrate during the pathogenesis of experimental DVT (35–39). The expression of E-selectin and VCAM-1 was almost completely absent in model groups of p50 null mice (Fig. 5, A and C). Our data, thus, argue for the exclusive regulation of these NF-κB targeting genes by p50 in our models of experimental DVT. As a consequence of inhibiting the p50-mediated inflammatory response, it is worth mentioning that the deposition of leukocytes, mainly macrophages and/or neutrophils, in the venous walls was dramatically decreased in Andro-treated mice (Fig. 6A) and p50 null mice (Fig. 6B), compared with their respective model groups.
FIGURE 5.
Expression of NF-κB targeting genes in deep vein thrombosis. A, immunohistochemical staining of E-selectin and VCAM-1 in cross-sections of inferior vena cava. Results displayed are representative of multiple sections of more than 5 samples from at least two separate experiments. B and C, results are also analyzed statistically as the mean ± S.D. value of triplicate measurements of two independent experiments (**, p < 0.01 versus model group). Bar scale for all images is 50 μm.
FIGURE 6.
Andro treatment and p50 deficiency suppress leukocyte infiltration in injured veins. Venous tissue from C57 mice (A) and B6 versus p50 null mice (B) were fixed, paraffin-embedded, sectioned, and H&E stained. Neutrophils, monocytes/macrophages, and lymphocytes were identified and counted under a microscope (oil immersion at ×1,000), based on standard histological criteria including nuclear size, morphology, and total cell size. Identification of macrophages and neutrophils were occasionally confirmed by staining with anti-CD68 or elastase Ab. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. value of five respective fields for each section (three sections per animal) examined (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus model group of C57 or B6).
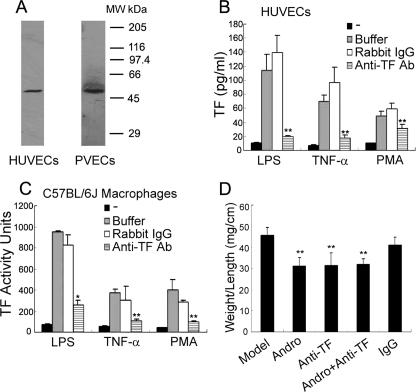
Blockade of TF Activity Attenuates Experimental DVT—To examine whether the beneficial effects of Andro treatment and p50 deletion were mainly due to down-regulation of TF, we tested whether our rabbit anti-mTF polyclonal Ab ablated TF activity in vitro and suppressed venous thrombosis in vivo. Indeed, this rabbit polyclonal Ab specifically recognized human and murine TF in whole cell lysates of stimulated HUVECs and murine macrophages (Fig. 7A). It also potently neutralized the TF activities of HUVECs (Fig. 7B) and murine macrophages (Fig. 7C), following challenge with LPS, TNF-α, and PMA.
FIGURE 7.
In vivo attenuation of venous thrombosis by TF Ab. A, specific binding of anti-mTF Ab to human and murine TF. Detergent lysates of stimulated HUVECs and murine macrophages were immunoblotted by the rabbit anti-mTF polyclonal Ab. B and C, inhibition of human and murine TF activity by anti-mTF Ab. HUVECs and murine macrophages were stimulated with LPS, TNF-α, and PMA, and the activity of human and murine TF was determined in the presence of rabbit preimmune IgG and anti-mTF Ab. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. value of triplicate measurements of three independent experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus rabbit IgG group). D, thrombotic mice were either untreated (n = 7) or treated with Andro (n = 13), anti-mTF Ab (n = 11), Andro plus the anti-mTF (n = 10), or rabbit preimmune IgG (n = 6). After 6 days, venous thrombi were removed, weighed, and measured for length. The weight was then normalized to length. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. value from two separate experiments (**, p < 0.01 versus model group).
Analogous to Andro, intravenous injection of this Ab decreased the weight/length ratio of venous thrombi (Fig. 7D), whereas preimmune rabbit IgG had no such effect. Importantly, combined administration of anti-mTF Ab plus Andro did not further reduce venous thrombosis (Fig. 7D), as compared with administration of this Ab alone. These findings indicate that the transcriptional regulation of TF mediated by p50 is at least one of the primary mechanisms contributing to the pathogenesis of experimental DVT.
DISCUSSION
The present study demonstrates the fundamental importance of NF-κB transcription factor p50 (presumably the p50/p65 heterodimer) in transcriptional regulation of TF in stimulated human and murine monocytes/macrophages and vascular endothelial cells in vitro and in the murine model of experimental DVT in vivo. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first in vivo demonstration of a partial suppression (∼50%) of venous thrombosis by targeting the p50-mediated transcriptional regulation of TF in stimulated vascular endothelial cells and activated monocytes/macrophages.
Whereas p50 is critically important to the modulation of TF during the pathogenesis of DVT, other possible contributors responsible for the remaining pathological lesions following the suppression of TF activity await to be identified. In this regard, the in vivo significance of transcriptional regulation of TF by Egr-1 and AP-1 in the diseased state warrants revisitation (5, 14, 15).
In the pathogenesis of venous thrombosis, the synergistic cooperation between thrombosis and inflammation is well documented (40–42). During the initiation and propagation of deep vein thrombosis, activated leukocytes, including neutrophils and macrophages, are recruited into the thrombi and vessel walls from the luminal of vessels through a cascade of cellular adhesive events. The selectin family of cell adhesion molecules mediates leukocyte tethering and rolling, which brings circulating leukocytes into proximity of cytokines and/or chemoattractants displayed on, or released from, activated endothelium (43–47). In coordination with extracellular stimuli through pertussis toxin-sensitive Gi-type heterotrimeric G protein-coupled receptor molecules, selectins also trigger inside-out signaling events that activate integrins for maximal adhesion (arrest) of leukocytes to endothelium (48–50).
We observed the induction of such NF-κB targeting genes as TF, E-selectin, and Vcam-1 and their inhibition by Andro treatment and p50 deletion in our models of experimental DVT (Figs. 3, C and D, and 5, A and B). As E-selectin and VCAM-1 are cell adhesion molecules for leukocytes expressed on stimulated endothelial cells, the down-regulation of their expression leads to a reduction of infiltrated and deposited leukocytes, including neutrophils and macrophages (Fig. 6, A and B). However, E-selectin and VCAM-1 expression must be considered in the context of the finding that the anti-mTF Ab duplicates the inhibitory effect of Andro treatment and p50 deletion on venous thrombosis (Fig. 7D). Although p50-mediated transcriptional regulation of TF is important pathologically, it should not be interpreted as definitive evidence for the functional insignificance of inflammatory processes in these pathological conditions. Instead, caution should be exercised in interpreting the data obtained from murine models of experimental DVT. More specifically, the simple ligation of the inferior vena cava in healthy mice might not accurately represent the clinical onset of diseases commonly associated with complex pathological changes in humans.
Notably, the p65/c-Rel heterodimer of NF-κB transcription factors has been previously shown to critically regulate TF expression (31). Our data presented in this study further indicates the essential role of the p50/p65 heterodimer in transcriptional regulation of TF in activated vascular endothelial cells and stimulated monocytes/macrophages. Importantly, we have provided the in vivo evidence for the functional significance of the p50/p65 heterodimer in modulation of TF expression during the pathogenesis of experimental DVT. Unfortunately, it is impossible for in vivo testing of the functional importance of p65/c-Rel for TF expression during arterial and venous thrombosis, as p65-/-/p50-/- and c-Rel-/-/p65-/- mice are embryonically lethal due mainly to extensive liver apoptosis (8–10). As the result, the definitive, in vivo functional significance of c-Rel-/-/p65-/- in venous thrombosis awaits to be tested experimentally using conditional knock-out of these candidate genes in mice.
In the previous studies (16, 18), we reported that Andro covalently conjugates reduced cysteine 62 of p50 as the underlying molecular mechanism for blockade of NF-κB oligonucleotide binding to nuclear proteins and prevention of NF-κB activation in inflammation and neointimal hyperplasia. Extending this line of investigation, we have now established the specificity of the inhibitory effect of Andro on p50 in vitro and in vivo, using the p50-deficient peritoneal macrophages and PVECs and the murine model of experimental deep vein thrombosis in p50 knock-out mice. On the basis of these encouraging findings, we are currently testing a variety of Andro derivatives, designed as small molecular weight antagonists of p50 for inhibition of NF-κB activation, for therapeutic prevention and treatment of inflammation, arterial restenosis, and venous thrombosis.
Acknowledgments
We thank Yi-Feng Xia for preliminary studies, Ronald R. Bach for insightful comments, and Michael Franklin for editing the manuscript.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant RO1AI064743. This work was also supported by an Asia-Pacific International Molecular Biology Network and Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology professorship, National Science Foundation of China Grants 30721065, 30623003, 30700409, 30771960, and 30630036, Ministry of Science and Technology of China Grants 2006CB943902, 2006AA02Z169, 2007CB947102, and 2007CB914501, Chinese Academy of Sciences Grants KSCX2-YW-R-67 and KJCX2-YW-H08, Shanghai Municipal Commission for Science and Technology Grants 06DZ22032 and 058014578, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences Grant 2007KIP203. The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
Footnotes
The abbreviations used are: TF, tissue factor; Andro, Andrographolide; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; PVEC, pulmonary vein endothelial cells; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; Ab, antibody; mTF, murine tissue factor; shRNA, short hairpin RNA; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation.
References
- 1.Tilley, R., and Mackman, N. (2006) Semin. Thromb. Hemostasis 32 5-10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Polgar, J., Matuskova, J., and Wagner, D. D. (2005) J. Thromb. Hemostasis 3 1590-1596 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Del Conde, I., Shrimpton, C. N., Thiagarajan, P., and López, J. A. (2005) Blood 106 1604-1611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Steffel, J., Luscher, T. F., and Tanner, F. C. (2006) Circulation 113 722-731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mackman, N. (1997) Thromb. Haemostasis 78 747-754 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Key, N. S., and Bach, R. R. (2001) Thromb. Haemostasis 85 375-376 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Morrissey, J. H. (2003) J. Thromb. Hemostasis 1 878-880 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ghosh, S., May, M. J., and Kopp, E. B. (1998) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16 225-260 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li, Q., and Verma, I. M. (2002) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2 725-773 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hayden, M. S., and Ghosh, S. (2008) Cell 132 344-362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yang, L., Cohn, L., Zhang, D. H., Homer, R., Ray, A., and Ray, P. (1998) J. Exp. Med. 188 1739-1750 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Campbell, I. K., Gerondakis, S., O'Donnell, K., and Wicks, I. P. (2000) J. Clin. Investig. 105 1799-1806 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hilliard, B., Samoilova, E. B., Liu, T. S., Rostami, A., and Chen, Y. (1999) J. Immunol. 163 2937-2943 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Parry, G. C., and Mackman, N. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269 20823-20825 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Oeth, P., Parry, G. C., and Mackman, N. (1997) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 17 365-374 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xia, Y. F., Ye, B. Q., Li, Y. D., Wang, J. G., He, X. J., Lin, X., Yao, X., Ma, D., Slungaard, A., Hebbel, R. P., Key, N. S., and Geng, J. G. (2004) J. Immunol. 173 4207-4217 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Geng, J. G., Bevilacqua, M. P., Moore, K. L., McIntyre, T. M., Prescott, S. M., Kim, J. M., Bliss, G. A., Zimmerman, G. A., and McEver, R. P. (1990) Nature 343 757-760 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang, Y. J., Wang, J. T., Fan, Q. X., and Geng, J. G. (2007) Cell Res. 17 933-941 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mercurio, A. M., Schwarting, G. A., and Robbins, P. W. (1984) J. Exp. Med. 160 1114-1125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang, B., Xiao, Y., Ding, B. B., Zhang, N., Yuan, X., Gui, L., Qian, K. X., Duan, S., Chen, Z., Rao, Y., and Geng, J. G. (2003) Cancer Cell 4 19-29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Marelli-Berg, F. M., Peek, E., Lidington, E. A., Stauss, H. J., and Lechler, R. I. (2000) J. Immunol. Methods 244 205-215 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ozcan, M., Morton, C. T., Solovey, A., Dandelet, L., Bach, R. R., Hebbel, R. P., Slungaard, A., and Key, N. S. (2001) Thromb. Haemostasis 85 250-255 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Janson, T. L., Stormorken, H., and Prydz, H. (1984) Haemostasis 14 440-444 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Andrews, B. S., Rehemtulla, A., Fowler, B. J., Edgington, T. S., and Mackman, N. (1991) Gene (Amst.) 98 265-269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mack, K. D., Wei, R., Elbagarri, A., Abbey, N., and McGrath, M. S. (1998) J. Immunol. Methods 211 79-86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wang, J. G., Mahmud, S. A., Thompson, J. A., Geng, J. G., Key, N. S., and Slungaard, A. (2006) Blood 107 558-565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nandiwada, S. L., Li, W., Zhang, R., and Mueller, D. L. (2006) J. Immunol. 177 401-413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Myers, D., Jr., Farris, D., Hawley, A., Wrobleski, S., Chapman, A., Stoolman, L., Knibbs, R., Strieter, R., and Wakefield, T. (2002) J. Surg. Res. 108 212-221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Myers, D. D., Hawley, A. E., Farris, D. M., Wrobleski, S. K., Thanaporn, P., Schaub, R. G., Wagner, D. D., Kumar, A., and Wakefield, T. W. (2003) J. Vasc. Surg. 38 1075-1089 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sullivan, V. V., Hawley, A. E., Farris, D. M., Knipp, B. S., Varga, A. J., Wrobleski, S. K., Thanapron, P., Eagleton, M. J., Myers, D. D., Fowlkes, J. B., and Wakefield, T. W. (2003) J. Surg. Res. 109 1-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Oeth, P. A., Parry, G. C., Kunsch, C., Nantermet, P., Rosen, C. A., and Mackman, N. (1994) Mol. Cell Biol. 14 3772-3781 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Whitley, M. Z., Thanos, D., Read, M. A., Maniatis, T., and Collins, T. (1994) Mol. Cell Biol. 14 6464-6475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Neish, A. S., Williams, A. J., Palmer, H. J., Whitley, M. Z., and Collins, T. (1992) J. Exp. Med. 176 1583-1593 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shu, H. B., Agranoff, A. B., Nabel, E. G., Leung, K., Duckett, C. S., Neish, A. S., Collins, T., and Nabel, G. J. (1993) Mol. Cell Biol. 13 6283-6289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wakefield, T. W., Linn, M. J., Henke, P. K., Kadell, A. M., Wilke, C. A., Wrobleski, S. K., Sarkar, M., Burdick, M. D., Myers, D. D., and Strieter, R. M. (1999) J. Vasc. Surg. 30 885-892 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Henke, P. K., Wakefield, T. W., Kadell, A. M., Linn, M. J., Varma, M. R., Sarkar, M., Hawley, A., Fowlkes, J. B., and Strieter, R. M. (2001) J. Surg. Res. 99 84-91 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Singh, I., Burnand, K. G., Collins, M., Luttun, A., Collen, D., Boelhouwer, B., and Smith, A. (2003) Circulation 107 869-875 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Modarai, B., Burnand, K. G., Humphries, J., Waltham, M., and Smith, A. (2005) Thromb. Haemostasis 93 801-809 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Modarai, B., Burnand, K. G., Sawyer, B., and Smith, A. (2005) Circulation 111 2645-2653 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wakefield, T. W., and Henke, P. K. (2005) Semin. Vasc. Surg. 18 118-129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Viles-Gonzalez, J. F., Fuster, V., and Badimon, J. J. (2005) Am. Heart. J. 149 Suppl. 1, S19-S31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wakefield, T. W., Strieter, R. M., Prince, M. R., Downing, L. J., and Greenfield, L. J. (1997) Cardiovasc. Surg. 5 6-15 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Springer, T. A. (1994) Cell 76 301-314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Laudanna, C., Kim, J. Y., Constantin, G., and Butcher, E. (2002) Immunol. Rev. 186 37-46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Furie, B., Furie, B. C., and Flaumenhaft, R. A. (2001) Thromb. Haemostasis 86 214-221 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.McEver, R. P. (2002) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14 581-586 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Geng, J. G., Chen, M., and Chou, K. C. (2004) Curr. Med. Chem. 11 2153-2160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ma, Y. Q., Plow, E. F., and Geng, J. G. (2004) Blood 104 2549-2556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Atarashi, K., Hirata, T., Matsumoto, M., Kanemitsu, N., and Miyasaka, M. (2005) J. Immunol. 174 1424-1432 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Woollard, K. J., Kling, D., Kulkarni, S., Dart, A. M., Jackson, S., and Chin-Dusting, J. (2006) Circ. Res. 98 149-156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]