Abstract
The aim of this study was to develop a sensitive and specific PCR for the detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA. The plasmid-located gene coding for the outer surface protein A (OspA [31-kDa protein]) was used as a target. Nucleotide sequence information from different B. burgdorferi ospA genotypes was used to design primers homologous to different genotypes. The sensitivity of the nested PCR differed from 1 fg to 1 pg of borrelial DNA, depending on the strain analyzed. No cross-reactions with DNA from spirochetes other than B. burgdorferi or with human DNA were observed. A total of 22 skin biopsy samples from patients with erythema migrans (EM [n = 10]) or acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (ACA [n = 12]) were examined for the presence of B. burgdorferi by nested PCR. Of 22 biopsies, 80% from EM patients and 92% from ACA patients were positive by PCR amplification. By comparison, 50% of the EM patients had elevated B. burgdorferi-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) and/or IgG antibody levels as tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using purified B. burgdorferi flagella as antigen. A total of 33% of ACA patients had elevated IgM titers, and all had high IgG titers in their sera. Only 30% of specimens from patients with EM and none from patients with ACA were positive by culture. All culture-positive specimens were also positive by PCR. Thus, the sensitivities of the PCR were 80 and 92%, respectively, for patients with EM and ACA on the basis of the clinical and histopathological diagnoses of Lyme disease. From these results, we conclude that PCR is a suitable method to detect B. burdorferi sensu lato DNA in skin biopsy samples and could be applied as an additional diagnostic tool.
Full text
PDF


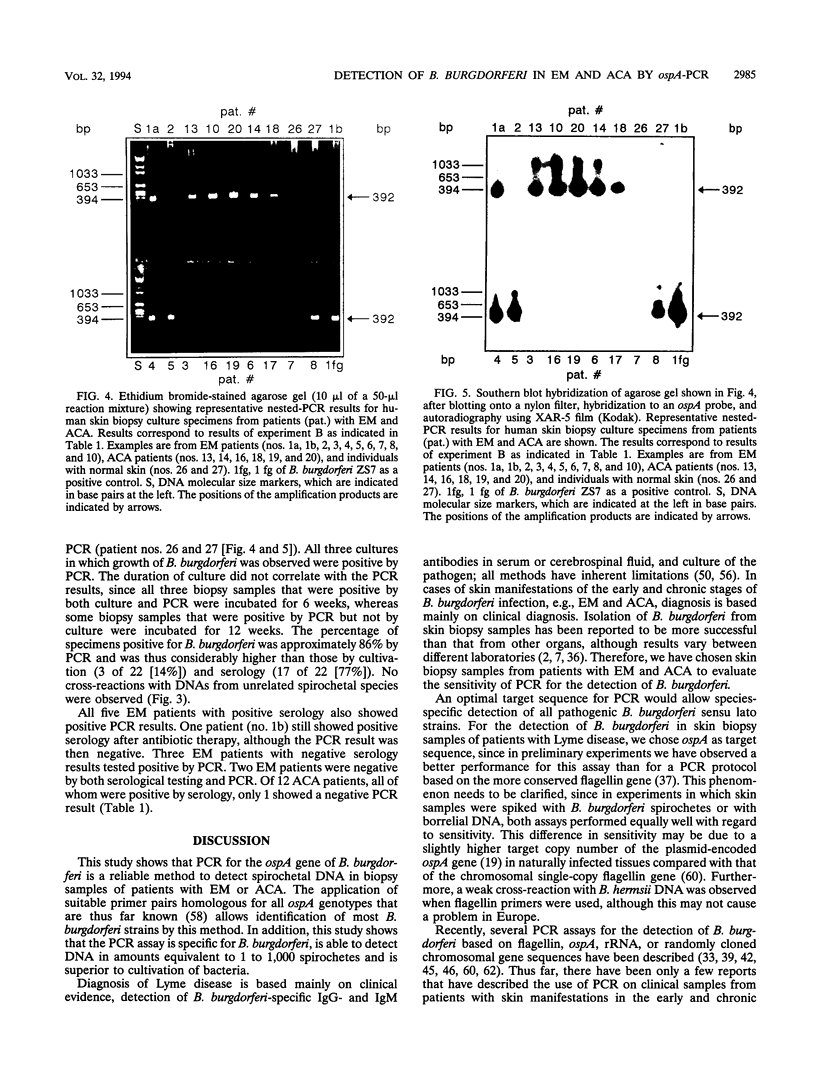



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong A. L., Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Beck D. S. Carditis in Lyme disease susceptible and resistant strains of laboratory mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Aug;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Early and late cutaneous manifestations in Ixodes-borne borreliosis (erythema migrans borreliosis, Lyme borreliosis). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:4–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Successful cultivation of spirochetes from skin lesions of patients with erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Apr;93(2):161–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Armstrong A. L., Peeples R. A. Kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi dissemination and evolution of disease after intradermal inoculation of mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):263–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W., Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Coleman L. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from erythema migrans lesions and perilesional skin. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):359–361. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.359-361.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W., Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Coleman L. Failure of Borrelia burgdorferi to survive in the skin of patients with antibiotic-treated Lyme disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Jul;27(1):34–37. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(92)70152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Molecular analysis of linear plasmid-encoded major surface proteins, OspA and OspB, of the Lyme disease spirochaete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Apr;3(4):479–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caporale D. A., Kocher T. D. Sequence variation in the outer-surface-protein genes of Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Biol Evol. 1994 Jan;11(1):51–64. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Antibody response in Lyme disease: evaluation of diagnostic tests. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):789–795. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debue M., Gautier P., Hackel C., Van Elsen A., Herzog A., Bigaignon G., Bollen A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in biological samples using the polymerase chain reaction assay. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jun;142(5):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90189-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiffert H., Ohlenbusch A., Fehling W., Lotter H., Thomssen R. Nucleotide sequence of the ospAB operon of a Borrelia burgdorferi strain expressing OspA but not OspB. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1864–1868. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1864-1868.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellinger W., Redl B., Stöffler G. Sequence of the complete osp operon encoding two major outer membrane proteins of a European Borrelia burgdorferi isolate (B29) Gene. 1992 Oct 12;120(1):127–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90021-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Sun X., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Borrelia burgdorferi strain 25015: characterization of outer surface protein A and vaccination against infection. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2256–2260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. D., Kong L. I., Miller F. W. Molecular detection of persistent Borrelia burgdorferi in a man with dermatomyositis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 Jul-Aug;10(4):387–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. L., Jurkovich P., Kramber J. M., Johnson R. C. Molecular detection of persistent Borrelia burgdorferi in the urine of patients with active Lyme disease. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):269–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.269-278.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy E. C., Stanek G. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in patients with Lyme disease by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Jul;44(7):610–611. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.7.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercogová J., Tománková M., Plch J., Jirous J., Hulínská D., Frösslová D., Barták P. Borrelia burgdorferi isolates from erythema migrans. Arch Dermatol Res. 1993;285(3):171–173. doi: 10.1007/BF01112922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch J., Barbour A. G. Linear- and circular-plasmid copy numbers in Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5251–5257. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5251-5257.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmeister E. K., Markham R. B., Childs J. E., Arthur R. R. Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and culture for detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in naturally infected Peromyscus leucopus and experimentally infected C.B-17 scid/scid mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2625–2631. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2625-2631.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horneff G., Huppertz H. I., Müller K., Voit T., Karch H. Demonstration of Borrelia burgdorferi infection in a child with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 Oct;152(10):810–812. doi: 10.1007/BF02073376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Mayer L. W., Barbour A. G. A single recombinant plasmid expressing two major outer surface proteins of the Lyme disease spirochete. Science. 1985 Feb 8;227(4687):645–646. doi: 10.1126/science.3969554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppertz H. I., Schmidt H., Karch H. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi by nested polymerase chain reaction in cerebrospinal fluid and urine of children with neuroborreliosis. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 May;152(5):414–417. doi: 10.1007/BF01955900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaulhac B., Nicolini P., Piemont Y., Monteil H. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Lyme borreliosis. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1440–1440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson M., Noppa L., Barbour A. G., Bergström S. Heterogeneity of outer membrane proteins in Borrelia burgdorferi: comparison of osp operons of three isolates of different geographic origins. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1845–1853. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1845-1853.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller T. L., Halperin J. J., Whitman M. PCR detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in cerebrospinal fluid of Lyme neuroborreliosis patients. Neurology. 1992 Jan;42(1):32–42. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Schaible U. E., Wallich R., Moter S. E., Petzoldt D., Simon M. M. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi associated antigens by monoclonal antibodies. Immunobiology. 1990 Nov;181(4-5):357–366. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger W. H., Pulz M. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in cerebrospinal fluid by the polymerase chain reaction. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Aug;35(2):98–102. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-2-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebech A. M., Hansen K. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in urine samples and cerebrospinal fluid samples from patients with early and late Lyme neuroborreliosis by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1646–1653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1646-1653.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebech A. M., Hindersson P., Vuust J., Hansen K. Comparison of in vitro culture and polymerase chain reaction for detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in tissue from experimentally infected animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Apr;29(4):731–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.4.731-737.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebling M. R., Nishio M. J., Rodriguez A., Sigal L. H., Jin T., Louie J. S. The polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in human body fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 May;36(5):665–675. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy D. C., Nauman R. K., Paxton H. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1089–1093. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1089-1093.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire B. S., Chandler F. W., Felz M. W., Huey L. O., Field R. S. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in human blood and urine using the polymerase chain reaction. Pathobiology. 1992;60(3):163–167. doi: 10.1159/000163717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers W., Meis J., Rosa P., Claas E., Nohlmans L., Koopman R., Horrevorts A., Galama J. Amplification of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in skin biopsies from patients with Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2401–2406. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2401-2406.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. D., Reed K. D., Vandermause M. F., Melski J. W. Isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from skin biopsy specimens of patients with erythema migrans. Am J Clin Pathol. 1993 Jan;99(1):104–107. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/99.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadelman R. B., Nowakowski J., Forseter G., Bittker S., Cooper D., Goldberg N., McKenna D., Wormser G. P. Failure to isolate Borrelia burgdorferi after antimicrobial therapy in culture-documented Lyme borreliosis associated with erythema migrans: report of a prospective study. Am J Med. 1993 Jun;94(6):583–588. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Young K. K., Barbour A. G. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Feb;4(1):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90041-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocton J. J., Dressler F., Rutledge B. J., Rys P. N., Persing D. H., Steere A. C. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA by polymerase chain reaction in synovial fluid from patients with Lyme arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 27;330(4):229–234. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401273300401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Telford S. R., 3rd, Rys P. N., Dodge D. E., White T. J., Malawista S. E., Spielman A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in museum specimens of Ixodes dammini ticks. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1420–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2402635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N. Polymerase chain reaction primers and probes derived from flagellin gene sequences for specific detection of the agents of Lyme disease and North American relapsing fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):99–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.99-114.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabb D. C., Lesher J. L., Jr, Chandler F. W. Polymerase chain reaction confirmation of Borrelia burgdorferi in benign lymphocytic infiltrate of dermis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Feb;26(2 Pt 1):267–268. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(08)80309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranki A., Aavik E., Peterson P., Schauman K., Nurmilaakso P. Successful amplification of DNA specific for Finnish Borrelia burgdorferi isolates in erythema chronicum migrans but not in circumscribed scleroderma lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Mar;102(3):339–345. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12371793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Hogan D., Schwan T. G. Polymerase chain reaction analyses identify two distinct classes of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):524–532. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.524-532.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Schwan T. G. A specific and sensitive assay for the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):1018–1029. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schempp C., Bocklage H., Lange R., Kölmel H. W., Orfanos C. E., Gollnick H. Further evidence for Borrelia burgdorferi infection in morphea and lichen sclerosus et atrophicus confirmed by DNA amplification. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 May;100(5):717–720. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12472369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz I., Bittker S., Bowen S. L., Cooper D., Pavia C., Wormser G. P. Polymerase chain reaction amplification of culture supernatants for rapid detection of Borrelia burgdorferi. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;12(11):879–882. doi: 10.1007/BF02000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz I., Wormser G. P., Schwartz J. J., Cooper D., Weissensee P., Gazumyan A., Zimmermann E., Goldberg N. S., Bittker S., Campbell G. L. Diagnosis of early Lyme disease by polymerase chain reaction amplification and culture of skin biopsies from erythema migrans lesions. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3082–3088. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3082-3088.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Pletschette M., Flamm H., Hirschl A. M., Aberer E., Kristoferitsch W., Schmutzhard E. European Lyme borreliosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:274–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Newman J. H., Spieler P. N., Bartenhagen N. H. Antibiotic therapy in Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):1–8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiernstedt G., Dattwyler R., Duray P. H., Hansen K., Jirous J., Johnson R. C., Karlsson M., Preac-Mursic V., Schwan T. G. Diagnostic tests in Lyme borreliosis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1991;77:136–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Helmes C., Schaible U. E., Lobet Y., Moter S. E., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. Evaluation of genetic divergence among Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by use of OspA, fla, HSP60, and HSP70 gene probes. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4856–4866. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4856-4866.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Moter S. E., Simon M. M., Ebnet K., Heiberger A., Kramer M. D. The Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum-associated 41-kilodalton antigen (flagellin): molecular cloning, expression, and amplification of the gene. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1711-1719.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Schaible U. E., Simon M. M., Heiberger A., Kramer M. D. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the outer surface protein A (OspA) of a European Borrelia burgdorferi isolate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8864–8864. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. V., Callegari P., Freundlich B., Keenan G., Eldridge D., Shin H., Kreitman M., McCallus D., Weiner D. B. Molecular diagnosis of Borrelia burgdorferi infection (Lyme disease). DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;11(3):207–213. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumstein G., Fuchs R., Hofmann A., Preac-Mursic V., Soutschek E., Wilske B. Genetic polymorphism of the gene encoding the outer surface protein A (OspA) of Borrelia burgdorferi. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181(2):57–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00189424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam A. P., Kuiper H., Vos K., Widjojokusumo A., de Jongh B. M., Spanjaard L., Ramselaar A. C., Kramer M. D., Dankert J. Different genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi are associated with distinct clinical manifestations of Lyme borreliosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;17(4):708–717. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.4.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]