Abstract
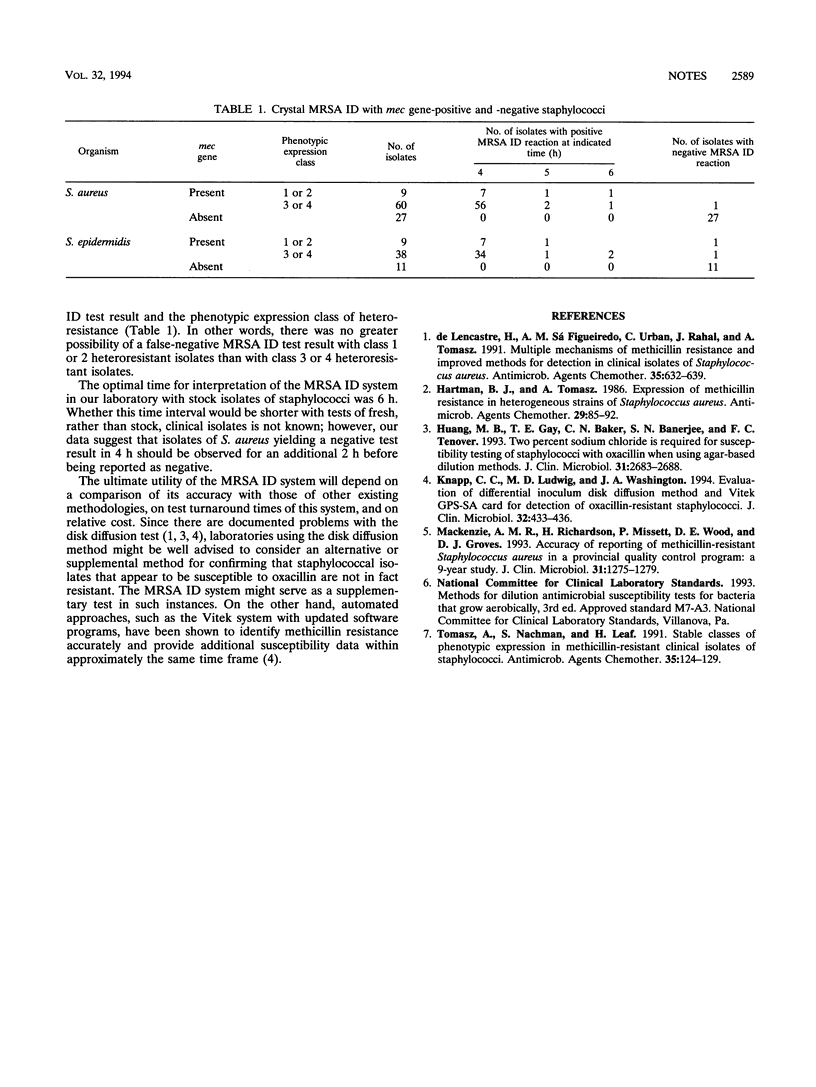
The BBL Crystal system (Becton Dickinson Microbiology Systems, Cockeysville, Md.) was evaluated for its accuracy in identifying oxacillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by testing of mec-specific-gene-positive and -negative isolates. Although the manufacturer makes no claim for use of the product for testing of staphylococci other than S. aureus, the product's potential utility in detecting oxacillin resistance in isolates of mec gene-positive and -negative Staphylococcus epidermidis was also explored. All mec gene-negative staphylococci yielded a negative MRSA ID test reaction. There was a close correlation between mec gene positivity and a positive reaction in the methicillin-resistant S. aureus identification system with 63 of 69 (91%) stock isolates of S. aureus yielding a positive result in 4 h, 66 of 69 (95%) yielding a positive result in 5 h, and 68 of 69 (99%) yielding a positive result in 6 h. The corresponding percentage agreements at 4, 5, and 6 h for mec gene-positive stock isolates of S. epidermidis were 87, 91, and 96%, respectively.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Expression of methicillin resistance in heterogeneous strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):85–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. B., Gay T. E., Baker C. N., Banerjee S. N., Tenover F. C. Two percent sodium chloride is required for susceptibility testing of staphylococci with oxacillin when using agar-based dilution methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Oct;31(10):2683–2688. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.10.2683-2688.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp C. C., Ludwig M. D., Washington J. A. Evaluation of differential inoculum disk diffusion method and Vitek GPS-SA card for detection of oxacillin-resistant staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Feb;32(2):433–436. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.2.433-436.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie A. M., Richardson H., Missett P., Wood D. E., Groves D. J. Accuracy of reporting of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a provincial quality control program: a 9-year study. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 May;31(5):1275–1279. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.5.1275-1279.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Nachman S., Leaf H. Stable classes of phenotypic expression in methicillin-resistant clinical isolates of staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lencastre H., Sá Figueiredo A. M., Urban C., Rahal J., Tomasz A. Multiple mechanisms of methicillin resistance and improved methods for detection in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):632–639. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


