Abstract
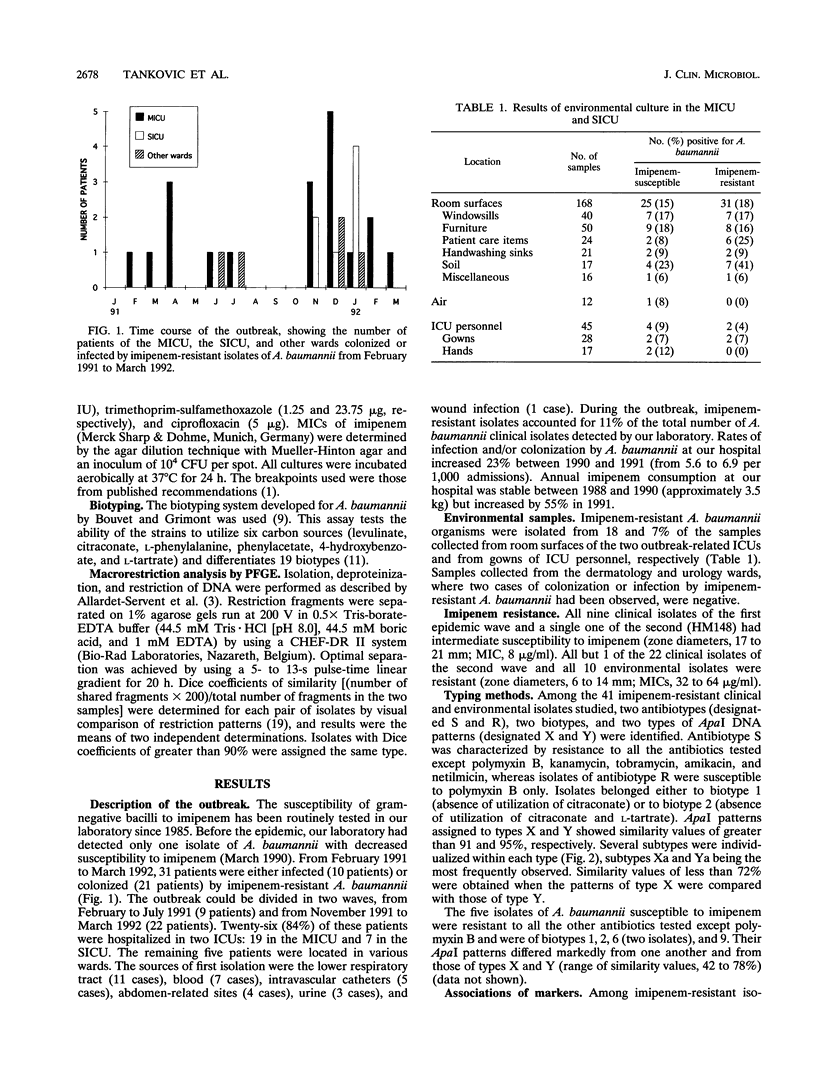
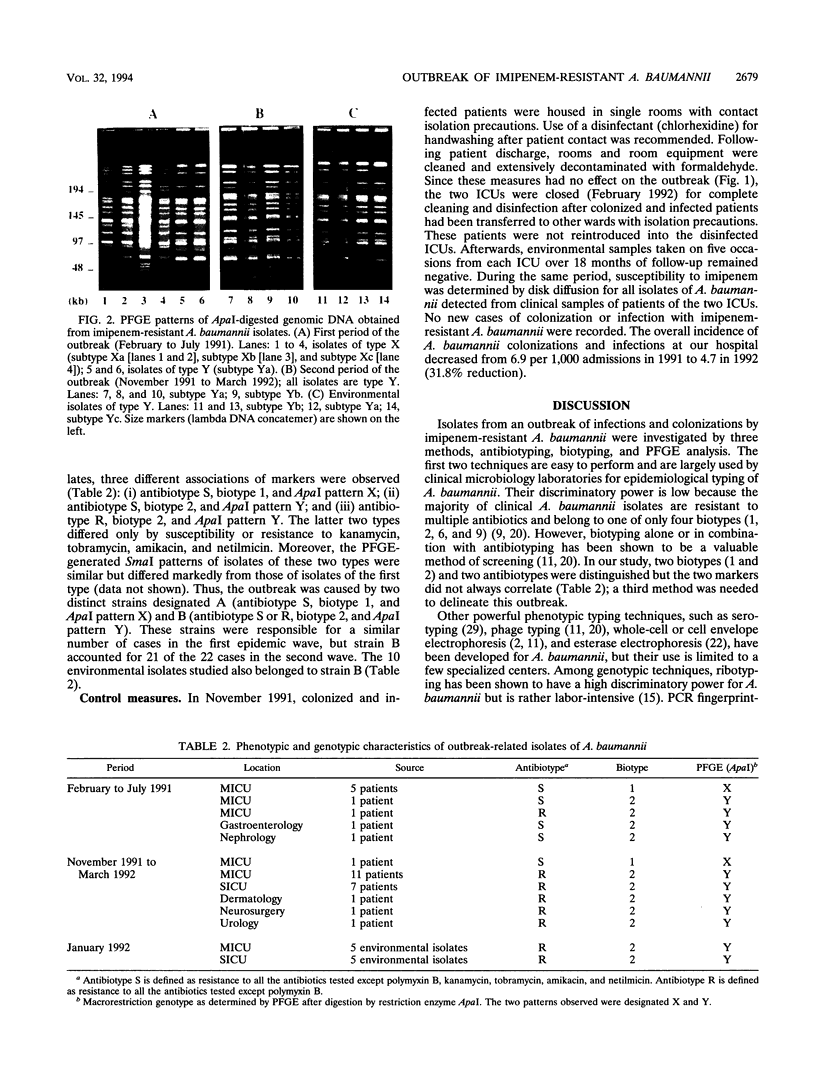
During a 13-month period, 31 patients hospitalized primarily in two intensive care units (ICUs) were either colonized or infected by imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Typing of the isolates by three methods (antibiotyping, biotyping, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis) revealed that two distinct strains were involved in the first 9 cases of the outbreak and that one of these strains, which had acquired a higher level of imipenem resistance as well as resistance to all aminoglycosides, accounted for 21 of 22 cases in the second part of the outbreak. ICU environmental contamination was recognized as an important reservoir of this epidemic strain. The outbreak ceased only after the ICUs were closed for complete cleaning and disinfection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M., Ismail F., Jackman P. J., Noble W. C. Fingerprinting Acinetobacter strains from clinical sources by numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):55–64. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allardet-Servent A., Bouziges N., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bourg G., Gouby A., Ramuz M. Use of low-frequency-cleavage restriction endonucleases for DNA analysis in epidemiological investigations of nosocomial bacterial infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2057–2061. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2057-2061.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen K. D., Green H. T. Hospital outbreak of multi-resistant Acinetobacter anitratus: an airborne mode of spread? J Hosp Infect. 1987 Mar;9(2):110–119. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(87)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alos J. I., Lambert T., Courvalin P. Comparison of two molecular methods for tracing nosocomial transmission of Escherichia coli K1 in a neonatal unit. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jul;31(7):1704–1709. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.7.1704-1709.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P. Isolation of Acinetobacter from soil and water. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):39–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.39-42.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck-Sagué C. M., Jarvis W. R., Brook J. H., Culver D. H., Potts A., Gay E., Shotts B. W., Hill B., Anderson R. L., Weinstein M. P. Epidemic bacteremia due to Acinetobacter baumannii in five intensive care units. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Oct;132(4):723–733. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P. J., Grimont P. A. Identification and biotyping of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Sep-Oct;138(5):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P. J., Jeanjean S. Delineation of new proteolytic genomic species in the genus Acinetobacter. Res Microbiol. 1989 May-Jun;140(4-5):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P. J., Jeanjean S., Vieu J. F., Dijkshoorn L. Species, biotype, and bacteriophage type determinations compared with cell envelope protein profiles for typing Acinetobacter strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.170-176.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle M., Tenney J. H., Weinstein M. P., Eickhoff T. C. Outbreak of a multiply resistant Acinetobacter in a surgical intensive care unit: epidemiology and control. Heart Lung. 1978 Jul-Aug;7(4):641–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cefai C., Richards J., Gould F. K., McPeake P. An outbreak of Acinetobacter respiratory tract infection resulting from incomplete disinfection of ventilatory equipment. J Hosp Infect. 1990 Feb;15(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(90)90128-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French G. L., Casewell M. W., Roncoroni A. J., Knight S., Phillips I. A hospital outbreak of antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter anitratus: epidemiology and control. J Hosp Infect. 1980 Jun;1(2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(80)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerner-Smidt P. Ribotyping of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter baumannii complex. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2680–2685. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2680-2685.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouby A., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bouziges N., Bourg G., Mesnard R., Bouvet P. J. Use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for investigation of hospital outbreaks of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1588–1591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1588-1591.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gräser Y., Klare I., Halle E., Gantenberg R., Buchholz P., Jacobi H. D., Presber W., Schönian G. Epidemiological study of an Acinetobacter baumannii outbreak by using polymerase chain reaction fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2417–2420. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2417-2420.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL L. B., HARTNETT M. J. MEASUREMENT OF THE BACTERIAL CONTAMINATION ON SURFACES IN HOSPITALS. Public Health Rep. 1964 Nov;79:1021–1024. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Jordens J. Z., Wang F. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from China characterized by digestion of total DNA with restriction enzymes. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):183–192. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003048x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly-Guillou M. L., Bergogne-Berezin E., Vieu J. F. A study of the relationships between antibiotic resistance phenotypes, phage-typing and biotyping of 117 clinical isolates of Acinetobacter spp. J Hosp Infect. 1990 Jul;16(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(90)90048-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly-Guillou M. L., Bergogne-Berezin E., Vieu J. F. Epidémiologie et résistance aux antibiotiques des Acinetobacter en milieu hospitalier. Bilan de 5 années. Presse Med. 1990 Mar 3;19(8):357–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouëdras P., Gras S., Sire J. M., Mesnard R., Donnio P. Y., Picard B., Avril J. L. Esterase electrophoresis compared with biotyping for epidemiological typing of Acinetobacter baumannii strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Sep 15;75(2-3):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90391-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal S. L. Sources of pseudomonas and acinetobacter species found in human culture materials. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 Dec;62(6):807–811. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/62.6.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherertz R. J., Sullivan M. L. An outbreak of infections with Acinetobacter calcoaceticus in burn patients: contamination of patients' mattresses. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):252–258. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struelens M. J., Carlier E., Maes N., Serruys E., Quint W. G., van Belkum A. Nosocomial colonization and infection with multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii: outbreak delineation using DNA macrorestriction analysis and PCR-fingerprinting. J Hosp Infect. 1993 Sep;25(1):15–32. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(93)90005-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAPLIN D., ZAIAS N. THE HUMAN SKIN AS A SOURCE OF MIMA-HERELLEA INFECTIONS. JAMA. 1963 Dec 7;186:952–955. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63710100030023a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjernberg I., Ursing J. Clinical strains of Acinetobacter classified by DNA-DNA hybridization. APMIS. 1989 Jul;97(7):595–605. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Acinetobacter baumannii serotyping for delineation of outbreaks of nosocomial cross-infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2713–2716. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2713-2716.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban C., Go E., Mariano N., Berger B. J., Avraham I., Rubin D., Rahal J. J. Effect of sulbactam on infections caused by imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter calcoaceticus biotype anitratus. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):448–451. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vila J., Almela M., Jimenez de Anta M. T. Laboratory investigation of hospital outbreak caused by two different multiresistant Acinetobacter calcoaceticus subsp. anitratus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):1086–1089. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.1086-1089.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ygout J. F., Housset B., Derenne J. P., Daguet G. L. Hospital-acquired Acinetobacter baumanii pneumonitis. Lancet. 1987 Apr 4;1(8536):802–802. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92822-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




