Abstract
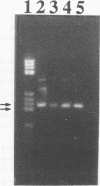
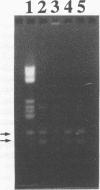
Several genes and sequences in Bordetella pertussis have been used as targets in diagnostic PCR assays. A previously developed single-step PCR assay for the detection of B. pertussis was based on an insertion sequence, IS480, that is present in about 70 to 80 copies in each genome. The diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, and reliability of this assay with aspirated and heat-treated samples from the nasopharynx of patients and their contacts was improved by the use of a nested PCR configuration. The nested PCR assay produced a 205-bp fragment with all of the 115 B. pertussis strains tested and was negative with all strains belonging to other Bordetella species (n = 44) as well as other bacteria commonly found in the upper respiratory tract (n = 115). The diagnostic value of the assay was verified by giving positive results for B. pertussis in all the 51 nasopharyngeal aspirates from culture-positive patients. The assay also detected 18 positive aspirates from a total of 196 culture-negative patients. A confirmatory cleavage of the 205-bp nested PCR product by MvaI gave in all cases two bands of 88 and 117 bp. In conclusion, this newly developed nested PCR assay was shown to be reasonably fast and uncomplicated, with an optimal sensitivity and a high degree of specificity for the diagnosis of B. pertussis in aspirated nasopharyngeal samples processed simply by heat treatment. The detection level in the nested PCR was about 10 bacteria per ml, or seven to eight insertion sequence copies per 10 microliters of boiled sample.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Douglas E., Coote J. G., Parton R., McPheat W. Identification of Bordetella pertussis in nasopharyngeal swabs by PCR amplification of a region of the adenylate cyclase gene. J Med Microbiol. 1993 Feb;38(2):140–144. doi: 10.1099/00222615-38-2-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson M., Granström G., Wretlind B., Granström M., Askelöf P. Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase activity in nasopharyngeal aspirates for rapid diagnosis of whooping cough in relation to culture and serology. Scand J Infect Dis. 1991;23(6):731–735. doi: 10.3109/00365549109024301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L. Pertussis: the disease and new diagnostic methods. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Oct;1(4):365–376. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.4.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glare E. M., Paton J. C., Premier R. R., Lawrence A. J., Nisbet I. T. Analysis of a repetitive DNA sequence from Bordetella pertussis and its application to the diagnosis of pertussis using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1982–1987. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1982-1987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström G., Wretlind B., Granström M. Diagnostic value of clinical and bacteriological findings in pertussis. J Infect. 1991 Jan;22(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(91)90842-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimprel E., Bégué P., Anjak I., Betsou F., Guiso N. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction, culture, and western immunoblot serology for diagnosis of Bordetella pertussis infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Oct;31(10):2745–2750. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.10.2745-2750.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallander H. O., Reizenstein E., Renemar B., Rasmuson G., Mardin L., Olin P. Comparison of nasopharyngeal aspirates with swabs for culture of Bordetella pertussis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jan;31(1):50–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.1.50-52.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallander H. O., Storsaeter J., Möllby R. Evaluation of serology and nasopharyngeal cultures for diagnosis of pertussis in a vaccine efficacy trial. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1046–1054. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Q., Mertsola J., Soini H., Skurnik M., Ruuskanen O., Viljanen M. K. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction with culture and enzyme immunoassay for diagnosis of pertussis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):642–645. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.642-645.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe J. E., Weiss A. Recovery of Bordetella pertussis from four kinds of swabs. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;6(2):203–205. doi: 10.1007/BF02018215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houard S., Hackel C., Herzog A., Bollen A. Specific identification of Bordetella pertussis by the polymerase chain reaction. Res Microbiol. 1989 Sep;140(7):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLafferty M. A., Harcus D. R., Hewlett E. L. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of a repetitive DNA element from the genome of Bordetella pertussis with characteristics of an insertion sequence. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Aug;134(8):2297–2306. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-8-2297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheat W. L., Hanson J. H., Livey I., Robertson J. S. Analysis of separate isolates of Bordetella pertussis repeated DNA sequences. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jun;135(6):1515–1520. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-6-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheat W. L., McNally T. Isolation of a repeated DNA sequence from Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Feb;133(2):323–330. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-2-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade B. D., Bollen A. Recommendations for use of the polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of Bordetella pertussis infections. J Med Microbiol. 1994 Jul;41(1):51–55. doi: 10.1099/00222615-41-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olcén P., Bäckman A., Johansson B., Esbjörner E., Törnqvist E., Bygraves J., McPheat W. L. Amplification of DNA by the polymerase chain reaction for the efficient diagnosis of pertussis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1992;24(3):339–345. doi: 10.3109/00365549209061340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onorato I. M., Wassilak S. G. Laboratory diagnosis of pertussis: the state of the art. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Feb;6(2):145–151. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198702000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J., Lowe F. Enrichment medium for the isolation of Bordetella. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):303–309. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.303-309.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizenstein E., Johansson B., Mardin L., Abens J., Möllby R., Hallander H. O. Diagnostic evaluation of polymerase chain reaction discriminative for Bordetella pertussis, B. parapertussis, and B. bronchiseptica. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;17(3):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(93)90094-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizenstein E., Morfeldt E., Granström G., Granström M., Löfdahl S. DNA hybridization for diagnosis of pertussis. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Aug;4(4):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90021-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossau R., Michielsen A., Jannes G., Duhamel M., Kersters K., van Heuverswyn H. DNA probes for Bordetella species and a colorimetric reverse hybridization assay for the detection of Bordetella pertussis. Mol Cell Probes. 1992 Aug;6(4):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(92)90003-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schläpfer G., Senn H. P., Berger R., Just M. Use of the polymerase chain reaction to detect Bordetella pertussis in patients with mild or atypical symptoms of infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;12(6):459–463. doi: 10.1007/BF01967443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zee A., Agterberg C., Peeters M., Schellekens J., Mooi F. R. Polymerase chain reaction assay for pertussis: simultaneous detection and discrimination of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2134–2140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2134-2140.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]