Abstract
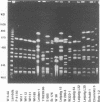
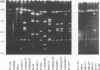
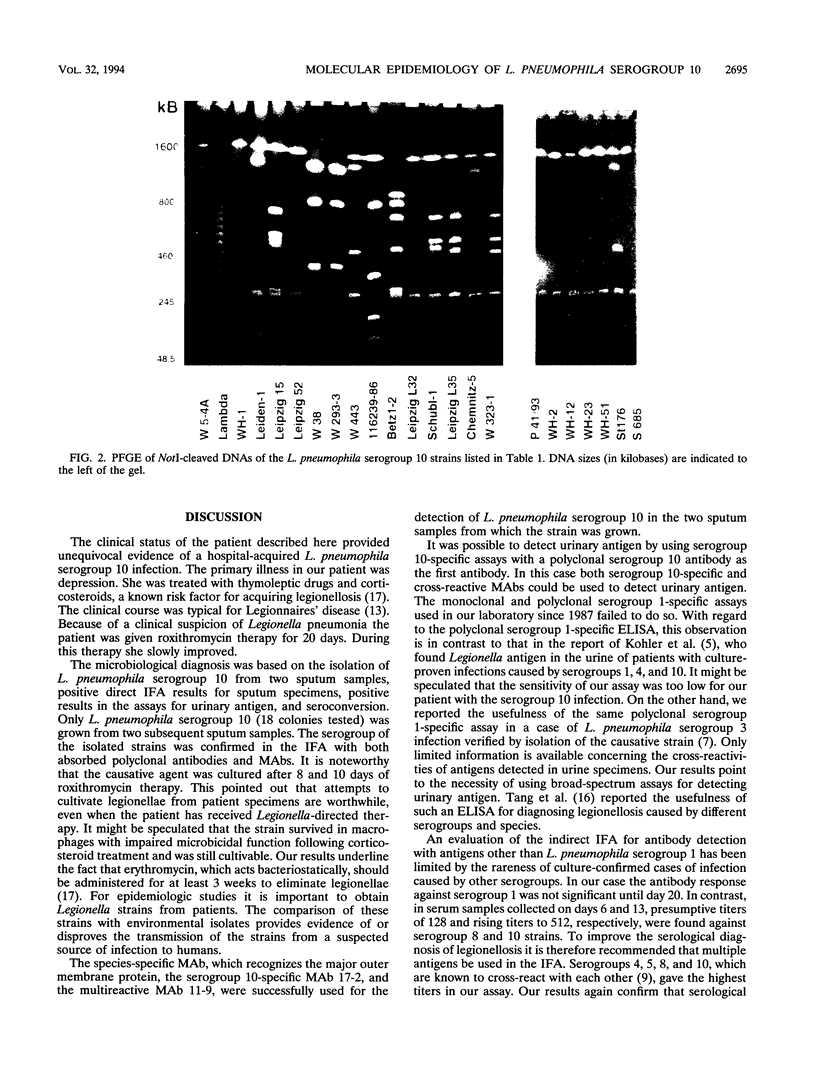
A 67-year-old woman was hospitalized with an acute pneumonia of the left lower lobe. Legionella pneumophila serogroup 10 was cultured from two sputum specimens taken on days 18 and 20 and was also detected by direct immunofluorescence assay by using a commercially available species-specific monoclonal antibody as well as serogroup 10-specific monoclonal antibodies. Antigenuria was detected in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays by using serogroup 10-specific polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. In the indirect immunofluorescence test rising antibody titers against serogroups 1, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 14, and 15 were found in serum, with the highest titers found against serogroups 8, 9, and 10. L. pneumophila serogroups 10 and 6 and a strain that reacted with serogroup 4 and 14 antisera were cultured from both central and peripheral hot water systems of the hospital. Macrorestriction analyses of the genomic DNAs by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis showed that the isolate from the patient was identical to the serogroup 10 strains from the hospital hot water system. In contrast, the genomic DNAs of 16 unrelated L. pneumophila serogroup 10 strains showed 12 different restriction patterns. Monoclonal antibody subtyping revealed only minor differences in L. pneumophila serogroup 10 strains isolated from different sources. In conclusion, macrorestriction analysis is a valuable tool for studying the molecular epidemiology of L. pneumophila serogroup 10.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson R. F., Thacker W. L., Wilkinson H. W., Fallon R. J., Brenner D. J. Legionella pneumophila serogroup 14 isolated from patients with fatal pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):382–382. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.382-.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Steigerwalt A. G., Epple P., Bibb W. F., McKinney R. M., Starnes R. W., Colville J. M., Selander R. K., Edelstein P. H., Moss C. W. Legionella pneumophila serogroup Lansing 3 isolated from a patient with fatal pneumonia, and descriptions of L. pneumophila subsp. pneumophila subsp. nov., L. pneumophila subsp. fraseri subsp. nov., and L. pneumophila subsp. pascullei subsp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1695–1703. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1695-1703.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helbig J. H., Lück P. C., Pilz C., Witzleb W. Common epitope on urinary antigen derived from different Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 strains recognized by a monoclonal antibody. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Sep;273(4):478–480. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. R., McKinney R. M., Tobin J. O., Bibb W. F., Watkins I. D., Ramsay D. Development of a standardized subgrouping scheme for Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):768–771. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.768-771.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler R. B., Wheat L. J., French M. L., Meenhorst P. L., Winn W. C., Jr, Edelstein P. H. Cross-reactive urinary antigens among patients infected with Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1 and 4 and the Leiden 1 strain. J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):1007–1012. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lück P. C., Bender L., Ott M., Helbig J. H., Hacker J. Analysis of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 6 strains isolated from a hospital warm water supply over a three-year period by using genomic long-range mapping techniques and monoclonal antibodies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3226–3231. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3226-3231.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lück P. C., Helbig J. H., Wunderlich E., Foelske H., Selbitschka M., Wenzel D., Pätzold L., Witzleb W. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 3 from pericardial fluid in a case of pericarditis. Infection. 1989 Nov-Dec;17(6):388–390. doi: 10.1007/BF01645553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lück P. C., Leupold I., Hlawitschka M., Helbig J. H., Carmienke I., Jatzwauk L., Guderitz T. Prevalence of Legionella species, serogroups, and monoclonal subgroups in hot water systems in south-eastern Germany. Zentralbl Hyg Umweltmed. 1993 Feb;193(5):450–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meenhorst P. L., Reingold A. L., Groothuis D. G., Gorman G. W., Wilkinson H. W., McKinney R. M., Feeley J. C., Brenner D. J., van Furth R. Water-related nosocomial pneumonia caused by Legionella pneumophila serogroups 1 and 10. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):356–364. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muder R. R., Yu V. L., Woo A. H. Mode of transmission of Legionella pneumophila. A critical review. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Aug;146(8):1607–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill M. A., Gorman G. W., Gibert C., Roussel A., Hightower A. W., McKinney R. M., Broome C. V. Nosocomial legionellosis, Paris, France. Evidence for transmission by potable water. Am J Med. 1985 Apr;78(4):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90399-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M., Bender L., Marre R., Hacker J. Pulsed field electrophoresis of genomic restriction fragments for the detection of nosocomial Legionella pneumophila in hospital water supplies. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):813–815. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.813-815.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonmaker D., Heimberger T., Birkhead G. Comparison of ribotyping and restriction enzyme analysis using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for distinguishing Legionella pneumophila isolates obtained during a nosocomial outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1491–1498. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1491-1498.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., McKinney R. M., Whittam T. S., Bibb W. F., Brenner D. J., Nolte F. S., Pattison P. E. Genetic structure of populations of Legionella pneumophila. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1021–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1021-1037.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]